High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Fluorometric Detection
of Brain Catecholamines in a Pharmacodynamic Study
Between Two Popular Antidepressants
Bryant M. Moeller, Jillissa C. Molnari and Alan L. Myers
Pharmaceutical, Biomedical and Administrative Sciences, College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences
BACKGROUND:
RESULTS:
RESULTS:
SUMMARY:
Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) account for over 100,000 deaths
annually.1
We developed an HPLC with fluoremetic detection method to
mouse brain catecholamines.
Bupropion (Wellbutrin) is a commonly prescribed antidepressant
that is also used in the management of smoking cessation.2 It works via
inhibition of dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE) re-uptake.2
The limit of detection for norepinephrine, dopamine and seroto
780 pg/ml, 3000 pg/ml and 400 pg/ml, respectively.
400
Sertraline (Zoloft) is a widely used selective serotonin re-uptake
inhibitor (SSRI) used in the treatment of depression and other mood and
anxiety disorders.3
Norepinephrine
350
300
Serotonin
Dopamine
250
250
200
200
150
150
100
100
50
50
0
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
Surprisingly, mice dosed with bupropion or bupropion + sertral
(compared to control) displayed significantly lower levels of DA,
5HT levels.
**
**
Current results are not predicative of a neurochemical PD DDI
bupropion and sertraline.
Future studies, such as microdialysis procedures, which explo
specific regions of the brain are required to accurately determine
signficant PD interaction exists between these two antidepressa
36
Minutes
OBJECTIVE:
CONCLUSIONS:
The overall aim of this study was to utilize a HPLC assay to evaluate
bupropion brain PD following repeated administration of sertraline in
mice.
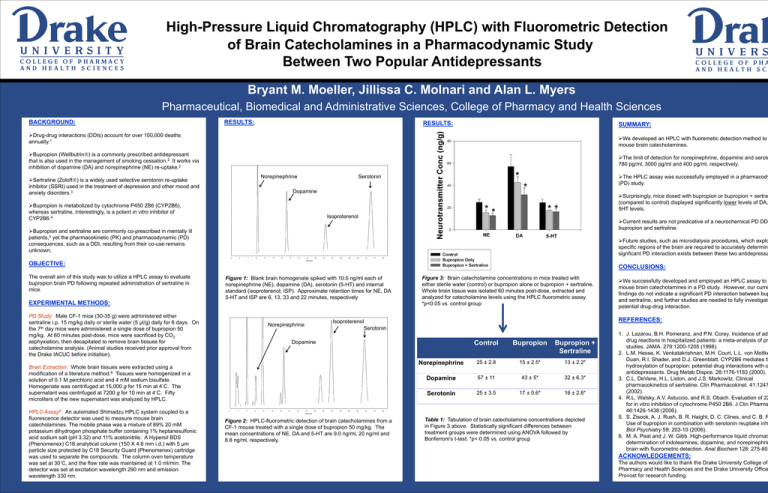
Figure 1: Blank brain homogenate spiked with 10.0 ng/ml each of
norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), serotonin (5-HT) and internal
standard (isoproterenol; ISP). Approximate retention times for NE, DA
5-HT and ISP are 6, 13, 33 and 22 minutes, respectively
EXPERIMENTAL METHODS:
PD Study: Male CF-1 mice (30-35 g) were administered either
sertraline i.p. 15 mg/kg daily or sterile water (5 µl/g) daily for 6 days. On
the 7th day mice were administered a single dose of bupropion 50
mg/kg. At 60 minutes post-dose, mice were sacrificed by CO2
asphyxiation, then decapitated to remove brain tissues for
catecholamine analysis. (Animal studies received prior approval from
the Drake IACUC before initiation).
HPLC Assay6: An automated Shimadzu HPLC system coupled to a
fluorescence detector was used to measure mouse brain
catecholamines. The mobile phase was a mixture of 89% 20 mM
potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer containing 1% heptanesulfonic
acid sodium salt (pH 3.32) and 11% acetonitrile. A Hypersil BDS
(Phenomenex) C18 analytical column (150 X 4.6 mm i.d.) with 5 µm
particle size protected by C18 Security Guard (Phenomenex) cartridge
was used to separate the compounds. The column oven temperature
was set at 30°C, and the flow rate was maintained at 1.0 ml/min. The
detector was set at excitation wavelength 290 nm and emission
wavelength 330 nm.
The HPLC assay was successfully employed in a pharmacody
(PD) study.
*
300
Isoproterenol
Bupropion and sertraline are commonly co-prescribed in mentally ill
patients,5 yet the pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD)
consequences, such as a DDI, resulting from their co-use remains
unknown.
400
Isoproterenol
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
350
Dopamine
300
Figure 3: Brain catecholamine concentrations in mice treated with
either sterile water (control) or bupropion alone or bupropion + sertraline.
Whole brain tissue was isolated 60 minutes post-dose, extracted and
analyzed for catecholamine levels using the HPLC fluorometric assay.
*p<0.05 vs. control group
350
Control
Bupropion
Bupropion +
Sertraline
Norepinephrine
25 ± 2.8
15 ± 2.5*
13 ± 2.2*
Dopamine
57 ± 11
43 ± 5*
32 ± 6.3*
Serotonin
25 ± 3.5
17 ± 0.6*
16 ± 2.8*
300
250
250
200
200
150
150
100
100
50
50
0
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
We successfully developed and employed an HPLC assay to
mouse brain catecholamines in a PD study. However, our curre
findings do not indicate a significant PD interaction between bup
and sertraline, and further studies are needed to fully investigate
potential drug-drug interaction.
REFERENCES:
400
mVolts
mVolts
Brain Extraction: Whole brain tissues were extracted using a
modification of a literature method.6 Tissues were homogenized in a
solution of 0.1 M perchloric acid and 4 mM sodium bisulfate.
Homogenate was centrifuged at 15,000 g for 15 min at 4°C. The
supernatant was centrifuged at 7200 g for 10 min at 4°C. Fifty
microliters of the new supernatant was analyzed by HPLC.
*
350
mVolts
mVolts
Bupropion is metabolized by cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6),
whereas sertraline, interestingly, is a potent in vitro inhibitor of
CYP2B6.4
400
36
Minutes
Figure 2: HPLC-fluorometric detection of brain catecholamines from a
CF-1 mouse treated with a single dose of bupropion 50 mg/kg. The
mean concentrations of NE, DA and 5-HT are 9.0 ng/ml, 20 ng/ml and
8.8 ng/ml, respectively.
Table 1: Tabulation of brain catecholamine concentrations depicted
in Figure 3 above. Statistically significant differences between
treatment groups were determined using ANOVA followed by
Bonferroni’s t-test. *p< 0.05 vs. control group
1. J. Lazarou, B.H. Pomeranz, and P.N. Corey. Incidence of adv
drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of pr
studies. JAMA. 279:1200-1205 (1998).
2. L.M. Hesse, K. Venkatakrishnan, M.H. Court, L.L. von Moltke
Duan, R.I. Shader, and D.J. Greenblatt. CYP2B6 mediates th
hydroxylation of bupropion: potential drug interactions with o
antidepressants. Drug Metab Dispos. 28:1176-1183 (2000).
3. C.L. DeVane, H.L. Liston, and J.S. Markowitz. Clinical
pharmacokinetics of sertraline. Clin Pharmacokinet. 41:1247
(2002).
4. R.L. Walsky, A.V. Astuccio, and R.S. Obach. Evaluation of 22
for in vitro inhibition of cytochrome P450 2B6. J Clin Pharma
46:1426-1438 (2006).
5. S. Zisook, A. J. Rush, B. R. Haight, D. C. Clines, and C. B. R
Use of bupropion in combination with serotonin reuptake inh
Biol Psychiatry 59: 203-10 (2006).
6. M. A. Peat and J. W. Gibb. High-performance liquid chromato
determination of indoleamines, dopamine, and norepinephrin
brain with fluorometric detection. Anal Biochem 128: 275-80
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
The authors would like to thank the Drake University College of
Pharmacy and Health Sciences and the Drake University Office
Provost for research funding.