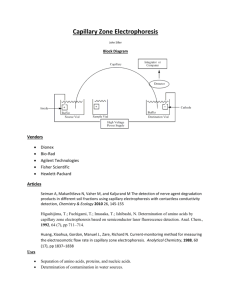
THE DRAWBACKS OF CAPILLARY
ELECTROPHORESIS
Cruces-Blanco, C., Gamiz-Gracia, L., Garcia-Campana A.M., Applications of Capillary
Electrophoresis in Forensic Analytical Chemistry Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2007
(26) 3
OVERVIEW
Review of capillary electrophoresis
Sensitivity issues
Stacking issues
Some specific flaws
THE CHEMISTRY OF CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS
Anode
Cathode
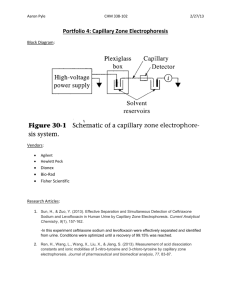
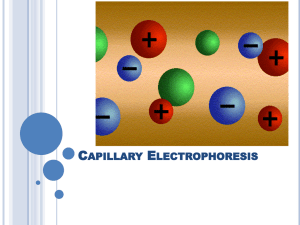
Electrophoresis is the differential movement of ions in an
electric field
Detection occurs as resolved components move past a
detector, typically UV, with output shown as peaks on a
baseline2
Separation suffers if injection volume exceeds 1%
of the column volume
Sample stacking can be done to increase the
concentration of the sample within the column
CE flows through the column electro-osmotically
rather than laminar
SENSITIVITY ISSUES
Sensitivity: the smallest signal an instrument can measure
The greater the sensitivity of the instrument, the better it can
differentiate compounds
Sensitivity defined as the slope of the signal vs. concentration
line
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO LOW SENSITIVITY
Small amount of analyte injected1
Tiny peak volumes1
UV-Vis detection is the most common detector1
Beers Law
A = ε*L*C
A: absorbance
ε: epsilon (L/mol*cm)
L: path length (cm)
C: concentration (mol/L)
LIMIT OF DETECTION IN CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS
CE typically uses “on tube”
analysis as the cell
The path length of the cell is the
internal diameter of the tube
~ 50 µm
Leads to LOD of ~ ppm
Detector portion of the tube must
be bare
Could lead to breakage of the tube
LIMIT OF DETECTION IN HPLC
HPLC uses 1 cm cells for UV
analysis
Increased path length leads to
increased absorbance
Leads to LOD of ~ ppb3
LENGTHENING OF THE CELL
Z shaped cells lengthen
the path length of the
cell
Path must not be so
long as to allow more
than one analyte
Determination of flow
rates for this is time
consuming
SAMPLE STACKING
the concentration of the samples must be
dramatically increased to obtain the same signalto-noise ratio as would result from a typical LC
experiment
Field stacking uses two buffers of differing
resistance to concentrate the sample
If
the sample matrix contains salts this will cause band
broadening and a decreased signal-to-noise ratio
Efficiency is limited by laminar flow
Flow
profile can become convex or concave causing band
broadening
Resolution can be decreased due to large injection volumes
used in stacking
pH in the capillary can be affected countering the
stacking effect
Ionic strength of the analyte must be significantly
lower than that of the background analyte
Large volume sample stacking involves using
reverse polarity, but the electrophoretic current
must be monitored carefully or analyte will be lost
In pH stacking if too much analyte is loaded the
separation efficiency is reduced
OTHER CURRENT PROBLEMS
Laser-induced fluorescence
More complex
More expensive
Limited excitation wavelengths
Lack of data regarding standard retention times and
peak areas
Inability to quantify analyte
Reproducibility comes into question
Irreproducible flow rates
Inconsistent injection volumes
Lack of data regarding the reliability of each method
used
Pre-treatment reduces time effectiveness and involves
the dilution of the analyte
SEPARATION METHODS
Substance being analyzed are of complex
composition
Identification is difficult using one method, but
multiple methodologies produce problems
Limits
development of a generally applicable method
Variations in SDS concentration, pH, addition of tetra-alkylammonium
salts, capillary diameter, and injection times
Makes
several runs necessary
Inappropriate conditions can cause
Sample
sticking to capillary walls
Lack of separation or focus in peaks
Decreased species stability leading to new species peaks
Inconsistent retention times
CONCLUSION
Capillary electrophoresis is a technique with
potential but currently has several problems
Sensitivity
issues
Sample stacking problems
Lack data regarding reliablility and reproducibility of
methods
No standardized method, determining appropriate test
conditions for unknown sample
Capillary electrophoresis is not suitable for
producing independently conclusive results
REFERENCES
1. Cruces-Blanco, C., Gamiz-Gracia, L., Garcia-Campana A.M., Applications of
Capillary Electrophoresis in Forensic Analytical Chemistry Trends in Analytical
Chemistry 2007 (26) 3
2. Cunico, R. L., Gooding, K.M., Wehr, T., Basic HPLC and CE of Biomolecules
1998 Bay Bioanalytical Laboratories, Inc
3. Harris, D. Quantitative Chemical Analysis 2003 W.H. Freeman and Company
4. Michalke, B. Potential and limitations of capillary electrophoresis inductively
coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1999, 14, 12971302
5. Osbourn, D.M., Weiss, D.J., Lunte, C.E. On-line preconcentration methods for
capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2000 August 21(14), 2768-2779