Rates of Reactions
advertisement

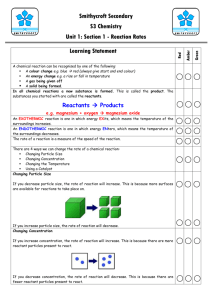
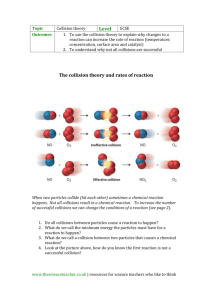
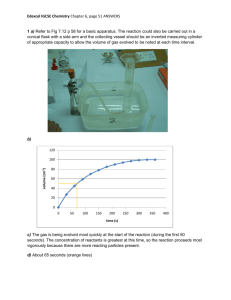
Rates of Reactions • States that particles are constantly moving • Molecules must be moving fast and hit hard for a bond to form (i.e. a chemical reaction occurs) • As particles of matter are moving, they collide or hit each other. • Slow moving particles just bounce off each other. • If the particles are fast and they hit hard enough, the atoms can rearrange themselves to form NEW compounds! • Collisions happen all the time, but most of them are not strong enough to cause a reaction. If we want a reaction to happen faster, we need to increase the total number of collisions. Factors Affecting Rates 1. Temperature Note: The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of reaction. low temperature high temperature When particles are moving faster, they collide with other particles more often, and with more energy. An increase in these collisions will result in chemical reactions. 2. Surface Area Note: The higher the surface area, the faster the rate of reaction. low surface area high surface area The particles on the outside of the reactants react first, so if there are more particles on the surface, then they can react faster. We can increase the surface area by breaking the reactants into smaller pieces. 3. CONCENTRATION Note: The higher the concentration, the faster the rate of reaction. low concentration high concentration An increase in concentration means there are more particles in a certain space. When more particles are packed together, they will collide more often with each other so more reactions occur. 4. CATALYSTS Note: The addition of a catalyst increases the rate of reaction. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction. The catalyst works by reducing the amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur. This means that more collisions can occur thus more reactions occur. no catalyst with catalyst EXAMPLE: MnO2 H2O2 H2O + O2 (Managanese dioxide is the catalyst) Think of a catalyst like a helicopter that helps you up a mountain so you don't have to climb! It makes it easier to go up the mountain, so more people can do it! Factors that affect the rates of reaction Questions! Read p.255, 260-264 and answer the questions below. 1. Write a definition for “rate of reaction”. 2. On p.260, the textbook discusses the collision model. Explain how figure 3 is an appropriate diagram for this discussion. 3. Look at figure 4 and summarize the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction. 4. Look at figure 6 and summarize the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction. Do you think this figure is an effective one for this factor? Explain. 5. (a) Write a definition for catalyst. (b) How does figure 9 relate to your definition? (c) How does figure 9 explain the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction? 6. (a) Write a definition for concentration. (b) How does concentration affect the rate of a reaction? (c) How does figure 5 relate the effect of concentration on the reaction of an acid with a metal?