Stockport Antibiotic Guidelines 2014
advertisement
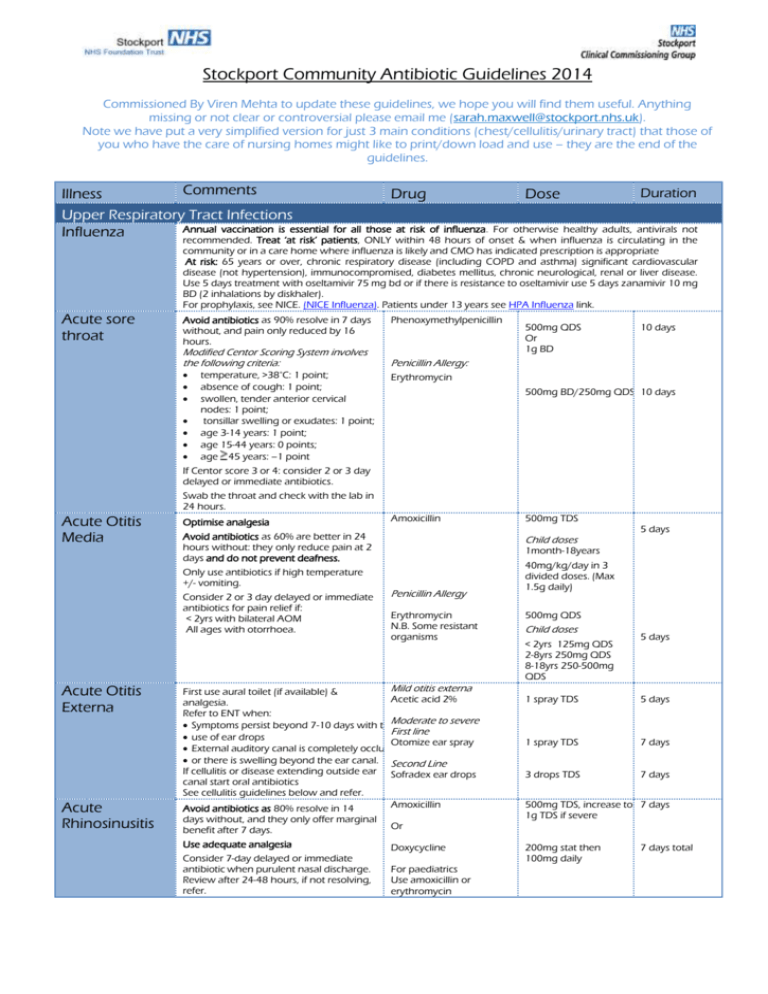
Stockport Community Antibiotic Guidelines 2014 Commissioned By Viren Mehta to update these guidelines, we hope you will find them useful. Anything missing or not clear or controversial please email me (sarah.maxwell@stockport.nhs.uk). Note we have put a very simplified version for just 3 main conditions (chest/cellulitis/urinary tract) that those of you who have the care of nursing homes might like to print/down load and use – they are the end of the guidelines. Comments Duration Illness Drug Dose Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Annual vaccination is essential for all those at risk of influenza. For otherwise healthy adults, antivirals not Influenza recommended. Treat ‘at risk’ patients, ONLY within 48 hours of onset & when influenza is circulating in the community or in a care home where influenza is likely and CMO has indicated prescription is appropriate At risk: 65 years or over, chronic respiratory disease (including COPD and asthma) significant cardiovascular disease (not hypertension), immunocompromised, diabetes mellitus, chronic neurological, renal or liver disease. Use 5 days treatment with oseltamivir 75 mg bd or if there is resistance to oseltamivir use 5 days zanamivir 10 mg BD (2 inhalations by diskhaler). For prophylaxis, see NICE. (NICE Influenza). Patients under 13 years see HPA Influenza link. Acute sore throat Avoid antibiotics as 90% resolve in 7 days without, and pain only reduced by 16 hours. Modified Centor Scoring System involves the following criteria: temperature, >38°C: 1 point; absence of cough: 1 point; swollen, tender anterior cervical nodes: 1 point; tonsillar swelling or exudates: 1 point; age 3-14 years: 1 point; age 15-44 years: 0 points; age 45 years: –1 point Phenoxymethylpenicillin 500mg QDS Or 1g BD 10 days Penicillin Allergy: Erythromycin 500mg BD/250mg QDS 10 days If Centor score 3 or 4: consider 2 or 3 day delayed or immediate antibiotics. Swab the throat and check with the lab in 24 hours. Acute Otitis Media Optimise analgesia Avoid antibiotics as 60% are better in 24 hours without: they only reduce pain at 2 days and do not prevent deafness. Only use antibiotics if high temperature +/- vomiting. Consider 2 or 3 day delayed or immediate antibiotics for pain relief if: < 2yrs with bilateral AOM All ages with otorrhoea. Acute Otitis Externa Acute Rhinosinusitis Amoxicillin Child doses 5 days 1month-18years Penicillin Allergy Erythromycin N.B. Some resistant organisms Mild otitis externa First use aural toilet (if available) & Acetic acid 2% analgesia. Refer to ENT when: Symptoms persist beyond 7-10 days with theModerate to severe First line use of ear drops Otomize ear spray External auditory canal is completely occluded or there is swelling beyond the ear canal. Second Line If cellulitis or disease extending outside ear Sofradex ear drops canal start oral antibiotics See cellulitis guidelines below and refer. Amoxicillin Avoid antibiotics as 80% resolve in 14 days without, and they only offer marginal benefit after 7 days. Or Use adequate analgesia Doxycycline Consider 7-day delayed or immediate antibiotic when purulent nasal discharge. Review after 24-48 hours, if not resolving, refer. 500mg TDS For paediatrics Use amoxicillin or erythromycin 40mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. (Max 1.5g daily) 500mg QDS Child doses < 2yrs 125mg QDS 2-8yrs 250mg QDS 8-18yrs 250-500mg QDS 5 days 1 spray TDS 5 days 1 spray TDS 7 days 3 drops TDS 7 days 500mg TDS, increase to 7 days 1g TDS if severe 200mg stat then 100mg daily 7 days total Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Note: Low doses of penicillins are more likely to select out resistance. Do not use quinolone (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin) or cefalexin first line due to poor pneumococcal activity. Reserve all quinolones (including levofloxacin) for proven resistant organisms .N.B. Note C.difficile risk Acute Cough, bronchitis Antibiotic little benefit if no co-morbidity Symptom resolution can take 3 weeks. Consider 7-14 day delayed antibiotic with symptomatic advice/leaflet. If really must give prescription, see under Acute exacerbation of COPD Treat exacerbations promptly with antibiotics if purulent sputum and increased shortness of breath and/or increased sputum volume. A third of exacerbations are due to viral infections amoxicillin 500 mg TDS 5 days or doxycycline 200 mg stat/100 mg OD 5 days Bronchiectasis Before starting antibiotics send a sputum sample for culture. Start empirical antibiotics immediately. If patient improving continue current antibiotics, despite sputum culture results. If not improving and sputum shows growth discuss with microbiology for alternative options. IV antibiotics are available in the community for appropriate patients Use CURB65 score to help guide and review: Confusion (new) Urea elevated above 7 mmol/L Respiratory rate >= 30 breaths/min Low Blood pressure, < 90 mm Hg systolic OR =<60 mm Hg diastolic Age >= 65 years. Give immediate IM benzylpenicillin or PO amoxicillin 1g if delayed admission/life threatening. IV antibiotics are available for the treatment of CAP in nursing home patients May need additional staphylococcal cover. Please discuss with microbiology. Empirical treatment: doxycycline 100 mg BD 14 days IF CURB65=0-1 amoxicillin 500mg – 1g TDS 7 days If atypical organisms suspected, add erythromycin. 500 mg QDS 7 days 200 mg stat/100 mg OD 7 days Communityacquired pneumonia treatment in the community BTS 2009 Guideline Pneumonia post influenza Meningitis Suspected meningococcal disease Acute exacerbation of COPD antibiotics or doxycycline CURB65 ≥2 Refer to hospital Transfer all patients to hospital IV or IM benzylpenicillin Age 10+ years: 1200 immediately. mg IF time before admission, give Children 1 - 9 yrs.: 600 (Ideally give IV. benzylpenicillin, unless hypersensitive i.e. mg Only give IM if history of difficulty breathing, collapse, Children <1 yr: 300 vein cannot be loss of consciousness, or rash. mg found) HPA If you want to consider alternative agents please discuss with microbiology. Prevention of secondary case of meningitis: Only prescribe following advice from Greater Manchester Public Health England on 08442250562 (ask for Duty Specialist) during office hours or outside normal working hours via the Health Protection on-call service who can be contacted through Tameside Hospital switchboard on 0161 922 6000. Urinary Tract Infections People > 65 years: do not treat asymptomatic bacteriuria; it is common but is not associated with increased morbidity. Please refer to leaflet Infection prevention guidelines for diagnosing a UTI in an older person. Catheter in situ: antibiotics will not eradicate asymptomatic bacteriuria; only treat if systemically unwell or pyelonephritis likely Use prophylactic antibiotics for catheter changes if likely history of catheter-change-associated UTI or patient is immunosuppressed For ESBL UTIs with no oral options for treatment, IV ertapenem is available for treatment at home. Simple UTIs in women i.e. no fever or flank pain. Complicated UTIs (No fever or flank pain) Can use urine dipstick to confirm clinical diagnosis – culture not usually necessary. Trimethoprim Or Nitrofurantoin (Please note nitrofurantoin is contraindicated in eGFR<60ml/min) For all men and female patients with Trimethoprim Diabetes, unresolved/ Or recurrent/recent UTI, symptoms for > 7 Pivmecillinam days, use of diaphragm, age >65 yr, abnormal UT, renally impaired, advise 7 days treatment with above antibiotics. 200mg BD 3 days 50mg QDS 3 days 200mg BD 7 days 400mg TDS 7 days It is good practice to send urine for culture in these patients. If resistant organisms or treatment failure Discuss with microbiology. N.B. In sexually active young men consider possibility of Chlamydia therefore also send urine for PCR testing. If Chlamydia positive give Azithromycin 1g stat dose and refer to GUM clinic for further testing and partner tracing. In all men also consider prostatic involvement which may need a longer course of treatment, see below. Acute Prostatitis Epididymoorchitis UTI in pregnancy UTI in children Acute Pyelonephritis Assume tissue invasion – send a urine sample for culture. Always treat as ‘complicated UTI. N.B. In sexually active young men consider possibility of Chlamydia therefore send urine for PCR testing and give Ofloxacin 200mg bd for 4 weeks instead. If Chlamydia positive refer to GUM clinic for further testing and partner tracing. 1st line Ciprofloxacin Always send urine for culture. Consider mumps and consider TB if patient is from a high prevalence country. If most probably due to STI: If <35years consider sexually transmitted infections and send urine for PCR testing. If >35 years infection will most likely be due to enteric organisms but always take a sexual history. Send MSU for culture & sensitivity and start empirical antibiotics Avoid trimethoprim if low folate status or on folate antagonist (e.g. antiepileptic or proguanil) ESBL positive UTIs 2 Line Trimethoprim If sensitive Ciprofloxacin Plus Doxycycline 200mg BD 4 weeks 500mg single dose for 14 days If most probably due to enteric organisms: Ciprofloxacin 500mg BD for 10 days First line: nitrofurantoin 50mg QDS (Avoid near to term approx. 36weeks) Second line: trimethoprim Or cefalexin Lower UTI: trimethoprim or nitrofurantoin Child ≥ 3 months: use positive nitrite to start antibiotics Send pre-treatment MSU for all. if susceptible, amoxicillin Second line: cefalexin Imaging: only refer if child <6 months or atypical UTI or recurrent UTI Second line: cefixime If admission not needed, send MSU for culture & sensitivities and start antibiotics If no response within 48 hours, admit. First line Ciprofloxacin If the patient has a UTI positive for ESBL there are usually not many oral options for treatment. If the organism grown is sensitive, fosfomycin 3g sachets can be used. This is unlicensed. These may not be stocked by community pharmacies so the patient may have to wait a day for them to be ordered in. 4 weeks 100mg BD Child <3 months: refer urgently for assessment (Non pregnant adults) 500mg BD nd 200 mg BD (off-label) Give folic acid if 1st trimester All for 7 days 500mg TDS Lower UTI See BNF for dosage 3 days Upper UTI Upper UTI: co-amoxiclav 7 days 500mg BD 7 days co-amoxiclav Fosfomycin Uncomplicated UTI: 500/125 mg TDS 14 days Complicated UTI: 3g sachet alternate days for three doses. Second line Renal impairment eGFR 10-50 3g sachet stat. 3g stat. Can give 3g stat then 3g after 72 hours for complicated UTI. eGFR less than 10 Avoid due to decreased urinary excretion. Metronidazole 2g If the patient needs IV ertapenem they can be referred for Home IV therapy. Gastro-intestinal Tract Infections Remember persistence in sending samples Giardiasis will be rewarded as cysts often release Threadworms episodically, but this is a condition that always needs treatment. Treat all household contacts at the same time PLUS advise hygiene measures for 2 weeks (hand hygiene, pants at night, morning shower) PLUS wash sleepwear, bed linen, dust, and vacuum on day one. If pregnant use hygiene methods Day 1 and 8 Or 400mg TDS >6 months: mebendazole (off-label if <2yrs) 100mg 5 days Stat 3-6 mths: piperazine+senna 2.5ml spoonful Stat, repeat after 2 weeks < 3mths: 6 wks hygiene especially in 1st trimester. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Consider test and treat in persistent uninvestigated dyspepsia Do not offer eradication for GORD Do not use clarithromycin or metronidazole if used in the past year for any infection as increased risk of resistance It is essential that NO doses are missed during eradication therapy. Symptomatic relapse DU/GU relapse: retest for H. pylori using breath or stool test OR consider endoscopy for culture & susceptibility First line PPI (use cheapest) PLUS clarithromycin (C) AND metronidazole (MTZ) or amoxicillin (AM) BD 250 mg BD with MTZ 500mg BD with AM 400 mg BD 1g BD Second line PPI PLUS bismuthate (De-nol tab®) PLUS 2 unused antibiotics Amoxicillin Metronidazole tetracycline NUD: Do not retest, offer PPI or H2RA BD 120mg QDS All for 7 days Relapse or MALToma 14 days (Continue PPI once daily after course has been completed) 1g BD 400mg TDS 500mg QDS 7 days Diverticulitis Severely unwell patients will need hospitalisation. Co-trimoxazole PLUS Metronidazole 960mg BD Cholecystitis/ Ascending cholangitis For less severe cases and follow on treatment after discharge from hospital the following antibiotics may be useful. Co-trimoxazole 960mg BD Infectious diarrhoea Refer previously healthy children with acute painful or bloody diarrhoea to exclude E. coli 0157 infection. Antibiotic therapy not indicated unless systemically unwell. If systemically unwell and campylobacter suspected (e.g. undercooked meat and abdominal pain), contact microbiology. Clostridium difficile Stop unnecessary antibiotics and/or PPIs. Send stool sample ASAP. 1st/2nd episodes Admit if severe: T >38.5; WCC >15, rising creatinine or signs/symptoms of severe colitis 3rd episode/severe 400mg TDS 7 days Alternative would be doxycycline and metronidazole but please discuss this with microbiologist first. metronidazole (MTZ) oral vancomycin 400 mg TDS 10 days 125mg QDS 10 days Do not give antidiarrhoeals Travellers’ Diarrhoea Only consider standby antibiotics for remote areas or people at high-risk of severe illness with travellers’ diarrhoea. If standby treatment appropriate give: ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice a day for 3 days (private Rx). If quinolone resistance high (e.g. south Asia): consider bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol) 2 tablets QDS as prophylaxis or for 2 days treatment. Genital Tract Infections People with risk factors should be screened for chlamydia, gonorrhoea, HIV, syphilis. Refer individual and partners to STI screening GUM service. Risk factors: < 25y, no condom use, recent /frequent change of partner or symptomatic partner Vaginal candidiasis Bacterial vaginosis All topical and oral azoles give 75% cure clotrimazole or oral fluconazole 500 mg pessary 150 mg orally stat stat clotrimazole 100 mg pessary night 6 nights clotrimazole 2% cream Apply BD 7 days Should be diagnosed clinically (fishy discharge, high pH, positive KOH test) oral metronidazole 400mg BD or 7 days Stat Less relapse at 4 wks with 7 day course of metronidazole than 2g stat or if cannot tolerate oral metronidazole Pregnancy; avoid oral azole, use intravaginal for 7 days Pregnant/breastfeeding: avoid 2g stat clindamycin 2% cream Treating partners does not reduce relapse Trichomoniasis Pelvic Inflammatory Disease 3rd or 4th degree perineal tear post vaginal delivery Treat partners and refer to GUM service In pregnancy or breastfeeding: avoid 2g single dose metronidazole. Consider clotrimazole for symptom relief (not cure) if metronidazole declined or not appropriate. Refer woman & contacts to GUM service Always test for gonorrhoea & chlamydia 28% of gonorrhoea isolates now resistant to quinolones If gonorrhoea likely (partner has it, severe symptoms, sex abroad) use ceftriaxone regimen or refer to GUM metronidazole clotrimazole metronidazole PLUS ofloxacin 2g 5g applicatorful at night 7 nights 400 mg BD or 2 g (preferred) 7 days stat 100 mg pessary at night 6 nights 400 mg BD 400 mg BD 14 days 14 days 500 mg IM 400 mg BD Stat If high risk of Gonococci Ceftriaxone PLUS Metronidazole PLUS 14 days 14 days doxycycline 100mg BD Prophylaxis against infection will be provided by the acute trust in the form of single intravenous antibiotics prerepair followed by up to five days of co-amoxiclav when deemed necessary. The patient will be given the full course from the ward. If infection develops (and this requires antibiotic treatment) please contact microbiology for advice. Skin Infections Impetigo Oral flucloxacillin For extensive, severe, or bullous impetigo, use oral antibiotics Reserve topical antibiotics for very localised lesions to reduce the risk of resistance Reserve mupirocin for MRSA. Eczema Cellulitis Mastitis and ductal candidiasis Leg Ulcers If penicillin allergic: oral erythromycin 500 mg QDS 7 days 500 mg QDS 7 days Topical treatment Fusidic acid TDS 5 days MRSA only Mupirocin TDS 5 days If no visible signs of infection, use of antibiotics (alone or with steroids) encourages resistance and does not improve healing. In eczema with visible signs of infection, use treatment as in impetigo If patient afebrile and healthy other than cellulitis, use oral flucloxacillin alone If river or sea water exposure, discuss with microbiologist. Be alert for Group A strep. NSAIDS may mask symptoms, if suspect please discuss with microbiologist. If febrile and ill, admit for IV treatment (IV teicoplainin is available for home IV treatment for non-facial cellulitis if patient does not require admission otherwise) NB if breast abscess, ensure surgeons are involved as drainage will be needed Ulcers always colonized. Antibiotics do not improve healing unless active infection If active infection, send pre-treatment swab Review antibiotics after culture results. flucloxacillin If penicillin allergic: 500 mg QDS erythromycin or clindamycin 500 mg QDS facial: co-amoxiclav 500/125 mg TDS Mastitis Flucloxacillin Add in clindamycin if infection is more severe or not settling Penicillin allergy – Clindamycin alone 1g QDS All for 7 days. If slow response continue for a further 7 days 600mg TDS 600mg TDS Total duration 7-14 days depending on severity and response. 600mg TDS If active infection: flucloxacillin 500 mg QDS or erythromycin 500 mg BD Grade 0-1 infection Flucloxacillin + Metronidazole 1g QDS 400mg TDS Doxycycline + Metronidazole 100mg BD 400mg TDS All for 7 days. If slow response continue for a further 7 days It is active infection if cellulitis/increased pain/pyrexia/purulent exudate/odour Diabetic feet If a wound is suspected to be infected, a wound swab should be taken (or if possible pus in a pot) and sent to Microbiology for investigation. Antibiotic cover may be requested at this time if it is suspected that the wound is deteriorating. A broad-spectrum antibiotic should be prescribed, which should then be changed if the Microbiology report identifies the presence of a different organism causing the infection. If infection is grade 4 patient should be admitted to hospital for intravenous antibiotics MRSA Grade 2 (>2cm cellulitis) Co-amoxiclav Penicillin allergy / High C diff risk Doxycycline + Rifampicin Grade 3 Infection Probes to bone Ciprofloxacin + Clindamycin If high C diff risk Doxycycline + Rifampicin 625mg TDS 100mg BD 300-600mg BD 750mg BD 600mg TDS Antibiotics may be needed for 2 weeks, and much longer if osteomyelitis is present or suspected. 100mgs BD 300-600mgs BD For MRSA screening and suppression, see Infection Prevention and control site. For active MRSA infection: Use antibiotic sensitivities to guide treatment. If severe infection or no response to monotherapy after 24-48 hours, seek advice from microbiologist on combination therapy. PVL S. aureus Penicillin allergy: 7 days should be prescribed initially, and continued as necessary, according to clinical signs of infection and inflammatory markers. If active infection, MRSA confirmed by lab results, infection not severe and admission not required If active infection confirmed doxycycline For 7 days 100 mg BD Panton-Valentine Leucocidin (PVL) is a toxin produced by 2% of S. aureus. Can cause severe invasive infections in healthy people. Send swabs and request to look for PVL producer if recurrent boils/abscesses or if not responding to flucloxacillin. People most at risk are those with a close contact in communities, sport or poor hygiene. If worried re this contact Microbiology urgently! Bites (Human, cat and dog) Scabies Fungal infection – skin Fungal infection – fingernail or toenail Herpes Zoster/Chicken Pox and Varicella Zoster/Shingles Headlice Surgical toilet is very important. In the case of animal bites a risk assessment of tetanus and rabies should be made. For human bites the risk of HIV/hepatitis B and C should be assessed. Special care and monitoring should be given to those at greater risk e.g. elderly, immunocompromised, asplenic and diabetic patients. Treat all home & sexual contacts within 24h. Treat whole body from ear/chin downwards and under nails. If under 2/elderly, also face/scalp Terbinafine is fungicidal so treatment time shorter than with fungistatic imidazoles. If candida possible, use imidazole If intractable: send skin scrapings. If infection confirmed, use oral terbinafine/itraconazole Scalp: discuss with specialist NHS Stockport only commissions treatment for fungal nail infection if 1. The patient is immunocompromised; or 2. the patient has peripheral vascular disease; or 3. the patient is diabetic; or 4. the nail is painful; or 5. the patient is due to undergo surgery on that limb; AND 6. There has been mycological confirmation. When terbinafine is the drug of choice only oral terbinafine should be prescribed as topical terbinafine has inferior efficacy. Please ensure that BNF guidelines for monitoring patients are followed and that patients do not continue treatment for longer than the recommended duration in The BNF. Terbinafine is more effective than azoles Liver reactions rare with oral antifungals If candida or non-dermatophyte infection confirmed, use oral itraconazole For children, seek specialist advice If pregnant seek advice from microbiologist (also seek advice if pregnant patient in contact with chicken pox case). Clinical value of antivirals is minimal unless secondary household case of chicken pox, facial/ophthalmic shingles, or severe pain and IF TREATMENT IS STARTED LESS THAN 2 DAYS AFTER THE COMMENCEMENT OF THE RASH. Be wary of Group A Streptococcus secondary infection in these patients. Predictors of shingles post-herpetic neuralgia include >50 years, severe pain, severe skin rash and prolonged prodromal pain. Dimeticone is effective against head lice and acts on the surface of the organism. Malathion, an organophosphorus insecticide, is an alternative, but resistance has been reported. A contact time of 8–12 hours or overnight treatment is recommended for lotions and liquids; a 2-hour treatment is not sufficient to kill eggs. In general, a course of treatment for head Co-amoxiclav 625mg TDS 7 days Doxycycline + Metronidazole 100mg BD 400mg BD 7 days permethrin 5% cream malathion 0.5% aqueous liquid 2 applications 1 week apart Topical terbinafine BD 1-2 weeks or topical imidazole or (athlete’s foot only): BD topical undecanoates (Mycota®) BD for 1-2 wks after healing (i.e. 4-6wks) First line; terbinafine 250mg OD fingers toes 6-12 weeks 3-6 months Second line: itraconazole 200mg BD fingers toes 7 days per month 2 courses 3 courses Superficial only: amorolifine 5% nail lacquer 1-2x/week fingers toes Pencicillin allergy If allergy: If indicated: aciclovir Second line for shingles if compliance a problem, as ten times cost 800 mg five times a day valaciclovir 6 months 12 months 7 days 7 days 1 g TDS (For children’s doses see BNFC) 1st line Dimeticone 4% lotion 2nd line Malathion 0.5% liquid Apply to dry hair and leave for at least 8 hours then shampoo Repeat treatment after 7 days Herpes Simplex Genital / Lip lice should be 2 applications of product 7 days apart to kill lice emerging from any eggs that survive the first application. All affected household members should be treated simultaneously. Head lice can be mechanically removed by combing wet hair meticulously with a plastic detection comb (probably for at least 30 minutes each time) over the whole scalp at 4-day intervals for a minimum of 2 weeks, and continued until no lice are found on 3 consecutive sessions; hair conditioner or vegetable oil can be used to facilitate the process. http://www.insectresearch.com/ps_faqlic e.htm (Lip) Topical aciclovir 5 times daily Acute/reoccurrence (genital) Aciclovir 400mg TDS OR 200mg 5 times daily Prevention of recurrence (genital) Aciclovir 5 days Max 1 year 400mg BD Eye Infections Conjunctivitis Most bacterial conjunctivitis is self-limiting. Fusidic acid has no Gram-negative activity and is not usually recommended as increased risk of resistance If severe: chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops and 1% ointment Second line: Fusidic acid 1% gel 2 hourly for 2 days then 4 hourly (whilst awake) at night All for 48 hours after resolution BD Dental Infections – For dental prescribers only This guidance is not designed to be a definitive guide to oral conditions. It is for GPs for the management of acute oral conditions pending being seen by a dentist or dental specialist. GPs should not be involved in dental treatment and advice should be sought from the patient’s dentist. If they don’t have a usual dentist they can call the Stockport dental helpline on 0161 476 9649, or if out of hours NHS Direct on 0161 337 2246 or by calling 111 from a land line telephone. Simple saline mouthwash ½ tsp salt dissolved in Always spit Temporary pain and swelling relief can be Mucosal glass warm water out after use. attained with saline mouthwash ulceration and Use antiseptic mouthwash: Rinse mouth for 1 Chlorhexidine 0.12-0.2% Use until If more severe & pain limits oral hygiene to (Do not use within minute BD with 5 ml inflammation lesions treat or prevent secondary infection. diluted with 5-10 ml 30 mins of toothpaste) (simple resolve or less water. The primary cause for mucosal ulceration pain allows gingivitis) or inflammation (aphthous ulcers, oral Hydrogen peroxide 6% oral hygiene lichen planus, herpes simplex infection, Rinse mouth for 2 (spit out after use) oral cancer) needs to be evaluated and mins TDS with 15ml treated. diluted in ½ glass warm water Commence metronidazole and refer to Metronidazole 400 mg TDS 3 days Acute dentist for scaling and oral hygiene advice necrotising Use in combination with antiseptic Chlorhexidine or see above dosing in Until oral mouthwash if pain limits oral hygiene hydrogen peroxide mucosal ulceration hygiene ulcerative possible gingivitis Pericoronitis Dental abscess Refer to dentist for irrigation & Amoxicillin 500 mg6 TDS 3 days debridement. If persistent swelling or systemic Metronidazole 400 mg TDS 3 days symptoms use metronidazole. Chlorhexidine or see above dosing in Until oral Use antiseptic mouthwash if pain and hydrogen peroxide mucosal ulceration hygiene trismus limit oral hygiene possible Regular analgesia should be first option until a dentist can be seen for urgent drainage, as repeated courses of antibiotics for abscess are not appropriate; Repeated antibiotics alone, without drainage are ineffective in preventing spread of infection. Antibiotics are recommended if there are signs of severe infection, systemic symptoms or high risk of complications. Severe odontogenic infections; defined as cellulitis plus signs of sepsis, difficulty in swallowing, impending airway obstruction, Ludwigs angina. Refer urgently for admission to protect airway, achieve surgical drainage and IV antibiotics The empirical use of cephalosporins, co-amoxiclav, clarithromycin, and clindamycin do not offer any advantage for most dental patients and should only be used if no response to first line drugs when referral is the preferred option. If pus drain by incision, tooth extraction or Amoxicillin2 or 500 mg TDS via root canal. Send pus for microbiology. Phenoxymethylpenicillin 500 mg – 1g QDS Up to 5 days True penicillin allergy: use clarithromycin review at 3days True penicillin allergy: or clindamycin if severe. Clarithromycin 500 mg BD If spreading infection (lymph node Severe infection add involvement, or systemic signs i.e. fever or Metronidazole or if allergy 400 mg TDS 5 days malaise) ADD metronidazole Clindamycin 5 days 300mg QDS Illness Comments Nursing home antibiotic guidelines Drug Dose Duration of TX Nursing home patients are at very high risk of Clostridium difficile infection so caution must be used when prescribing antibiotics. Antibiotics must only be prescribed if absolutely indicated and for the shortest possible time. Where possible, do not use the following classes of antibiotics which have been found to be more likely to give rise to Clostridium difficile infection: Clindamycin, Cephalosporins, Quinolones, Beta lactam / beta lactamase inhibitors e.g. co-amoxiclav Every patient prescribed PPIs should have these reviewed. If there is not a good indication for their use they should be stopped in a safe manner or the dose reduced or changed to an H2 receptor antagonist. For certain conditions, patients can have once or twice daily IV antibiotics if appropriate to avoid being admitted to hospital. See the table below for the options available. As the patient is resident in a nursing Doxycycline 100mg BD on day one For 7 days Pneumonia home, pneumonia should be treated then 100mg daily as a hospital acquired pneumonia, as thereafter. including IV treatment different bacteria could be responsible Review at 24-48hours Ertapenem aspiration for the infection than in a simple 1g OD community acquired pneumonia. pneumonia Cellulitis Flucloxacillin Or Doxycycline Or Azithromycin IV treatment Teicoplanin UTI Trimethoprim Or Pivmecillinam 1g QDS 100mg BD 500mg OD 5 days then review and may need a further five days 1.2g stat then 600-800mg OD Review after 48hours 200mg BD 200mg tds IV treatment If ESBL positive UTI and patient does not require hospital admission Ertapenem 7-14 days depending on severity and response Treat for total 7 days in women and 14 days in men 1g OD Antibiotic group August 2014 Review date August 2015 Adapted from HPA – Management of infection guidance for primary care for consultation and local adaptation. Originally produced 2000, last reviewed Nov 2012, last revised Feb 2013. http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1279888711402 References can be provided on request Contact details for microbiologist at Stepping Hill Hospital Tel:01614194491 or email non urgent queries to snt-tr.pathologyenquiries@nhs.net IV antibiotics are available for certain conditions. To discuss treatment options or any concerns, please discuss with microbiology. For training resources and patient information leaflets please see RCGP Target antibiotics toolkit (http://www.rcgp.org.uk/clinical-and-research/target-antibiotics-toolkit.aspx) Useful links NICE clinical knowledge summaries CKS British association for sexual health and HIV BASHH