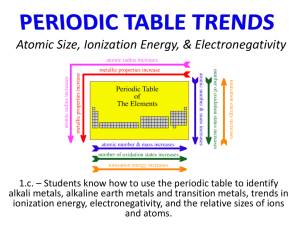
Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. AP Practice Problems Unit 3
advertisement

Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. AP Practice Problems Unit 3 – Periodic Table Multiple Choice (no calculator) For questions 1-3, one or more of the following responses will apply; each response may be used more than once or not at all in these questions. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Hg Si Cu Zn Ag 1. This element is commonly used in the manufacture of semiconductors. (P3.5) 2. This element is a liquid at room temperature. (P3.6) 3. After oxygen, this is by far the most common element in the earth’s crust. (P3.7) 4. Which of the following statements is true regarding sodium and chlorine? (P3.9) a. Sodium has a greater electronegativity and a larger first ionization energy. b. Sodium has a larger first ionization energy and a larger atomic radius. c. Chlorine has a larger atomic radius and a greater electronegativity. d. Chlorine has a greater electronegativity and a larger first ionization energy. 5. Which of the following is true of the alkali metal elements? (P3.13) a. They usually take the +2 oxidation state. b. They have oxides that act as acid anhydrides. c. They form covalent bonds with oxygen. d. They are generally found in nature in compounds. e. They have relatively large first ionization energies. 6. Which of the following has the smallest ionic radius? (P3.15) a. b. c. d. e. O2FNa+ Mg2+ Al3+ 7. The ionization energies for an element are listed in the table below. (P3.19) First Second Third Fourth Fifth 8eV 15eV 80eV 109eV 141eV Based on the ionization energy table, the element is most likely to be a. b. c. d. e. sodium. magnesium. aluminum. silicon. phosphorous. Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. 8. A researcher listed the first five ionization energies for a silicon atom in order from first to fifth. Which of the following lists corresponds to the ionization energies for silicon? (P3.20) a. 780 kJ, 13,675 kJ, 14,110 kJ, 15,650 kJ, 16,100 kJ b. 780 kJ, 1,575 kJ, 14,110 kJ, 15,650 kJ, 16,100 kJ c. 780 kJ, 1,575 kJ, 3,220 kJ, 15,650 kJ, 16,100 kJ d. 780 kJ, 1,575 kJ, 3,220 kJ, 4,350 kJ, 16,100 kJ e. 780 kJ, 1,575 kJ, 3,220 kJ, 4,350 kJ, 5,340 kJ For questions 9-13, one or more of the following responses will apply; each response may be used more than once or not at all in these questions. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) sodium strontium uranium bromine bismuth 9. Trends in the periodic table show that elements become more metallic in character from the top of a group to the bottom. Which of these is an element whose properties are opposite those of the element at the top of its group? (B2.1) 10. The halogen in this group is (B2.2) 11. The element that contains 38 protons is (B2.3) 12. There are only two liquid elements at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. One of these is (B2.4) 13. The atom with the largest radius is (B2.5) 14. The differentiating electrons for transition elements are (B2.6) a. b. c. d. e. d electrons s electrons p electrons f electrons valence electrons 15. The best way to estimate the boiling point of Pd is to (B2.7) a. average the boiling points of Rh and Ag b. average the boiling points of Ni and Pt c. average the boiling points of Ir and Cu d. average the boiling points of Co and Au e. None of the above will work. 16. In which of the following pairs is the first element expected to have the higher electronegativity than the second? (B2.8) a. b. c. d. e. O, P Cs, Rb I, Br Al, P Sb, As 17. A solid element has two valence electrons. That element must be (B2.10) a. b. c. d. e. a halogen a noble gas a radioactive element an alkali metal an alkaline earth metal Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. 18. Which of the following is expected to have the largest third ionization energy? (B2.13) a. b. c. d. e. Be B C N Al 19. Which pair of elements is expected to have the most similar properties? (B2.14) a. b. c. d. e. Potassium and lithium Sulfur and phosphorous Silicon and carbon Strontium and barium Fluorine and iodine 20. Most elements on the periodic table are (B2.15) a. b. c. d. e. nonmetals liquids gases metals metalloids 21. The chemical symbol for antimony is (B2.18) a. b. c. d. e. Sn Ti Sb K At 22. In which pair of elements is the larger atom listed first? (B2.19) a. b. c. d. e. K, Ca Na, K Cl, S Mg, Na O, N 23. Which of the following is LEAST likely to be a metalloid? (B2.20) a. b. c. d. e. As Hg Ge Si Sb Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. Essays 1. Explain each of the following in terms of atomic and molecular structures. (P3.1) a. The first ionization energy for magnesium is greater than the first ionization energy for calcium. b. The first and second ionization energies for calcium are comparable, but the third ionization energy is much greater. c. Solid sodium conducts electricity, but solid sodium chloride does not. d. The first ionization energy for aluminum is lower than the first ionization energy for magnesium. 2. Use your knowledge of the periodic table to answer the following questions. (P3.3) a. Explain the trend in electronegativity from P to S to Cl. b. Explain the trend in electronegativity from Cl to Br to I. c. Explain the trend in atomic radius from Li to Na to K. d. Explain the trend in atomic radius from Al to Mg to Na. Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. Answer Key – Unit 3: Periodic Table Multiple Choice 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. D 5. 6. 7. 8. D E B D 9. E 10. D 11. B 12. D 13. C 14. A 15. B 16. A 17. E 18. A 19. D 20. D 21. C 22. A 23. B Essays 1. (a) Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. The outermost electron in Ca is at the 4s energy level. The outermost electron in Mg is at the 3s level. The outermost electron in Ca is at the higher energy level and is more shielded from the nucleus making it easier to remove. (b) Calcium has two electrons in its outer shell. The second ionization energy will be larger than the first but still comparable because both electrons are being removed from the same energy level. The third electron is much more difficult to remove because it is being removed from a lower energy level, so it will have a much higher ionization energy than the other two. (c) Solid sodium exhibits metallic bonding, in which the positively charged sodium ions are held together by a sea of mobile, delocalized electrons. These electrons move freely from nucleus to nucleus, making solid sodium a good conductor. Sodium chloride exhibits metallic bonding, in which positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chlorine ions hold fixed places in a crystal lattice. The electrons are localized around particular nuclei and are not free to move about the lattice. This makes solid sodium chloride a bad conductor of electricity. (d) The valence electron to be removed from magnesium is located in the completed 3s subshell, while the electron to be removed from aluminum is the lone electron in the 3p subshell. It is easier to remove the electron from the higher-energy 3p subshell than from the loer energy (completed) 3s subshell, so the first ionization energy is lower for aluminum. 2. (a) Electronegativity is the pull of the nucleus of one atom on the electrons of other atoms; it increases from P to S to Cl because nuclear charge increases. This is because as you move from left to right across the periodic table, atomic radii decrease in size. Increasing nuclear charge means that Cl has the most positively charged nucleus of the three and will exert the greatest pull on the electrons of other atoms. (b) Electronegativity is the pull of the nucleus of one atom on the electrons of other atoms; it decreases from Cl to Br to I because electron shells are added. The added electron shells shield the nucleus, causing it to have less of an effect on the electrons of other atoms. Therefore, iodine will exert the least pull on the electrons of other atoms. Princeton 2012/Barron 4th ed. (c) Atomic radius increases from Li to Na to K because electrons are being added in higher energy levels, which are farther away from the nucleus; therefore, the K atom is the largest of the three. (d) Atomic radius increases from Al to Mg to Na because protons are being removed from the nucleus while the energy levels of the valence electrons remain unchanged. If there are fewer positive charges in the nucleus, the electrons of Na will be less attracted to the nucleus and remain farther away.