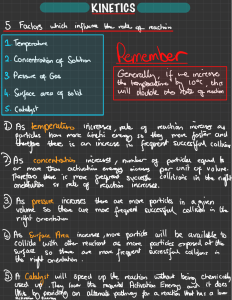
Rate of Chemical Reactions Unit 1 MYP 4 Unit: Particles on the move Key Concept: Systems Related Concept: Consequences and Conditions Global Context: Scientific and Technical Innovation (methods, products, processes and solutions) Statement of Inquiry: Improving existing systems & minimising consequences requires the manipulation of conditions of existing processes or development of new methods ATL: Thinking: Critical Thinking Learner Profile: Thinkers Content Agenda Signs of Chemical reaction Defining reaction rate The Collision theory Factors affecting reaction rate What are the signs of chemical reaction? ● Change of color. ● Change of odor. ● Change of Temperature. ● Evolution of a gas (formation of bubbles) ● Change in state of matter ● Input or release of energy/heat ● Explosion ● Sound ● Precipitate (formation of a solid) not in this ex How to define the Reaction Rate? The speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds. It is often expressed in terms of either: ● the concentration of a product that is formed in a unit of time Or ● the concentration of a reactant that is consumed in a unit of time. Engage: Lab Investigation Sodium Thiosulfate + Hydrochloric acid Na2S2O3 (aq) + 2HCl (aq) Sodium Chloride + Water + Sulphur + Sulfur Dioxide 2NaCl (aq) + H2O(l) + S(s) + SO2(g) Factors affecting the rate of reaction: ● Concentration ● Temperature ● Surface area ● Presence or absence of Catalyst / Inhibitor ● Reactivity of metals Phet Collorado In order for a reaction to take place, what do you think should happen? Study: Collision Theory States that reacting particles must collide in the correct orientation and with enough kinetic energy that they form products If reactant particles do not collide with enough energy and with right orientation, they will not react together. In reality, only a small fraction of the overall collisions, are effective collisions, that result in a chemical reaction. Activation energy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wbGgIfHsx-I Watch this video to find out what is activation energy? What must happen for a reaction to happen? What affects reaction rate? Concentration With an increase in the concentration of any reacting substance, the chances for collisions between molecules are increased because there are more molecules per unit of volume. Temperature As temperature increases, molecules gain energy and move faster and faster. Therefore, the greater the temperature, the higher the probability that molecules will be moving with the necessary activation energy for a reaction to occur upon collision. Surface Area If the surface area of a reactant is increased: more particles are exposed to the other reactant. there is a greater chance of particles colliding, which leads to more successful collisions per second. the rate of reaction increases. Catalysts and inhibitors A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of the reaction without being consumed by the reaction itself. It works by lowering the activation energy by providing an alternative pathway that requires less energy to produce the activated complex. Like enzymes, a biological catalyst. Inhibitors A catalyst inhibitor is a substance that decreases the rate of, or prevents, a chemical reaction, i.e. it opposes the effect of a catalyst. Activate HW On Managebac Worksheet