HBIntegu
advertisement
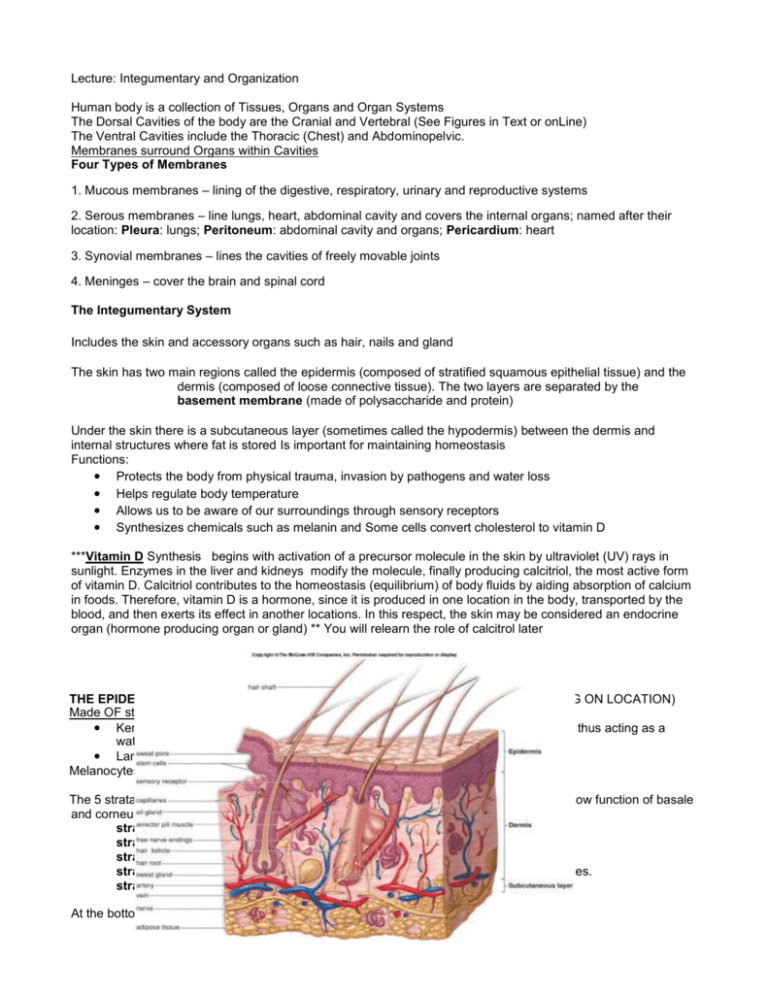
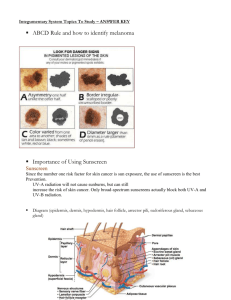
Lecture: Integumentary and Organization Human body is a collection of Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems The Dorsal Cavities of the body are the Cranial and Vertebral (See Figures in Text or onLine) The Ventral Cavities include the Thoracic (Chest) and Abdominopelvic. Membranes surround Organs within Cavities Four Types of Membranes 1. Mucous membranes – lining of the digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems 2. Serous membranes – line lungs, heart, abdominal cavity and covers the internal organs; named after their location: Pleura: lungs; Peritoneum: abdominal cavity and organs; Pericardium: heart 3. Synovial membranes – lines the cavities of freely movable joints 4. Meninges – cover the brain and spinal cord The Integumentary System Includes the skin and accessory organs such as hair, nails and gland The skin has two main regions called the epidermis (composed of stratified squamous epithelial tissue) and the dermis (composed of loose connective tissue). The two layers are separated by the basement membrane (made of polysaccharide and protein) Under the skin there is a subcutaneous layer (sometimes called the hypodermis) between the dermis and internal structures where fat is stored Is important for maintaining homeostasis Functions: ● Protects the body from physical trauma, invasion by pathogens and water loss ● Helps regulate body temperature ● Allows us to be aware of our surroundings through sensory receptors ● Synthesizes chemicals such as melanin and Some cells convert cholesterol to vitamin D ***Vitamin D Synthesis begins with activation of a precursor molecule in the skin by ultraviolet (UV) rays in sunlight. Enzymes in the liver and kidneys modify the molecule, finally producing calcitriol, the most active form of vitamin D. Calcitriol contributes to the homeostasis (equilibrium) of body fluids by aiding absorption of calcium in foods. Therefore, vitamin D is a hormone, since it is produced in one location in the body, transported by the blood, and then exerts its effect in another locations. In this respect, the skin may be considered an endocrine organ (hormone producing organ or gland) ** You will relearn the role of calcitrol later THE EPIDERMIS: The thin, outermost layer of the skin (THICKNESS VARIES DEPENDING ON LOCATION) Made OF stratified squamous epithelial tissue, Has several types of cells: ● Keratinocytes: Cells in the uppermost cells are dead and become filled with keratin thus acting as a waterproof barrier ● Langerhans cells are a type of white blood cell that help fight pathogens Melanocytes produce melanin that lend to skin color and protection for UV light The 5 strata of the epidermis: from bottom (closest to dermis) to top (on surface). Please know function of basale and corneum. stratum basale ( these are the stem cells also melanocytes) stratum spinosum stratum granulosum stratum lucidum thin,clear layers found only in epidermis of the lips,palms and soles. stratum corneum (top dead cells filled with keratin) At the bottom of the stratum basale is the basement membrane The Dermis: Made of dense fibrous connective tissue Papillary layer, upper, contains a thin arrangement of collagen fibers.Undulates with the epidermis to prevent epidermis from sliding. This layer responsible form fingerprint. Reticular layer, lower, is thicker, made of thick collagen fibers that are arranged parallel to the surface of the skin Dermis Contains blood vessels, many nerve cell (sensory receptors) and glands, hair follicle ● Nerves transmit sensations of pain, itch, and temperature. ● Specialized nerve cells called Meissner's and Vater-Pacini corpuscles that transmit the sensations of touch and pressure. ● The hair follicles are situated here with the erector pili muscle that attaches to each follicle. ● Glands : Sebaceous (oil) glands, apocrine (scent) glands are associated with the follicle. Eccrine (sweat) gland not associated with hair Separating the Dermis from the Skeletal Muscles is the Subcutaneous Layer It is a layer of fat and connective tissue and houses larger blood vessels and nerves. Important is the regulation of temperature of the skin itself and the body. CANCER OF SKIN (carcinoma is cancer of epithelial tissue and sarcoma is of connective tissue) is caused by damage tot he DNA in the cells. 2 of the 3 types that arise in the epidermis: Basal cell carcinoma is the most common yet least deadly form of skin cancer.Arises in cells called basal keratinocyt Melanoma is the most deadly form of skin cancer but is the least common. Arises in melanocytes,or pigment- producing c What can you do to help prevent Cancer? Stay out of the sun between 10am-3pm Wear protective clothing (tight weave, treated sunglasses, wide-brimmed hat) Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15 and protects from UV-A and UV-B rays Don’t use tanning beds BURNS: First-degree burns, the mildest of the three, are limited to the top layer of skin: These burns produce redness, pain, and minor swelling. The skin is dry without blisters. Healing time is about 3 to 6 days; the superficial skin layer over the burn may peel off in 1 or 2 days. Second-degree burns are more serious and involve the skin layers beneath the top layer:These burns produce blisters, severe pain, and redness. The blisters sometimes break open and the area is wet looking with a bright pink to cherry red color. Healing time varies depending on the severity of the burn. Third-degree burns are the most serious type of burn and involve all the layers of the skin and underlying tissue: The surface appears dry and can look waxy white, leathery, brown, or charred. There may be little or no pain or the area may feel numb at first because of nerve damage. Healing time depends on the severity of the burn. Deep second- and third-degree burns (called full-thickness burns) will likely need to be treated with skin grafts, in which healthy skin is taken from another part of the body and surgically placed over the burn wound to help the area heal. The skin is more permeable to fat based solvents than water based solvents. The lipid based substances and solvents can cross the plasmamembrane better and can damage vital organs like the kidney and brain. Hives are welts, redded bumbs, that indicate sites of local inflammation. They are a sign of an alergic reaction. Cyanosis is a blue coloring to the skin, often due to a lack of oxygen.