The Utilization of Care Plans in the Provision of Respiratory Care
advertisement

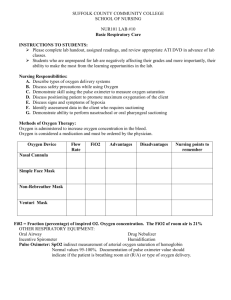
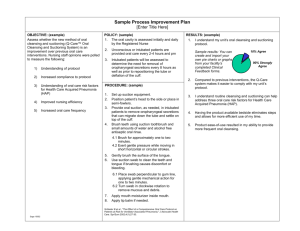
Policy 7-3-59 Page 1 of 3 UTMB RESPIRATORY CARE SERVICES PROCEDURE-Nasotracheal Suctioning Nasotracheal suctioning Formulated: 11/03 Effective: Reviewed: 12/03/03 5/31/05 NASOTRACHEAL SUCTIONING Purpose Scope To standardize the use of Naso-tracheal suctioning, a component of bronchial hygiene therapy NTS is intended to remove accumulated secretions, blood, vomitus, and other foreign material from the trachea that cannot be removed by the patient’s spontaneous cough or other less invasive procedures. NTS has been used to avoid intubation that was solely intended for the removal of secretions. NTS refers to the insertion of a suction catheter through the nasal passage and pharynx into the trachea in order to aspirate accumulated secretions or foreign material Audience Physician’s Order Indications Contra Indications Possible Hazards/Com plications All licensed respiratory therapist of the Respiratory Care Services Department Order for NTS or Naso-tracheal suctioning Frequency of NTS or Naso-tracheal suctioning The need to maintain a patent airway and remove secretions or foreign material from the trachea in the presence of the inability to clear secretions, audible evidence of secretions in the large/central airways that persist in spite of patient’s best cough effort. Occluded nasal passages Nasal Bleeding, Epiglottitis or croup Acute head, facial, or neck injury Coagulopathy or bleeding disorder Laryngospasm Irritable airway Upper respiratory tract infection Mechanical trauma Hypoxia/hypoxemia Cardiac dysrhythmias/arrest Bradycardia Increase in blood pressure Hypotension Respiratory Arrest Policy 7-3-59 Page 2 of 3 UTMB RESPIRATORY CARE SERVICES PROCEDURE-Nasotracheal Suctioning Nasotracheal suctioning Procedure Formulated: 11/03 Effective: Reviewed: 12/03/03 5/31/05 Uncontrolled coughing Gagging/vomiting Laryngospasm Bronchoconstriction/bronshospasm Pain Nosocomial infection Atelectasis Misdirection of Catheter Increased ICP Assesses patient and patient airway; determines preferred naris Preoxygenates patient for at least 30 seconds Adjusts suction to appropriate level; lubricates naris or nasopharyngeal airway with water-soluable lubricant Removes pillow and positions patient’s head. Puts on sterile gloves and maintains clean technique throughout procedure Attaches catheter to suction source Reassures patient; removes oxygen source Inserts catheter into the nare Passes catheter into the oropharynx and into trachea; confirms positioning Advances catheter until resistance is met (without suction applied) Applies suction and rotates/ withdraws catheter for a maximum of 10 to 15 seconds. Frequently assesses patient for oxygenation status, including pulse oximetry Re-oxygenate patient for at least 1 minute. Reassesses patient and repeat if necessary. Policy 7-3-59 Page 3 of 3 UTMB RESPIRATORY CARE SERVICES PROCEDURE-Nasotracheal Suctioning Nasotracheal suctioning Formulated: 11/03 Effective: Reviewed: Discontinuation of orders Patients will be evaluated after every treatment. A complete pulmonary assessment will be done every 72 ours as indicated. Based on the assessment, the therapist will make recommendations for changes in therapy or discontinuance as needed. References AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines: “Nasotracheal Suctioning,” Respiratory Care 1992;37:898-901 12/03/03 5/31/05 Butler, Thomas J., Close, Janice R., Close , Robert J. Laboratory Exercises for Competency in Respiratory Care.1998:255.