Chapter 16 Case Study
advertisement

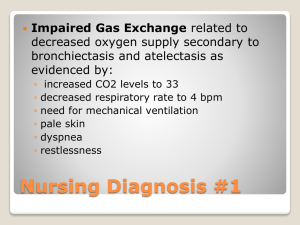
Case Study A.B. is an 11 year old Asian female. She was a full term infant born via vaginal delivery. Her past history is significant for Biliary Atresia. She had a Kasai procedure at 2 months of age in attempt to treat her condition. There is no significant family history. She has a healthy 6 year old sister. She received an orthotopic liver transplant at age 9, secondary to end stage liver disease. Over the course of the year and a half prior to transplant, she had elevated liver enzymes (AST, ALT, GGT, Bilirubin (unconjugated and conjugated), elevated PT, PTT and INR, unstable electrolytes (increased potassium and decreased magnesium), jaundice, pruritus, ascites, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly. She was evaluated for end stage liver disease secondary to extrahepatic Biliary Atresia. She received a percutaneous needle liver biopsy and abdominal ultrasound with Doppler which demonstrated worsening liver function. She underwent a full transplant evaluation and the decision was made to proceed with listing for liver transplantation. Prior to transplant, a G-Button was placed to facilitate the administration of bolus feeds to optimize nutritional status. Today she is a well developed, active 11 year old. The father’s concerns include apparent weight loss (patient has lost three pounds since previous visit), possible noncompliance with her medication regimen and concerns that she is spending time with a “bad crowd”, requesting a navel piercing and constant requests to “go tanning”. She is reportedly a picky eater and often skips breakfast. She eats lunch at school and reports that this usually consists of soda, and pizza or chicken nuggets. Her dad reports that she eats a lot of “junk food” and does not drink much water or other clear liquids. Father complains that although she is doing well in school and is active in other activities, including cheerleading and FFA (Future Farmers of America) where she is raising a calf, she does not want to eat dinner with her family or participate in family activities. Her current prescribed medication regimen includes Prograf and Magnesium. She admits to “sometimes” forgetting her medicines which lead to fights with parents. There are currently no complaints of jaundice, pruritus, fever, cough, congestion, bleeding, bruising, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, tremors, or pain. Child, s/p solid organ transplant Nursing Diagnosis: Nutrition, altered, less than body requirements Nursing Diagnosis: Body image disturbance, risk for Nursing Diagnosis: Self esteem disturbance, risk for Plan: Assess current growth and develop Review diet history for past three days Determine patient/family knowledge of pre-teen nutritional needs Evaluate current view of self (patient) Implementation: Discuss current height/weight expected for age with pt/family Refer to transplant dietitian to review current dietary intake and educate patient/family on appropriate food choices and caloric intake Provide patient/family with dietary intake and weight tracking tool Set weight and intake goals Consult Child Life Specialist (or other appropriate team member) to offer tools to increase self esteem for patient and family Offer information about patient and family support groups Encourage patient to attend transplant camp or other activities to interact with transplant patients Evaluation: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Review diet tracking tool with patient and family in one week Monitor weight monthly and discuss results with family Feedback from parents and patient Achievement of goals Attendance at support group or other activities Non-compliance, risk for Health maintenance, altered Knowledge deficit, medical regimen Caregiver role strain, high risk for Family processes, altered Plan: Assess patient knowledge of current medical regimen Evaluate patient and family understanding of risks associated with non-compliance with medical regimen Assess coping skills of patient and family Implementation: Provide medication tracking tool/calendar Patient to verbalizes plan to “remember” medications Discuss signs and symptoms of rejection Discuss appropriate family activities Refer parents to support group Refer patient and family to transplant social worker for psychosocial evaluation and support Offer communication tools to family Discuss consequences of inappropriate behavior Evaluation: Patient and family feedback Review tracking tool for medication compliance Attendance at support groups Patient verbalizes risks of non-compliance Feedback from social worker Nursing Diagnosis: Infection, high risk for Nursing Diagnosis: Knowledge deficit, therapeutic regimen Plan: Identify high risk behaviors in the immunosuppressed patient Discuss signs and symptoms of infection Implementation: Discuss high risk behaviors (piercings, tattoos, fungal spores associated with hay, contact with animal feces) with patient and family Review signs/symptoms of infection Offer alternative activities Encourage hand washing and other infection preventative measures Review increased risk of cancer in post transplant patient Encourage use of sunscreen, hats, and sunglasses Evaluation: Feedback from patient/family Verbalize signs/symptoms of infection Avoidance of high risk activities Evaluate patient’s utilization of sunscreen Additional information Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Diagnosis Risk Factors Outcomes Nursing Interventions Risk for infection Depressed immune system Immunosuppression medications Potential for high risk behavior(s) Potential for exposure to pathogens (animals) Frequent use of tanning bed Verbalize signs and symptoms Teach signs and of infection symptoms of infection (ie. warmth, erythema, Will understand importance of fever, discharge) prophylactic medication complicance Review dosage and administration of Patient will demonstrate prophylactic appropriate hand washing medications techniques Instruct and educate on Patient and family will avoidance of high risk verbalize appropriate oral care behaviors (tatoos, piercings, sexual Patient and family will activities, tanning) verbalize high risk behaviors Encourage frequent and appropriate handwashing and instruct on appropriate daily hygiene (oral care and bathing) and use of sunscreen Avoid large crowds and ill contacts Avoid high risk animals/excrement/hay Review immunization schedule for patient and sibling Altered nutrition: less than body requirements Inadequate food intake Unwillingness to eat Pt and family understand nutritional requirements Refer to dietitian for nutritional assessment and education Consume adequate nutrition Lack of information or misconception Maintain appropriate weight for height (BMI) Patient participates in family meals Patient verbalizes appropriate food choices Monitor weight weekly and instruct on appropriate technique (same scale, same time) Review need for increased fluid intake with activity Encourage appropriate nutritional intake Encourage appropriate clear liquid intake Encourage frequent small meals Body image disturbance Change in social behavior Change in lifestyle Fear of reaction of peers Negative feelings about appearance Feeling of powerlessness Verbalizes ability to adjust to Acknowlege patient’s changes in body due to feelings to changes in developmental stage body and life-style Will make positive body image statements Observe coping mechanisms during times of stress Will voice concerns with peer reactions Review with family alternative coping Identifies factors that are techniques uncontrollable Identify and explore Participates in plan of care patient’s strengths Makes decisions regarding care and treatment when possible Allow patient to participate in plan of care Assess family level of acceptance of patient’s body changes Encourage family to provide positive feedback related to body image Noncompliance with prescribed regimen Lack of knowledge of need for ongoing medication Will verbalize understanding of need for long term treatment and medications Encourage appropriate peer interaction Discuss implications related to noncompliance Health beliefs Feelings of powerlessness Describes consequence of non-compliance Family and patient actively involved in treatment plan States appropriate health goals Review medication regimen with patient and family Work with client to develop tool for tracking medication administration Identify and discuss concerns that patient has with regimen or side effects of medication Monitor patient’s ability to follow directions and problem solve Encourage family to allow patient to actively participate in plan of care Involve family in providing positive feedback to patient