Atomic Structure

Material Properties
Atomic Structure determines:
Physical Properties
Chemical Properties
Biological Properties
Electromagnetic Properties
CE 336
Physical Properties
Density
Mass
Structure
Permeability
Moisture content susceptibility
CE 336
Physical Properties
Specific gravity
Color
Texture
Shape
CE 336
Chemical Properties
Resistance to deterioration
Oxidation
Solubility
CE 336
Biological Properties
Bacterial growth
Hazard/exposure consideration
Resistance to infestation
Biodegradability
CE 336
Electromagnetic Properties
Conductance
Galvanic potential
CE 336
Material Selection
Strength
Serviceability
Deflections
Adaptability to future
Durability
CE 336
Material and Testing
Standards
ASTM /ASME Standards
AASHTO, State Highway,
EPA, HUD, US-Army
BOCA,ICBO, ICC, ISO
AISC/ACI/AITC
minimum quality standards, minimum application standards
Some may be performance standards
CE 336
Primary Bonds
Types of primary bond
1. Ionic - transfer of electrons
Metallic and non metallic elements
Sodium chloride salt
Na
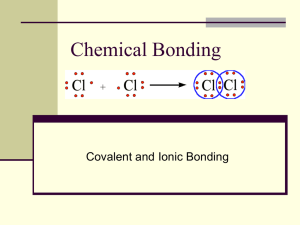
2. Covalent - sharing with adjacent atoms
Polymeric materials
Hydrogen gas Metal ions
Electron cloud
3. Metallic - mass sharing of electrons
All metal
H H
+ + + +
+ + +
+ + + +
+ + +
+ + + +
CE 336
Cl
Ionic Bonds
Electrons transferred
Strong attractive forces between atoms
Solids at room temps
High melting temperature
CE 336
Ionic Bonds
Solution-good conductors
Solid-poor conductors
Soluble in polar solvents, water
Insoluble in nonpolar solvents, organic solvents.
CE 336
Ionic Bonds
Low energy metals bonding to high energy nonmetals
Ca+2 +O-2 =
CaO
Exothermic in formation
CE 336
Attractive Forces
NaCl
Force
c
.
95
1
1
1 .
81
2
c
0 .
131
MgO
Force
c
.
65
2
2
1 .
40
2
c
0 .
951
CE 336
Covalent Bonds
Electrons are shared in joint orbital
Can lead to small molecules with polarity
No “bonding” between molecules, but some attraction and repulsion (secondary bonds).
CE 336
Covalent Bonds
Gases, liquids,
(mech. weak substances)
Can lead to long extended networks
Ceramics, diamond
(high binding energy)
Polymer chains (weak between chains)
CE 336
Metallic Bonds
Metal – “element with 1, 2, or 3, valence electrons”
No clearly defined molecules
Electron cloud &
Electronic bond
+ + + + + + +
+ + +
+ + +
+ +
+ +
+
+ +
+ +
+ + +
+ +
+ + +
+ +
+
+ +
+ + + +
Equilibrium of repulsive forces
CE 336
Secondary Bonds - van der
Waals Bonds
Weak compared to primary bonds
Result from dipoles - electrostatic attraction
Dipole occurs when have separation of positive and negative portion of atom or molecule
Cl H
+ -
H
O
Causes gasses to liquefy
Water also a dipole
CE 336
H
105
°
Strengths of Different Types of
Bonds
Bonding Type Material Energy Melt kJ/mole Temp.°C
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
Hydrogen van der Waals
NaCl
Si
Fe
H
2
O
Cl
640
450
406
51
31
801
1410
1538
0
-101
Source: Callister, Materials Science and Engineering
CE 336
Structure of Materials
Crystalline
“Repeated pattern or arrangement of atoms”
Ordered systems not necessarily crystalline
Laminar or small ordered systems arranged in disorganized manner
Amorphous
Random molecular structure
CE 336
Material Classification
Metallic Solids
Metallic bonding
Steel, iron, aluminum, copper, other metals
Crystalline
Organic Solids
Primarily covalent and van der Waals bonding
Asphalt, plastics, wood
Largely amorphous (although not entirely)
CE 336
Material Classification
*Note the change
Inorganic Solids (ceramics)
Primarily ionic and covalent bonding
Portland cement, bricks, glass, aggregates, minerals
Largely crystalline (but not entirely)
CE 336
Bonding and Structure of
Materials
(Generally Speaking)
Material Bonding Structure
Steel Metallic Crystalline
Aggregates
/ Minerals
Portland
Cement
Asphalt
Polymers
Wood
Glass
Ionic, Covalent Crystalline, Some
Amorphous
Ionic, Covalent, van der
Waals
Amorphous,
Crystalline
Covalent, van der Waals Amorphous
Covalent, van der Waals Amorphous
Covalent, van der Waals Crystalline,
Amorphous
Covalent
CE 336
Amorphous
(unaltered)
Crystalline Structures
CE 336
Crystalline Materials
Atoms arranged in repeating and regular array
Unit cells individual crystals structural part
Unit cell - smallest repeating unit
Body centered cubic (BCC)
Face centered cubic (FCC)
Hexagonal close-packed (HCP)
CE 336
Concepts of Crystalline
Structure
Coordination number
Number of “nearest neighbors”
Here 8 for BCC
One at each corner
Atomic Packing Factor (APF)
APF = Volume of atoms in cell
Total volume of cell
CE 336
Body Center Cubic Structure
CE 336
Face Centered Cubic
Structure
CE 336
Hexagonally Close Packed
6 around 1 on top
6 around 1 on bottom
3 at mid-height
CE 336
Body Center Cubic Structure
Pure Iron
(600°C to 910°C)
Low Carbon Steel
(723°C to ~1400°C)
Some Aluminum Alloys
CE 336
Face Centered Cubic
Structure
Pure aluminum
(-269°C to melting)
Pure iron
(910°C to 1403°C )
CE 336
Defects in Crystals
Point
Line
Area
Volume
CE 336
Point Defects
Crystal contains many - many unit cells
Explain permanent (plastic) deformation in metals
Defects
Interstitial
vacancy - missing
interstitial - extra
Impurities
Interstitial - extra
Carbon in iron
Substitutional
Copper alloy in nickel
CE 336
Source: Callister, Materials Science and Engineering
Lattice Defects
Imperfections in arrangements of atoms
edge dislocation - line defect
CE 336
Arrangements of Crystals
Grain boundary
CE 336
Types of Interfaces?
Amorphous Structure
CE 336