Gout
advertisement

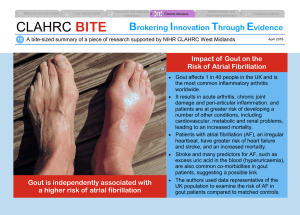
GOUT TAHIRA KHAN UG-3B 1 INTRODUCTION: • GOUT is known as the “disease of kings “ and “rich man’s disease”. • Gout (also known as podagra when it involves the big toe) • it is a medical condition usually characterized by recurrent attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis-red, tender, hot, swollen joints • Gout is a kind of arthritis that occurs when uric acid builds up in blood and causes joint inflammation. • Gout effects more men then woman in them occurs after menopause http://www.jfootankleres.com/content/pdf /1757-1146-4-13.pdf 2 CAUSES • • • • • Hyperuricemia is the underlying cause of gout. diet, genetic predisposition, or underexcretion of urate Low uric acid level in blood the exact cause is unknown. Partly genetic cause in the genes contributing to about 60% of variability in uric acid level • Three genesSLC2A9, SLC22A12 and ABCG2 have been found to commonly be associated with gout, and variations in them can approximately double the risk • Loss of function mutations in SLC2A9 and SLC22A12 cause hereditary hypouricaemia by reducing urate absorption and unopposed urate secretion www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov SYMPTOMS • • • • • • • • • gouty arthritis Acute gouty arthritis in big toe(podagra) Kidney stones Acute pain in joints Uric acid crystal depositon in the form of tophi Tophi in ear lobe, achilles ankle and elbow Fatigue Mailase High uric acid levels http://www.aafp.org/afp/1999/0215/p925. html TYPES OF GOUT • Depending upon the symptoms and severity of disease gout is classified into • Acute gout • Chronic gout 5 ACUTE GOUT • Acute gout is a painful condition that typically affects one joint • Symptoms usually involve only one or a few joints. The big toe, knee, or ankle joints are most often affected. • throbbing, crushing, or excruciating pain • joint appears warm and red • fever. • The attack may go away in a few days, but may return from time to time. Additional attacks often last longer. • After a first gouty attack, people will have no symptoms. Half of patients have another attack. http://www.aafp.org/afp/1999/0215/p925. html CHRONIC GOUT • Those with chronic arthritis symptoms include: • joint damage and • loss of motion in the joints. • joint pain and other symptoms most of the time. • Tophi below the skin around joints or in other places. Tophi usually develop only after a patient has had the disease for many years. http://www.aafp.org/afp/1999/0215/p925. html DIAGNOSTIC TESTS • • • • • • • Synovial fluid analyis (shows uric acid crystals) Uric acid – blood BUN (blood urea nitrogen Joint x-rays (may be normal) Synovial biopsy Uric acid – urine Creatnine level 8 BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR GOUT: 9 EXAMINATION OF SYNOVIAL FLUID • ASPIRATION: • The health care provider uses a needle attached to a syringe to draw out fluid from the affected joint. • LAB ANALYSIS: • The fluid sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. Testing can reveal the presence of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which will nearly always confirm a diagnosis of gout. The laboratory can also test the sample for infection. • The procedure itself can cause infection, though this occurs in less than 0.1% of patients. Aspiration sometimes eases the patient's symptoms by reducing swelling and pressure on the tissue surrounding the http://www.umm.edu/patiented/articles/what_risk_factors_gout_000093_5.htm#ixzz2BBsc1QLS joint. TREATMENT • • • • NSAID,s Colchicine Uricosuric agents Allopurinol COLCHICINE Produces its anti-inflammatory effects by binding to the intracellular protein tubulin, preventing its polymerization leading to the inhibition of leukocyte migration into affected area. Inhibits the synthesis & release of leukotrienes. 11 CONTINUED URICOSURIC AGENTS: NSAIDS: ALLOPURINOL • Probenecid & Sulfinpyrazone • They are weak organic acids .Sulfinpyrazone is a metabolite of • phenylbutazone. Inhibits pain & inflammation. Inhibits synthesis of uric acid by inhibiting xanthine oxidase enzyme Inhibits urate crystal phagocytosis by decreasing the migration of granulocytes into the inflammatory area. Indomethacin 12 13 14