BONE & JOINT INFECTIONS
advertisement
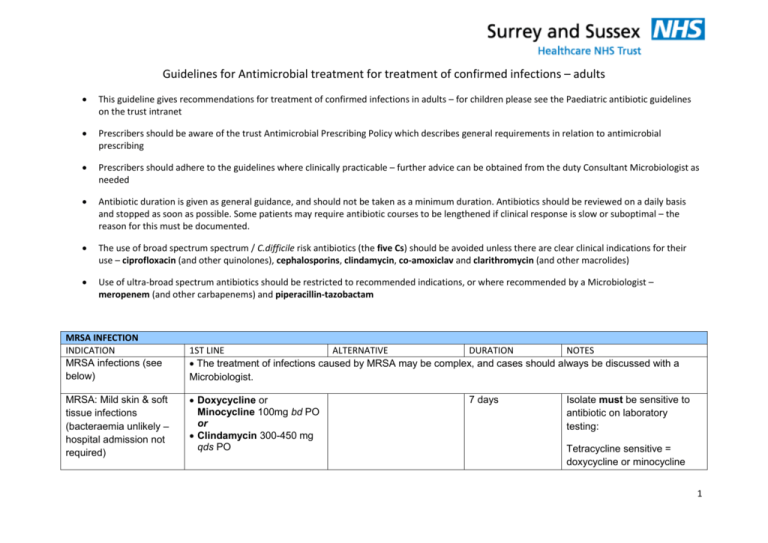
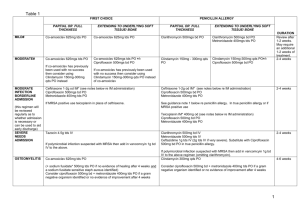
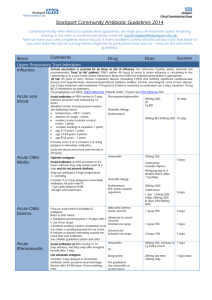
Guidelines for Antimicrobial treatment for treatment of confirmed infections – adults This guideline gives recommendations for treatment of confirmed infections in adults – for children please see the Paediatric antibiotic guidelines on the trust intranet Prescribers should be aware of the trust Antimicrobial Prescribing Policy which describes general requirements in relation to antimicrobial prescribing Prescribers should adhere to the guidelines where clinically practicable – further advice can be obtained from the duty Consultant Microbiologist as needed Antibiotic duration is given as general guidance, and should not be taken as a minimum duration. Antibiotics should be reviewed on a daily basis and stopped as soon as possible. Some patients may require antibiotic courses to be lengthened if clinical response is slow or suboptimal – the reason for this must be documented. The use of broad spectrum spectrum / C.difficile risk antibiotics (the five Cs) should be avoided unless there are clear clinical indications for their use – ciprofloxacin (and other quinolones), cephalosporins, clindamycin, co-amoxiclav and clarithromycin (and other macrolides) Use of ultra-broad spectrum antibiotics should be restricted to recommended indications, or where recommended by a Microbiologist – meropenem (and other carbapenems) and piperacillin-tazobactam MRSA INFECTION INDICATION MRSA infections (see below) MRSA: Mild skin & soft tissue infections (bacteraemia unlikely – hospital admission not required) 1ST LINE ALTERNATIVE DURATION NOTES The treatment of infections caused by MRSA may be complex, and cases should always be discussed with a Microbiologist. Doxycycline or Minocycline 100mg bd PO or Clindamycin 300-450 mg qds PO 7 days Isolate must be sensitive to antibiotic on laboratory testing: Tetracycline sensitive = doxycycline or minocycline 1 MRSA: Uncomplicated UTI Nitrofurantoin 50-100mg qds PO MRSA: conjunctivitis (non-severe) C. difficile INFECTION INDICATION Clostridium difficileassociated disease (CDAD) Trimethroprim 200mg bd PO or Doxycycline 100mg bd PO 7 days Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops 2-hourly initially, then 4- to 6-hourly as infection responds Gentamicin 0.3% eye drops 2-hourly initially, then 4- to 6-hourly as infection responds Until 48 hours after resolution. 1ST LINE Metronidazole 400mg tds PO ALTERNATIVE Vancomycin 125mg qds PO (for severe disease – WCC >15 x 109/L, rapid rise in creatinine or symptoms/signs of severe colitis) DURATION 10 days (for non-severe disease - <5 stools/day and WCC <15x109/L) Metronidazole 500mg tds IV (only in patients who cannot tolerate oral/nasogastric medications). Recurrent disease (up to 30% of patients) 1st recurrence: Use metronidazole 400mg tds PO (or, only if recommended by Consultant Microbiologist, fidaxomicin 200mg bd PO sensitive Erythromycin sensitive = Clindamycin sensitive Discuss with Ophthalmology if severe infection. Check sensitivity from Microbiology report NOTES -The broad-spectrum antibiotic(s) that pre-disposed to CDAD should be stopped wherever possible. -Nasogastric administration can be used if the patient cannot tolerate oral medication. -Review or stop unnecessary proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) -For more information, including management of severe disease and tapering vancomycin regimen, refer to Clostridium difficile infection – Guideline for Patient Management 2 -DO NOT use vancomycin by IV route for treatment of C.difficile infection for 10 days) 2nd (or subsequent) recurrence – use vancomycin 125mg qds PO. GASTRO-INTESTINAL INFECTIONS INDICATION 1st LINE ALTERNATIVE DURATION NOTES Salmonella enteritis Antibiotics do not reduce the duration or severity of uncomplicated infection, but do significantly increase the risk of bacterial relapse.12 Antibiotic treatment should be considered only for those at risk of bacteraemia & its complications: neonates, elderly, immunosuppressed, cardiac valvular or mural abnormalities, prosthetic cardiac valves or vascular grafts. 16 For "at risk" patients, who require antibiotics, the regimen of choice is Ciprofloxacin 500mg – 750mg bd PO. Please discuss with Duty Consultant Microbiologist. This is a notifiable disease Campylobacter enteritis17 Erythromycin 250mg qds PO Discuss with Microbiologist 5-7 days Antibiotics should be reserved for patients with: high fever (> 38.5C) + bloody diarrhoea or more than 8 stools per day symptoms worsening at diagnosis or persisting longer than 1 week This is a notifiable disease 3 Bacillary dysentery (Shigella species) Ciprofloxacin 500mg bd PO Trimethoprim 200 mg bd PO 3-5 days Antibiotics should be reserved for patients with: high fever (> 38.5C) + bloody diarrhoea or more than 8 stools per day symptoms worsening at diagnosis or persisting longer than 1 week where there is an increased risk of spread, eg for patients or residents requiring hands-on care This is a notifiable disease E coli O157 Antibiotics should not be given routinely because there is evidence that this increases the risk of developing haemolyticuraemic syndrome13 Typhoid fever Cefotaxime 1-2g tds IV Azithromycin 500mg once daily or 10 days (cefotaxime) Ciprofloxacin 500-750mg bd PO (only where shown to be sensitivie) 7 days (azithromycin or ciprofloxacin) Typhoid fever is a notifiable disease Note increasing incidence of ciprofloxacin resistance, especially from Indian subcontinent. Use ciprofloxacin only where isolate has been shown to be sensitive Azithromycin is alternative for oral therapy, or as additional agent if poor 4 Giardiasis Metronidazole 400mg tds PO Metronidazole 2g od PO (avoid 2g OD dosing regimen in pregnancy) 5 days for tds regimen 3 days for od regimen Helicobacter pylori infection Omeprazole 20mg bd plus Clarithromycin 500mg bd plus Amoxycillin 1g bd (all PO) If penicillin-allergic: Omeprazole 20mg bd plus Clarithromycin 250mg bd plus Metronidazole 400mg bd (all PO) 7 days If Metronidazole resistance likely e.g. not from EU/North America: Tinidazole 500mg bd PO instead TB INFECTION INDICATION TB 1ST LINE ALTERNATIVE response OD dosing must not be used in pregnant patients Notifiable disease Screening and/or treatment of household contacts recommended - Suspected active infection must be confirmed before Rx, e.g. by stool antigen if never treated before or by breath testing if previously treated. - Complicated PUD, e.g. haemorrhage, perforation, requires Omeprazole 20mg od for further 4 weeks. - Treatment failure and alternative regimens should be discussed with Consultant Gastroenterologist. DURATION NOTES The Joint TB Committee of the British Thoracic Society recommends that all cases of TB (including extrapulmonary disease) should be managed under the direct advice of a Respiratory Physician. Tuberculosis is a notifiable disease GENITO-URINARY INFECTION 5 INDICATION 1ST LINE ALTERNATIVE DURATION NOTES Genital Chlamydia Azithromycin 1g stat PO Doxycycline 100mg bd PO Doxycycline for 7 days. Refer to GUM for advice on further management and contact tracing. Gonorrhoea (anogenital) Ceftriaxone 500mg stat IM Discuss with GUM / Microbiology Stat dose. Refer to GUM for advice on further management and contact tracing. Not applicable. 5 days Refer to GUM for advice on further management and contact tracing. Plus Azithromycin 1g stat PO Genital herpes Aciclovir 200mg 5x daily PO Syphilis A positive Syphilis antibody ELISA (or TPHA FTA) indicates previous treponemal infection, which, in combination with a positive IgM , indicates active disease. Refer to GUM for advice on management and contact tracing. Previous untreated infection and current active infection require treatment; such cases 6 should be managed by GUM. VIRAL INFECTION INDICATION Chickenpox/zoster Uncomplicated 1ST LINE Aciclovir 800mg x 5 daily PO ALTERNATIVE Not applicable. DURATION 7 days. NOTES Only effective if started < 24 hours of onset of rash Chickenpox/zoster Complicated Aciclovir 10mg/kg tds IV (usually 750mg tds IV) Not applicable. 10 days for pneumonitis and encephalitis; otherwise 5 days. Complications include: persistent fever and/or appearance of new vesicles after 5 days of the onset pneumonitis encephalitis Herpes simplex encephalitis Aciclovir 10mg/kg tds IV (usually 750mg tds IV) Not applicable. At least 10 days, possibly 14-21 days. Ensure adequate hydration with IV acyclovir – risk of renal toxicity For encephalitis need to give all treatment IV PARASITIC INFECTION INDICATION Falciparum malaria 1ST LINE Uncomplicated malaria (see notes) Quinine 600mg (of quinine salt*) tds PO plus ALTERNATIVE Discuss all cases of complicated malaria with Infectious Diseases Physician. DURATION Quinine plus Doxycycline and/or Clindamycin for 7 days NOTES Seriously ill patients require IV Quinine, and their management must be discussed with a Infectious Diseases Physician. Doxycycline 200mg od PO 7 or Clindamycin 450mg tds PO Complicated malaria or if patient vomiting: Quinine 20mg/kg (max 1.4g) IV loading dose of quinine salt over 4h No loading dose if patient taking quinine or mefloquine already during the previous 12 hours).T Then 10mg/kg** (max 700mg) infused over 4 hours every 8 hours plus Doxycycline 200mg od PO or Clindamycin 450mg tds IV/PO When stable and able to swallow, switch to oral quinine 600mg tds PO, plus doxycycline or clindamycin as above. Hospital of Tropical Diseases UCL: tel 0845 155 5000 and ask for Duty Doctor for Tropical Medicine Complicated malaria = one or more of: Impaired consciousness or seizures Parasite count ≥ 2% Hb ≤ 8g/dL Spontaneous bleeding/DIC Haemoglobinuria (without G6PD deficiency) Renal impairment or pH <7.3 Pulmonary oedema or ARDS Shock ( may be due to Gram negative sepsis) Malaria is a notifiable disease – notify to the CCDC at the local HPU * Valid for quinine hydrochloride, dihydrochloride and sulphate. Not valid for quinine bisulphate which contains smaller amount of quinine. * *Maintenance dose should be reduced to 5 -7mg/kg of quinine salt in patients with severe renal impairment, severe hepatic impairment, or 8 Vivax malaria Chloroquine 625 mg of base stat PO then 310 mg of base PO after 6-8 hours Not applicable. Primaquine for 14 days if parenteral treatment is required for more than 48 hours. *Patients should be tested for G6PD deficiency before commencing primaquine then 310 mg of base PO od for 2 days followed by: Primaquine* 30mg od PO 9