Periodic Table: Elements, Properties & Trends

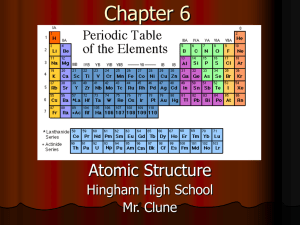
The Periodic Table
Elements are arranged in groups based on properties
The Periodic Table
Dmitri Mendeleev arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangements to predict the properties of missing elements.
The Periodic Table
The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
The atomic number is the total number of protons in the nucleus.
The electron mostly determines the properties of an element.
The Periodic Table
Indium:
______ protons
______ electrons
49 49
The Periodic Table
GROUPS vertical columns
Old 1A - 8A new 1 - 18
Periods - horizontal rows
Magnesium is in the same group as calcium.
Magnesium is in the same period as phosphorus.
The three classes of elements are: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids .
The Periodic Table
Metals include the majority of the elements.
Pt is a metal.
Si is a metalloid.
Kr is a nonmetal.
Metals are shiny, malleable (hammered into sheets), ductile (drawn into wires), solid at room temperature, and good conductors of electricity.
The Periodic Table
Nonmetals are poor conductors of electricity, often gases at room temperature, and brittle if solid.
Metalloids have some properties of metals and nonmetals.
Group 1A - alkali metals
Group 2A - alkaline earth metals
Group 7A - halogens
Group 8A - noble gases
Groups 1A through 7A representative elements
Group B - transition metals
The Periodic Table
Aluminum is a representative element.
Copper is a transition metal.
Na is an _______________________
Mg is an _______________________
F is a ________________________
Ne is a ______________________
Ag is a ______________________
The Periodic Table
Na is an alkali metal
Mg is an alkaline earth metal
F is a halogen
Ne is a noble gas
Ag is a transition metal
The Periodic Table
There are 5 electrons in the valence level of an element in Group 5A.
N, P, As, and Sb have the same number of electrons in their valence levels.
The Periodic Table
The electron configuration for an element in the halogen group should always end with ns 2 np 5 .
The electron configuration of the element chlorine ends in 3s 2 3p 5 .
The Periodic Table
Noble gases (inert gases) have their highest occupied s and p sublevels filled.
Fe contains an electron in a d sublevel.
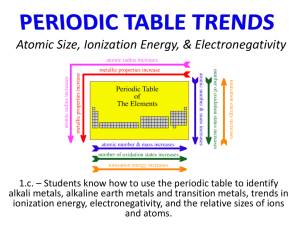
Atomic size
The atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group in the periodic table.
As you move down a group in the periodic table, atomic size generally increases
Atomic size
The atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period in the periodic table.
Lithium has the largest atomic radius in the second period.
As the number of electrons added to the same energy level increases, atomic size generally decreases.
Atomic size
List the symbols for sodium, sulfur, and cesium in order of increasing atomic radii _____________________ The largest atom in Group 1A is
______________
The smallest atom in Group 7A is
______________
Atomic size
List the symbols for sodium, sulfur, and cesium in order of increasing atomic radii: S, Na, Cs
The largest atom in Group 1A is Fr.
The smallest atom in Group 7A is F.
Ions & Ionization
Ions form when electrons enter or leave atoms.
Ions & Ionization
The charge of a cation is positive.
Cations are smaller than the original atom.
An anion has a negative charge. Anions are larger than the original atom.
Ions & Ionization
Removing one electron from an atom results in the formation of an ion with a
1+ charge.
Ions & Ionization
Ionization energy - energy required to move an electron out of an atom
Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom and increases from left to right on the periodic table.
Ions & Ionization
Among Na, K, and Cs, which element has the lowest ionization energy?
Which is larger, K or K+?
Which is smaller, Li, Li+, F, or F- ?
Ions & Ionization
Among Na, K, and Cs, which element has the lowest ionization energy?
Cs
Which is larger, K or K+?
K
Which is smaller, Li, Li+, F, or F- ?
Li +
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a compound to attract electrons
Electronegativity
Electronegativity values tend to decrease from top to bottom and increase from left to right.
Electronegativity
Which element in each pair has a higher electronegativity value?
Mg, Ne
Cl, F
C, N
As, Ca
Electronegativity
Which element in each pair has a higher electronegativity value?
Mg, Ne Mg
Cl, F F
C, N N
As, C As
Electronegativity
Cs has one of the lowest electronegativity values.
Electronegativity
Valence (outer) electrons may be transferred from one atom to another.
Group Valence electrons
1A
2A
3A
Lose 1
Lose 2
Lose 3
Resulting charge
1 +
2 +
3 +
5A
6A
7A
Gain3
Gain 2
Gain 1
3
-
2
-
1
-
Electronegativity
What charge would Na likely have in a compound? _______
What charge would Mg likely have in a compound? _______
What charge would Al likely have in a compound? _______
Electronegativity
What charge would Na likely have in a compound? 1+
What charge would Mg likely have in a compound? 2+
What charge would Al likely have in a compound? 3+
Electronegativity
What charge would O likely have in a compound? _______
What charge would F likely have in a compound? _______
Electronegativity
What charge would O likely have in a compound? 2-
What charge would F likely have in a compound? 1-