General Science Chapter 23 Notes

Chapter 23
Earth’s Surface
23.1 Fresh Water
• Earth is 71% water
• 97% is salt water
• 3% is freshwater
• Most freshwater is in the form of groundwater- water found underground in cracks and between particles of rock and soil.
• Some freshwater is found in lakes, streams, water vapor, and clouds.
The Water Cycle
• The water cycle is made up of several processes, including evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, and the eventual return of flowing water to the ocean.
• Evaporation- liquid to vapor (gas)
• Transpiration- when water vapor is released from the leaves of trees and other plants
• Condensation- when water vapor expands and cools, water vapor forms droplets which crystallize at lower temperatures
• Precipitation- when water droplets or ice crystals get too heavy, they fall as rain, sleet, snow, hail, or freezing rain
Fresh Water
• A small portion of Earth’s fresh water is located in the atmosphere, streams, and lakes. Most is located in groundwater and glaciers.
• Glaciers- large masses of moving ice and snow on land
• Runoff- water that flows over Earth’s surface, goes into streams
• Tributary- smaller stream that flows into a larger river
• Watershed- area of land that contributes water to a river system
(Rocky Mountains to Appalachian)
• Saturated zone- region where the pore spaces are entirely filled with groundwater
• Water table- top of saturated zone
• Permeable- water can pass through
• Aquifer- permeable rock saturated with water
• Impermeable- water cannot pass through
23.2 Weathering and Mass Movement
• Erosion- the process that wears down and carries away rock and soil
• Erosion acts through weathering, the force of gravity, and through the movement of streams, groundwater, glaciers, wind, and waves.
• Erosion forms canyons, caves
Weathering
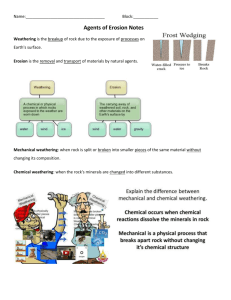
• Weathering is the process by which rocks are chemically altered or physically broken down into fragments at or near Earth’s surface
• There are two forms of weathering: mechanical and chemical. They cause rocks to disintegrate or decompose.
• Mechanical weathering- process of physically breaking rock into smaller fragments
• Abrasion- rocks scrape or grind against one another
• Chemical weathering- process in which rock is broken down by chemical reactions, such as water, acid, and oxidation
Rates of Weathering
• The rate at which mechanical and chemical weathering take place depends on three main factors: temperature, the availability of water, and the type of rock.
• High temperature and abundant rainfall lead to a higher rate of weathering.
• Limestone and marble rapidly weather.
Mass Movement
• Mass movement- the downward movement of rock and soil due to gravity
• Through the process of mass movement, gravity moves loose material down a slope.
• Landslide- rapid movement of large amounts of rock and soil
• Mudflow- rapid mass movement of soil and other sediment mixed with water
• Creep- soil gradually moves down a slope (caused from ice)
• Slump- weak layers of soil or rock suddenly move downslope as a single unit
23.3 Water Shapes the Land
• Deposition- the process in which sediment is laid down in new locations, usually by flowing water
• Saltation- process of particles bouncing along a stream bottom
• A stream’s ability to erode depends mainly on its speed.
Features Formed by Water Erosion
• Water erosion forms V-shaped valleys, waterfalls, meanders, and oxbow lakes.
• V-shaped valley- contains rapids and waterfalls, occur at stream’s source
• Flood plain- flat area along a stream that is entirely covered only during times of flood
• Meander- slight curving of river, looks like a loop
• Oxbow lake- a separate, curved lake formed when sediments cut off river
Features Formed by Water Deposition
• Features deposited by flowing water include alluvial fans and deltas.
• Alluvial fan- when a stream flows out the mountains and onto plains, it slows down, sediments settle, and a fan-shaped deposit of sediment is left
• Delta- a mass of sediment deposited where a river enters a large body of water
Groundwater Erosion
• The processes of chemical weathering causes much groundwater erosion, including the formation of caves and sinkholes.
• Stalactite- on cavern ceiling, icicle-like formation
• Stalagmite- pillar of minerals on cavern floor
• Sinkhole- weakened limestone can collapse suddenly
23.4 Glaciers and Wind
• Glaciers form in places where more snow falls than melts or sublimates.
• Continental glacier- thick sheet of ice that covers a huge area, such as a continent or large island
• Valley glacier- glacier that occurs in a high mountain valley
• Plucking- glacial ice widens cracks in bedrock beneath the glacier
• Glaciers cause many distinctive features in the landscape, including cirques, horns, U-shaped valleys, and glacial lakes
• Cirque- valleys formed from valley glaciers
• When a glacier melts, it deposits its load of sediment, creating a variety of landforms.
• Till- glacial sediment
• Moraine- mound of sediment at the downhill end of the glacier and along its sides, formed by till
Wind Erosion and Deposition
• Wind erodes the land by deflation and abrasion.
• Deflation- wind picks up and carries away loose surface material
• Abrasion- wind blows sand against other rocks, sandblasting
• Features deposited by wind include sand dunes and loess deposits
• Dune- deposit formed from windblown sand
• Loess (less)- deposit formed from windblown dust
23.5 The Restless Oceans
• Salinity- the proportion of dissolved salts in water (35g/kg water)
• Light and temperature decrease with depth, whereas pressure increases.
• Continental shelf- gently sloping plain forms an apron of shallow water along the edges of most continents
• Surface current- large stream of ocean water that moves continuously in about the same path.
• Winds blowing across the surface of the ocean cause the continuous flow of surface currents
• Deep ocean currents are caused by differences in the density of ocean water
• Upwelling- movement of water from the deep ocean to the surface
• In upwelling, winds blow warm surface water aside. This allows cold water from the deep ocean to rise and take the place of the warmer water.
• Two physical processes, hydraulic action and abrasion, are responsible for much wave erosion
• Longshore drift- the process that moves sand along a shore
23.6 Earth’s History
• Relative age- of a rock is compared to the ages of other rocks above or below it in a sequence of rock layers
• Law of superposition- if rock layers are undisturbed, younger rocks lie above older rocks, and the oldest rocks are at the bottom
• Geologists use the law of superposition to determine the relative ages of sedimentary rocks from the sequence of rock layers and the fossils within each layer.
• Extinct- no longer exists
• Index fossil- easily identified, occurred over a large area, and lived during a well-defined period of time
• Absolute age- time that has passed since the rock formed, determined by radioactive dating
A Brief History of Earth
• Era- major stage in Earth’s history
• Period- smaller unit of era
• Mass extinction- when many creatures die in a short time
• Precambrian time- 4.6 Billion to 544 Million years ago,
Earth was formed, one-celled organisms
• Paleozoic Era- 544 to 248 Million years ago, clam and worm, fish, flood
• Mesozoic Era- 248 to 65 Million years ago, dinosaurs
• Cenozoic Era- 65 Million years ago to now, ice age, mammals, humans