Chapter 5 Section 3
Lipids
Mrs. Kerstetter
Biology
Lipids
Lipids
Lipids are generally not soluble in water.
Which means they are HYDROPHOBIC
Lipids are made mostly from carbon and hydrogen
atoms.
Lipid structure
Lipids
The common categories of lipids are:
fats
oils
waxes
steroids
Lipids
What is the function of lipids?
Lipids
Lipids can be used to store energy.
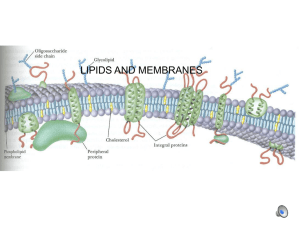
Some lipids are important parts of biological
membranes and waterproof coverings. In other
words…BOUNDARIES
Some circulate in the body as chemical signals to
other cells
Lipids
Many lipids are formed when a glycerol molecule
combines with compounds called fatty acids.
If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid chains is
joined to another carbon atom by a single bond, the
lipid is said to be SATURATED.
The term saturated is used because the fatty acids contain
the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms.
Lipids
If there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond
in a fatty acid, it is UNSATURATED.
Lipids whose fatty acids contain more than one
double bond are polyunsaturated.
Lipids that contain unsaturated fatty acids tend to be
liquid at room temperature.
Saturated fats are SOLIDS at room temperature.
Steroids
= a lipid molecule in which the C skeleton forms 4
fused rings
-all steroids have a core set of 4 fused rings, but
they are different in the kinds and locations of
functional groups attached to the rings
Steroids
Classified as lipids because they are
hydrophobic
Functions:
1. Circulate in body as chemical signals
2. Starting point for other steroids
Estrogen and testosterone are sex hormones cause
major differences in female and male sexual
characteristics
Steroids
Cholesterol
Best known steroid
Found in molecules that surround your cells
Starting point for making other hormones
Bad Rep…Why?
High levels of LDL and VLDL are linked to
increase risk of cardiovascular disease