Chapter 15 Blue Book
advertisement

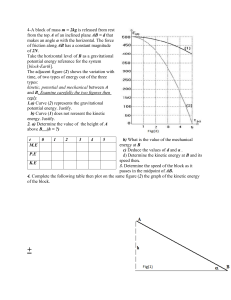
Chapter 15 Flash Cards Answers 1. List four examples of nonrenewable energy resources. Coal Oil Natural Gas Uranium 2. The energy of motion is Kinetic Energy called ___________. Energy 3. Work is a transfer of _________. 4. Name two factors that affect the kinetic energy of an object. Mass Speed 5. Give three examples of an object with elastic potential energy. A stretched rubber band A wind-up toy A bouncing basket ball 6. State the law of conservation of energy. Energy can not be created or destroyed but only changed from one form to another. 7. Walking converts what type of energy into mechanical energy? Chemical 8. The mechanical energy of an object kinetic equals its ___________energy plus potential ____________ energy. 9. A 5-kilogram box is sitting on top of a bookshelf that is 2 meters high. What is the box’s gravitational potential energy? PE = mgh PE = (5kg)(9.8m/s2)(2m) PE = 98 Joules 10.The energy stored in gasoline chemical energy. is ________ 11. A 40-kilogram boy is running at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the boy’s kinetic energy? KE = 1/2mv2 KE = (0.5)(40kg)(3m/s)2 KE = 180 Joules 9 m2/s2 12.Why is the gravitational potential energy of an object 1 meter above the moon’s surface less than its potential energy 1 meter above Earth’s surface? The moon has less gravity to pull down on the object. 13. A drawback of solar energy is that climate its usefulness depends on the _______. 14.The potential energy of the pendulum bob increases the most E between locations C and ______. thermal 15.When an object’s ________ energy increases, it becomes warmer. 16. A benefit of a hydrogen fuel cell is water that its only byproduct is ________. 17. Solar cells convert what type of energy into electrical energy? Electromagnetic (light) 18. What three factors affect an object’s gravitational potential energy? Mass Gravity Height 19. Energy and work are measured in Joule the SI unit called the _________. 20. Turning off unused lights or appliances is an example of energy conservation ____________.