Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) Presentation
advertisement

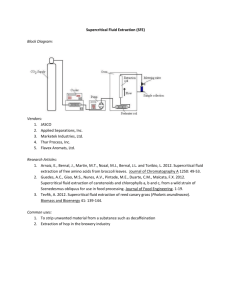
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Supercritical fluids Occur above a critical temperature and a critical pressure, Show both gaseous and liquid properties for Density Diffusion coefficient and Viscosity Are very good solvents Are frequently cheap, innocuous, non-toxic Can easily be removed by evaporation Give GC/LC hybrid behaviour – make great mobile phases Source:http://www.selectscience.net/products/analy tical+preparative-sfc-instrument/?prodID=12418 SFC is particularly useful for analytes that are: Non-volatile Easily thermally-decomposed and/or Unsuitable for spectroscopic or electrochemical detection and thus cannot be analysed by GC or HPLC Created with MindGenius Business 2005® Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Mobile:Stationary phase equilibrium Dependent on partition, strongly influenced by solvation power of the supercritical fluid Instrumentation: modified HPLC equipment: Thermostatted column oven Back-pressure device between column and detector (narrow capillary at end of column) Detection may be conducted in gas phase Mobile Phase Any supercritical fluid (commonly CO2, N2O, NH3, 1-Butane) CO2 becomes supercritical at T>31ºC, P>7400KPa Stationary Phase Variety, generally “cannibalised” from HPLC or GC May be packed (like HPLC) Or open-tubular siloxane coated (like GC) Created with MindGenius Business 2005® Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Retention and Resolution Quicker than HPLC N similar to that for GC Suffers from band broadening (diffusion) like GC Optimisation: Pressure gives solvent power and thus RT . e.g.(Hexadecane at 70atm RT=25min, 90 atm RT=5min). May use gradient or isobaric elution. Temperature (for similar reasons) Organic modifiers (e.g. MeOH) Detection Often uses HPLC detectors (UV etc) SFC allows easy interface with MS or IR Also allows use of Flame Ionisation Detector (FID) Eluent easily removed for further analysis Applications Wide range including: Drugs, foods, pesticides, polymers, surfactants…. Created with MindGenius Business 2005®