Amines - Virginia State University
advertisement

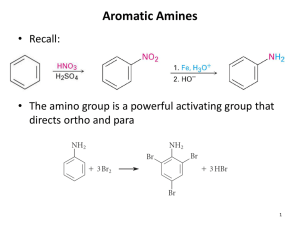
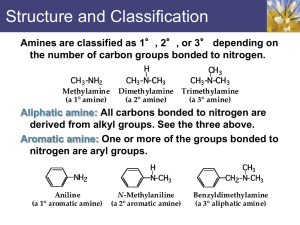
Organic Chemistry II The Chemistry of Amines Dr. Ralph C. Gatrone Department of Chemistry and Physics Virginia State University Spring, 2010 1 Chapter Objectives • Nomenclature • Properties • Preparation • Reactions • Spectroscopy Spring, 2010 2 Nomenclature NH H3C • Alkyl amines H3C NH2 primary amine CH3 secondary amine CH3 H3C N CH3 H3C CH3 + N CH3 CH3 tertiary amine quaternary ammonium salt NH Ph Ph NH2 primary amine • Aryl amines secondary amine Ph Ph N Ph Ph tertiary amine Spring, 2010 Ph H3C + N CH3 CH3 quaternary ammonium salt 3 Alkyl Amines and Aryl Amines • Much of their chemistry is similar • Differences are substantial Spring, 2010 4 Nomenclature • Primary Amines – Add the word amine to the akyl substituent H3C NH2 methyl amine – Replace e with suffix “amine” in parent NH2 cyclopentanamine – Use “amino” as substituent when two functional groups are present COOH o-aminobenzoic acid NH2 Spring, 2010 5 Nomenclature • Secondary and Tertiary Amines – Symmetrical – add “di” or “tri” to alkyl group H3C NH CH3 dimethylamine CH3 trimethylamine CH3 H3C N – Unsymmetrical – N-substituted primary amine CH3 N H3C CH3 N,N-dimethylpropylamine Spring, 2010 6 Aryl Amines • Phenylamine NH2 aniline Spring, 2010 NH CH3 N-ethylaniline 7 Heterocyclic Amines N H N pyridine pyrrole N H indole N H N H piperdine N pyrroidine quinoline Spring, 2010 8 Heterocyclic Amines N N quinolizidine indolizidine Spring, 2010 9 Properties of Amines • Similar to ammonia • sp3 hybridized N • Tetrahedral geometry • Can be chiral • Generally not resolvable • due to pyramidal inversion process • Barrier to inversion is ~25kJ/mol Spring, 2010 10 Properties • • • • • • Amines with < 5 carbons are water soluble Readily hydrogen bond Highly associated structures Higher boiling points than alkanes of similar MW Low MW amines have distinctive fish-like odor Pentane-1,5-diamine (cadaverine) has disgusting odor Spring, 2010 11 Industrial Applications • Insecticides • Pharmaceuticals Spring, 2010 12 Basicity of Amines • Nitrogen has lone pair of electrons • Dominates chemistry of amines • Basic and nucleophilic – React with acids accepting a proton – React with alkyl halides • Stronger bases than alcohols and ethers • Kb values indicate base strength • Large Kb (small pKb) indicates stronger base • Generally consider the pKa of ammonium salt Spring, 2010 13 pKa value R + NH3 + H2O R NH2 + H3O+ R NH2 H3O+ Ka = R + NH3 (Ka)(Kb) = Kw = 1.0 X 10-14 pKa + pKb = 14 Spring, 2010 14 Some Amines and pKa Values of the ammonium ion NH3 9.26 H3C NH2 10.65 11.27 N H 10.76 Et3N 5.25 NH2 4.63 Spring, 2010 N 15 Basicity • Aryl amines are less basic than alkyl amines • The N in amides are non-basic • Poor nucleophile as well • Primary and secondary amines are acidic as well • pKa value is approximately 40 Spring, 2010 16 Basicity • Aryl amines are less basic because the lone pair is often delocalized in the aromatic ring • Substituents on ring can make the nitrogen • • more or less basic Electron donating groups increase basicity Electron withdrawing groups decrease basicity Spring, 2010 17 Preparation of Amines • Reduction LAH R C O R R LAH Spring, 2010 NH2 R NH2 CH2 N NH2 H2 /Pt or SnCl2/HCl NO2 R NH2 N + N N - LAH R CH2 NH2 18 Preparation of Amines • Nucleophilic substitution NH3 R R2NH R X NH2 R R R X N R RNH2 R X Spring, 2010 R R3N R NH R R X R + N R R 19 Preparation of Amines • Reductive Amination of Ketones/Aldehydes O NH2 NH3 H2-Ni or NaBH4 • Reaction proceeds via the imine • NH3, primary and secondary amines work Spring, 2010 20 Reactions of Amines • Alkylation and Acylation of Amines • Most general reactions • Fully covered elsewhere Spring, 2010 21 Reactions of Amines • Hoffmann Elimination • Alkene formation • NH2 is poor leaving group • Reaction requires making it a better LG • Hoffmann Elimination coverts amine into quaternary ammonium salt by reacting with CH3I Spring, 2010 22 Hoffmann Elimination Details NH2 xs CH3I H3C + N CH3 I H3C Ag2O Reaction proceeds via E2 mechanism Product is the less substituted alkene Spring, 2010 23 Aromatic Substitution of Amines • NR2 strongly activating • o, p directing • Often get poly substituted products Br NH2 NH2 Br2 in HOAc Br Br difficult to not get tri-substituted product Spring, 2010 24 Aromatic Substitution of Amines • Friedal-Crafts akylation • Does not work with amines • Fridal-Crafts acylation • Does not work with amines • Amides provide less reactive alternative to amines which allow substitution to occur Spring, 2010 25 Substitution of Amides O NH Br2 in HOAc Br O NH2 Ac O 2 NH CH3 CH3 O NH O H3C Cl AlCl3 Spring, 2010 CH3 H3C O 26 Substitution of Amides • Amide provides – Less activating, o,p directing substituent – Readily removed if needed using aqueous base Spring, 2010 27