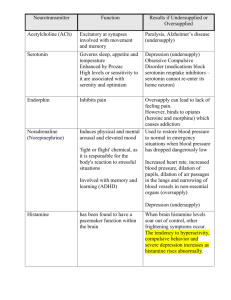
How do Dopamine, Serotonin influence
the Mood, Sleep, Attention, Learning?
54陳芷安 91蔡逸松
What Is the Difference Between
Dopamine & Serotonin?
Similarities
• Neurotransmitters
• mood and emotion, regulate appetite, sex,
aggression
• mental illnesses, such as depression, bipolar
disorder and schizophrenia.
Serotonin‘s Role
Dopamine‘s Role
• emotion, appetite and
sensory perceptions
• sleep, pain perception,
body temperature,
blood pressure and
hormonal activity.
• movement, mood,
motivation and pleasure
• Decreased
→Parkinson's disease
• Increased
→schizophrenia
• learning, aggression
and cognitive
processes(認知過程)
.
Dopaminergic Pathway in the Brain
1.Mesolimbocortical pathway
VTA→limbic system: 1.amygdala
2.nucleus accumbens
3.hippocampus
2.Mesostratal pathway
中腦(黑質)
midbrain(substantia nigra)
→striatum(紋狀體)(caudate
nucleus and putamen)
(尾狀核和殼核)
皮質邊緣路徑
1.
2.
皮質底層路徑
Serotonergic Pathway in the Brain
1.→視丘、下視丘、基底節
basal ganglia、海馬、皮質
2. →小腦、脊髓
At least four interacting neural systems underlie sleep…
SLEEP MECHANISM
Sleep:
• EEG
(Electroencephalography)
• The reticular formation wakes up the forebrain (Upstream activation)
An extensive region of the
brainstem (extending from
the medulla through the
thalamus) that is involved in
arousal.
Forebrain System:
display SWS
Brainstem System :
wake up the forebrain
Pontine System :
trigger REM sleep
Hypothalamic System :
affects the other 3 brain
regions and determine
whether the brain will be
awake or asleep
Thalamus丘腦
Basal forebrain基底前腦
Basal ganglia基底節
Midbrain
Upper pons
Lower pons
Upper mudulla
Raphe Nuclus中縫核
Locus Coeruleus藍斑
Sleep
Serotonin
melatonin↑: REM
serotonin ↑: awake and active
Light→serotonin (power)
→pineal gland (synthesis)
→melatonin
dark →melatonin
Dopamine
• Normal secretion
↓
Increase dreaming
↓
Sleep well
Mood
Serotonin
Dopamine
Symptoms of Low Level
• Difficulty focusing
• The smallest task can seem
like a chore.
• Chronic fatigue
• Appetite/sleep disturbance
• Low libido
• Low to no self-esteem
• Social withdrawal
Effect
• affection
• feeling
• excited, happy
• Dopamic nurons in VTA is the
basic unit of nuron which
promote the emotional brain
Medial Regions of the Brain Involved in Emotions
杏仁核
海馬
海馬旁迴
The study of brain mechanisms at work during economic decision making.
NEUROECONOMICS
Brain Reward Systems
• Early studies: establishing the generality of their
function and their neurochemical bases.
• Animal experiments: animals can withstand
electric shock, exert significant physical effort,
and even reduce food intake to obtain electrical
stimulation in appropriate brain areas.
Value Assessment
To augment reward-producing behaviors:
• Generating learning signals
•
學習的機制: Montague, P.R. et al. (1996) A framework for mesencephalic
dopamine systems based on predictive Hebbian learning. J. Neurosci. 16, 1936–
1947 http://www.jneurosci.org/content/16/5/1936.full.pdf+html
• Adaptively updating goal states and
attentional focus in working memory
•
注意力的機制: Braver, T.S. and Cohen, J.D. (2000) On the control of control: the
role of dopamine in regulating prefrontal function and working memory. In
Attention and Performance (Monsell, S. and Driver, J., eds), pp.713–737, Academic
Press
Learning
Serotonin
Dopamine
• Hippocampus accepted
serotonin.
• 1.increase: hippocampus
activated, learn and
memorize better
• 2.reduce: forgettable,
Degenerative
brain or atrophy.
• rewarding experiences
release
Dopamine
increases motivation or desire
towards the reward
induce learning
Limbic System (恐懼制約)
• Amygdala杏仁核
• Nucleus accumbens伏隔核
• Hippocampus海馬
*Long-term potentiation:
synaptic plasticity
*Learning→ synaptic changing→transmitter changing
Attention
• Selective awareness of perceptual receptivity,
involving the activation of certain brain
regions.
Attention (ADHD for example)
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
• A common, childhood-onset neurodevelopmental
disorder.
• Inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity.
• More frequent in males than females
• Several genes on the X chromosome have been
studied as candidate risk factors for ADHD
including the 5-HT2C receptor (HTR2C) gene.
• Pathogenesis of ADHD: dopaminergic,
serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmitter
systems
5-HT2C receptor
• A subtype of 5-HT receptor that binds the
endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT)
• A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is
coupled to Gq/G11 and mediates excitatory
neurotransmission.
• The 5-HT2C receptor (HTR2C) gene is located on
human chromosome Xq24.
Findings
• Polymorphism may be involved in the
development of ADHD.
• Promoter activity: Single nucleotide
substitution polymorphisms (SNP) in the
upstream region of the 5-HT2C
• Findings: SNP in the 5-HT2C
Reference
1. eHow.com
• How Does Serotonin Affect Mood?
• How Does Serotonin Affect Sleep?
• What Is the Difference Between Dopamine?
• http://www.ehow.com/how-does_4686190_serotoninaffect-mood.html
2. BMC Research Notes
• Investigation of the serotonin 2C receptor gene in attention
deficit hyperactivity disorder in UK samples
• http://www.biomedcentral.com/1756-0500/2/71
3. Wikipedia
4. S. Marc Breedlove, Mark R. Rosenzweig, Neil V. Watson,
“Biological Psychology”, page.90-93, 544-546,439-441,
460-462,227-228
5. Alan G. Sanfey, George Loewenstein, Samuel M. McClure
and Jonathan D. Cohen, "Neuroeconomics: cross-currents
in research on decision-making", TRENDS in Cognitive
Sciences Vol.10 No.3 March 2006, Page.108-110
http://sds.hss.cmu.edu/media/pdfs/loewenstein/NeuroEco
nCrossCurrent.pdf
6.危芷芬, Atkinson & Hilgard’s Introduction to Psychology,
page.210-225, 233-235, 328-330
7.尹艳茹, "睡眠生理-覺醒和睡眠的基本機轉", 南方醫科大
學基礎醫學院生理學教研室
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/1f81bb671ed9ad51f01df2bc
.html