Chemistry - Lyons USD 405

Chemistry
Icy Hot Lab
Safety
Wear your safety goggles at all times!
Keep loose clothing and hair back and away from the Bunsen burner flame.
The beakers will get hot! Use the beaker tongs to remove the beaker and dispose of boiling water in the sink.
While you wait
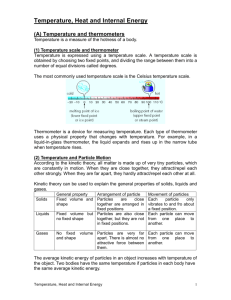
Sketch a diagram illustrating the particles of solid water (ice), liquid water, and water vapor (gas).
Describe the shape, volume, and mass of water as it changes from one phase (state) to the next. For example: Solid water has a constant shape – meaning the cubes of ice hold their shape when dumped onto the table.
While you wait
Pick up a copy of the Energy and Kinetic
Theory of Matter Reading.
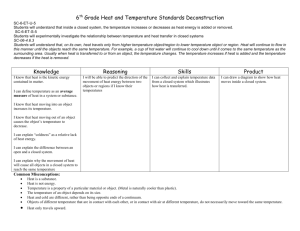
Read page 1. In your chemistry journal, list the three guiding principles used to understand energy.
Read page 2. Use a graphic organizer to compare / contrast money and energy.
Energy Reading page 2
What are the three energy “accounts” used to explain changes in substances or their arrangements in chemistry.
What are the three ways to transfer energy into or out of a substance?
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy can be transferred from one
“account” to another during chemical or physical processes.
Total energy (like mass) before the change equals the total energy (mass) after the change as long as no energy (mass) enters or leaves the system.
1
st
Law of Thermodynamics
If energy is transferred into or out of the system, the change in energy equals the energy transferred by heating, working, or radiating.
ΔE = Q + W + R
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Matter is made up of tiny particles that are in constant motion.
Kinetic Theory of Matter Simulation
Kinetic Theory of Matter
These particles exert long range attractions and short range repulsions on each other. Attractions reduce the interaction energy (E i
) while repulsions increase interaction energy.
Phase Change Simulation
Kinetic Theory of Matter
A warmer sample has (on average) faster moving particles than a cooler sample.
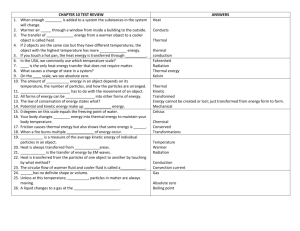
Icy Hot Lab Results
Energy Transferred (Heat)
Discussion Questions: Chemical or
Physical Change?
Was the observed phase changes a chemical change of a physical change?
How do you know?
Discussion Questions: Endothermic or Exothermic Change?
Endothermic change – Change caused by the transfer of energy (heat) into a substance.
Exothermic change – Change caused by the transfer of energy (heat) out of a substance.
Where the phase changes you observed in the lab exothermic or endothermic?
Discussion Questions: Kinetic
Energy or Interaction Energy?
Was the energy transferred to the substance stored as kinetic energy? How can you tell from the Temperature vs. Time graph?
Was the energy transferred to the substance stored as interaction energy?
How can you tell from the Temperature vs.
Time graph?
Discussion Questions: Heating
Slowly or quickly?
How would the Temperature vs. Time graph change if we used two bunsen burners instead of one?