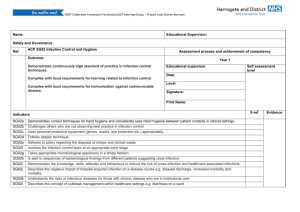
Document
advertisement

Echinostomiasis 棘口吸虫病 组员:梁彪、蔡万杰、李浩欣、李攀 演讲:梁彪 一、Morphology病原形态 Species (种类) 1. Echinostoma revolutum 卷棘口吸虫 2.E. paraulum 接睾棘口吸虫 3.Echinoparyphium recurvatum 去领棘缘吸虫 4.Hypoderaeum conoideum 似锥低颈吸虫 5.Patasiger nitidus 光洁锥棘吸虫 Echinostoma revolutum • 棘口吸虫\Echinostoma_sp_Fluke.jpg Host:chicken、duck、goose Location:rectum(直肠)、cecum(盲肠)、small intestine(小肠) Length:8.0–9.5 mm Width:1.2–2.1 mm Color: pinkish red Shape: leaflike(叶状), elongated (细长) Morphology 二、Life cycle 二、Life cycle • echinolc_副本.jpg Eggs become miracidium(毛蚴), producing a sporocyst (胞蚴). And Mother rediae(母雷蚴) emerge. Mother redia asexually reproduce daughter redia(子雷 蚴), which also multiply. Each rediae then develop into a cercariae(尾蚴), which develops into metacercaria(囊蚴) . 三.Epidemiology 流行病学 Distribution The prevalence(流行) of Echinostomiasis is very broad, not only an endemic infectious disease in United States countries, but also can be imported by overseas travelers from the Asian or Europe . Infection(感染) Echinostomiasis is parasitic zoonoses. The first human infection was reported in Taiwan in 1929. Be prevalent all over the country,especially in southern China. infection rate: Fuzhou 26.41%; Kunming 57.4%; in Guangdong : Chicken:39.13%; Duck:62%; Goose:46.6% Symptoms (症状) no obvious symptoms while mild infection, In severe infection, clinical manifestations(临床症 状) are fatigue(乏力), poor appetite(食欲不 良), diarrhea(腹泻), mucus(粘液) in stool , anorexia(厌食 ), edema(浮肿), anemia(贫 血) , weight loss, stunted growth, or even combined with other diseases. 2、The pathological changes in animal experiments mainly catarrhal(卡他 性) inflammation(炎症) of the intestinal mucosa(肠粘膜) and superficial(上 皮) loss, congestion(充血) and inflammatory cell infiltration(浸润), may occur secondary to infection, concurrent with E. coli(大肠杆菌). 五、Diagnosis(诊断) Sedimentation method ( 沉淀法) Treatment 1. Albendazole(丙硫咪唑) 15mg/kg . 2. Praziquintal(吡喹酮) 40 mg/kg, single dose 3. Niclosamide(氯硝柳胺)5060mg/kg,oral. 4. Bithionol(硫双二氯酚),100-200 mg/kg, chicken, oral. 30mg/kg,duck, goose oral