Name
advertisement
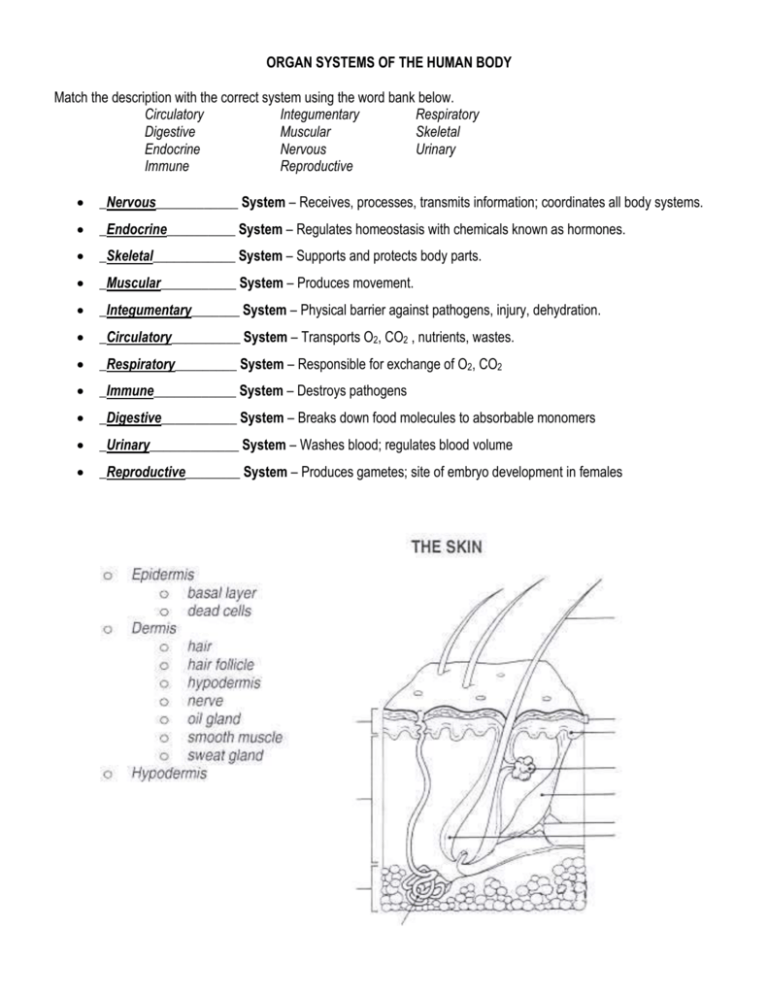
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE HUMAN BODY Match the description with the correct system using the word bank below. Circulatory Integumentary Respiratory Digestive Muscular Skeletal Endocrine Nervous Urinary Immune Reproductive _Nervous____________ System – Receives, processes, transmits information; coordinates all body systems. _Endocrine__________ System – Regulates homeostasis with chemicals known as hormones. _Skeletal____________ System – Supports and protects body parts. _Muscular___________ System – Produces movement. _Integumentary_______ System – Physical barrier against pathogens, injury, dehydration. _Circulatory__________ System – Transports O2, CO2 , nutrients, wastes. _Respiratory_________ System – Responsible for exchange of O2, CO2 _Immune____________ System – Destroys pathogens _Digestive___________ System – Breaks down food molecules to absorbable monomers _Urinary_____________ System – Washes blood; regulates blood volume _Reproductive________ System – Produces gametes; site of embryo development in females INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (pp. 807-809) I. Function Protection Sensory Information Regulation of Body Temperature Vitamin Production – The skin produces Vitamin _D__, needed for _strong bones__, when exposed to _sunlight__. II. Structure – The skin is composed of three layers: A. Epidermis 1. Basal Layer – Contains cells that are actively going through _mitosis_______. As new cells are produced, older cells are _pushed toward surface________. There are two important proteins made by specialized cells in the epidermis: a. Keratin - _Waterproofs__ skin. b. Melanin - _Dark brown___ pigment; protects skin from _UV light________ 2. Outer Layer – As the epidermal cells are pushed away from blood vessels, they _die____ so the outermost epidermal layer consists of _dead___ cells filled with _keratin___ that are eventually _sloughed off______. B. Dermis – Inner, thicker layer that contains _collagen____ for strength and _elastin___ for elasticity. Structures found in the dermis include: 1. Blood vessels – Provide _O2___ and _glucose____ to cells; remove _wastes_______. Also help to maintain a constant body temperature. Heat can be conserved when blood vessels near the surface of the skin _constrict_____, or heat can be released when blood vessels _dilate__________. 2. Hair follicles - _Mitosis____ occurs in follicle to produce hair. Hair consists of _dead___ cells filled with _keratin____. Small muscles are attached to each follicle that pull hairs upright when stimulated by _cold, fear______ 3. Nail follicles – Produced in same manner as hair. Purpose of nails is to _protect___ fingertips & toetips. 4. Sensory receptors 5. Glands – There are two types of glands located in the dermis: a. Oil – Produce oil to _lubricate skin_______ b. Sweat - _Evaporation_____ of the perspiration produced by these glands requires energy in the form of _heat____, which is drawn from the skin and results in cooling. C. Hypodermis – Innermost layer that stores _fat____. III. Skin Damage & Disorders A. Burns – Classified according to depth of damage 1. First degree – Damage only to _epidermis_____. Skin appears _red___, but without _blisters____. May be caused by _sun, brief contact with hot object________ 2. Second degree – Damage through _epidermis__ to _dermis_. Most painful of all burns. Skin is _red___ with _blisters____. May be caused by _longer exposure to sun, hot objects______. 3. Third degree – Destroys _epidermis____; damage extends into _dermis_. Skin usually appears _blackened, charred____. May be caused by _fire, electricity, chemicals, NOT sun!__ B. Skin Cancer – Most important risk factor is _sun exposure__________. The most serious type of skin cancer is _melanoma______.