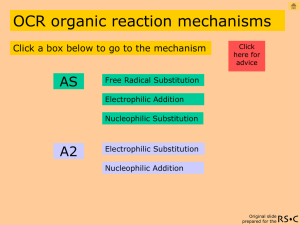
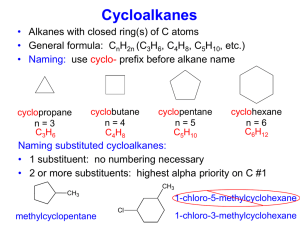
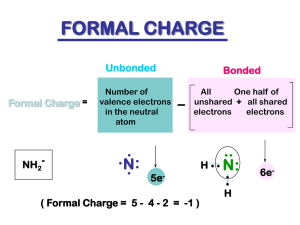
Ch01-acids-ques-09
advertisement

Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding Acids and Bases Acids & Bases/ Organic Chemistry Dr. Ron Rusay Fall 2009 Models of Acids and Bases •Arrhenius: Acids produce H+ & bases produce OH ion in aqueous solutions . •Brønsted-Lowry: Acids are H+ donors & bases are proton acceptors. •HCl + H2O Cl + H3O+ acid base Comprehensive Tutorial Acid & Base Principles in Organic Chemistry Highly recommended viewing Acid-Base Equilibrium Conjugate Acid/Base Pairs •HA(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + A(aq) acid 1 base 2 conj acid 2 conj base 1 •conjugate acid: formed when the proton is transferred to the base. •conjugate base: everything that remains of the acid molecule after a proton is lost. http://chemconnections.org//organic/Movies%20Org%20Flash/ ConjugateAcidBaseActivity.swf QUESTION: 1 Aniline, C6H5NH2, was isolated in the 1800s and began immediate use in the dye industry. What is the formula of the conjugate acid of this base? A. B. C. D. E. C6H5NH2+ C6H5NH3+ C6H5NH– C6H5NH+ C6H5NH2 Weak Acids • Weak acids are only partially ionized in solution. H3O+(aq) + A-(aq) HA(aq) + H2O(l) HA(aq) [H 3O ][A- ] Ka [HA] H+(aq) + A-(aq) or [H ][A- ] Ka [HA] • Ka is the acid dissociation constant. Organic Acids & Bases • Organic acids are weak acids, eg. Acetic acid. • However, there can be substantial differences in their relative strengths. What could you use to compare relative acidities? • Organic bases are weak bases and relate to ammonia. • However, there can be substantial differences in their relative strengths. What could you use to compare relative basicity? Conjugates Ka x Kb = ? Kw What do pKa and pKb refer to? -log Ka or -log Kb 14 pKa + pKb = ? Remember: pH + pOH = pKw Which is the stronger acid? methanol Which is the stronger base? methylamine QUESTION: 2 Use information on the table above to determine which of the following bases would have the weakest conjugate acid: OC6H5–; C2H3O2–; A. B. C. D. OC6H5– C 2 H 3 O2 – OCl– NH3 OCl–; NH3 QUESTION: 3 Use information on the table above to determine the order of increasing base strength for the following bases: OC6H5–; C2H3O2–; ClO2–; A. B. C. D. OC6H5– < NH3 < C2H3O2– < ClO2– C2H3O2– < ClO2– < NH3 < OC6H5– ClO2– < C2H3O2– < NH3 < OC6H5– NH3 < OC6H5– < C2H3O2– < ClO2– NH3 Acid and Base Equilibria The equilibrium favors the weaker of the acid vs. its conjugate acid or base vs. its conjugate. Weak wins! • Weak is favored! http://chemconnections.org/organic/Movies%20Org%20Flash/acid-base-eq.swf QUESTION: 4 Consider the following equilibria. Identify the weaker of the two: acid vs. its conjugate acid in each reaction. Which reactions favor formation of product? O O 1. 2. + NH3 CH3 C pKa=4.7 OH + NH3 OH 4. + NH4 pKa=9 O O O CH3 C 3. CH3 C pKa=36 HCl + CH3OH Kpa=15.5 HCl + CH3OH pKa-=–7 CH3 CCH + NH2 5. pKa =26 6. CH3 CH3 + pKa=50 CH3 COH2 + NH2 pKa=–6 A. All do: 1-6 B. 1, 4, 5 H–Cl–H + CH 3O pKa < –15 C. 2, 3, 6 Cl D. 1, 5 + CH3 OH2 pKa=–2.5 CH3 CC + E. None do. NH 3 Kap=36 NH2 CH3 CH2 + NH3 pKa=36 Worksheet 5: Acids & Bases http://chemconnections.org/organic/chem226/226assign-09.html#Worksheets Organic Acids & Bases • Organic molecules in context can be considered as behaving relatively as weak acids or weak bases. • Formal Charge is important in considering which. • Knowing the Formal Charge allows a prediction. • (+) positive atoms behave acid-like, (-) negative atoms behave base-like. • This can be used in predicting how molecules will react--- or don’t react, and the products of reactions. Formal Charge / Acids & Bases Electrophiles / Nucleophiles / Reactivity .. CH3 H3C : O: N CH3 CH3 H 3C N .. CH 3 H O: :: CH 3 Base / nucleophile .. N H3 C : : -1 CH 3 : O: H3 C .. : O: CH3 :: CH3 C: H3C H3C CH3 +1 Acid / electrophile H .. H H3C O H H O H :: CH3 :O .. .. CH2 C CH3 CH 3 H3C O: CH3 H3C : O: .. H3 C O : :: H3 C CH3 CH2 Worksheet 1 http://chemconnections.org/organic/chem226/226assign-09.html#Worksheets Structure and Acid-Base Properties Important factors that effect acidity in binary compounds, eg HCl (having only two elements): • Bond Length (shorter = stronger bonds; lower acidity) • Bond Strength (longer = weaker bonds; higher acidity: more dissociation, more protons [hydronium ions] in solution) • Bond Polarity (smaller e.n. differences favor higher acidities) Select & explain which is the stronger acid: HBr or HF. Therefore HBr is a stronger acid than HF. Strength of Oxyacids (Three atoms: ternary vs. binary) Push-Pull electronic effects on the proton. QUESTION: 5 • Rank 1.0M solutions of HBrO, HIO and HClO in order of increasing acidity. HBrO , Ka = 2.1 x 10-8 HIO , Ka = 2.3 x 10-11 HClO , Ka = 3.0 x 10-8 A) HBrO < HIO < HClO B) HIO < HBrO < HClO C) HClO < HBrO < HIO D) HIO < HClO < HBrO Question: 6 True (A) / False (B) • HBrO4 is a weaker acid than HBrO2. • • • • HClO2 , Ka = 1.2 x 10-2 HBrO , Ka = 2.06 x 10-8 HIO , Ka = 2.3 x 10-11 HClO , Ka = 3.0 x 10-8 QUESTION: 7 • Rank 1.0M solutions of HBrO, HIO and HClO in order of increasing pH HBrO , Ka = 2.1 x 10-8 HIO , Ka = 2.3 x 10-11 HClO , Ka = 3.0 x 10-8 A) HBrO < HIO < HClO B) HIO < HBrO < HClO C) HClO < HBrO < HIO D) HIO < HClO < HBrO QUESTION: 8 • Use the concept of push-pull. Rank the following organic acids in order of decreasing acidity. 1) Br-CH2COOH 2) I-CH2COOH • A) 2 > 1 > 3 B) 3 > 2 > 1 • C) 2 > 3 > 1 D) 1 > 2 > 3 3) CH3COOH QUESTION: 9 Rank the following acids in order of decreasing acidity. A) ClCH2COOH C) Cl3CCOOH 1) A > B > C > D 2) D > C > B > A B) Cl2CHCOOH D) CH3COOH 2) C > B > A > D 3) B > C > A > D Question: 10 True (A) / False (B) Trichloroacetic acid, Cl3CCOOH, is more acidic than trifluoroacetic acid, F3CCOOH. An Organic Base in Context Erythroxylon spp. • It is very valuable. The leaves are chewed by indigenous tribes in the Andes to boost their energy. • It has been used as a psycho-therapeutic, an opthalmic anesthetic and was purportedly used in a popular beverage that is at the heart of a $20 billion corporation. • However, both its base and conjugate acid are currently controlled substances under U.S. Federal Regulations: Title 21 secs. 329.1 & 1308.12 (1987). • Can you name the beverage and the base? The beverage reportedly produced using the extract of leaves of Erythroxylon coca: The compound: cocaine, is an organic base: Merck Index, #2450, 11th ed.: Caution: May be habit forming…. Acid -Base Chemistry (Physical Properties) CH3 .. N CO2CH3 O2C "Crack" Cocaine What structural feature makes cocaine a base? What simple compound can you relate it to? • m.p. 98 oC • b.p. (very volatile > 90 oC) Solubility: • Water: 1.67 x 10-3 g/mL • CHCl3: 1.43 g/mL • Ether: 0.29 g/mL “Regular” Cocaine Conjugate Acid of Cocaine (Physical Properties) • m.p. >195 oC H Cl + CH3 Solubility: N CO2 CH3 • Water: 2.5 g/mL • CHCl3: 0.08 g/mL O2 C • Ether: insoluble Cocaine Hydrochloride What accounts for the differences in solubilities of the base and conjugate acid? Acid -Base Reactions CH3 .. N CH3 CO2CH3 O2C + H Cl + N H Cl - CO2 CH3 O2 C Cocaine Hydrochloride Acid Base Reactions CH3 + N H Cl CH3 .. N - CO2CH3 + O2C OH - CO2CH3 O2C "Crack" Cocaine Which form, Acid or its Conjugate Base? The pH of a solution (its surroundings) determines which and is related by the following equation. HA pK a pH log A • A compound will exist primarily in its acidic form if the pH of the solution is < than its pKa • A compound will exist primarily in its basic form if the pH of the solution is > than its pKa • NOTE: A buffer solution maintains a nearly constant pH within certain parameters. A weak acid RCO2H with a pKa = 5.2 50% acid 50% base 99% acid 1% base 90% acid 10% base 10% acid 90% base 1% acid 99% base QUESTIONS from Worksheet: The pKa of a general anesthetic, sodium pentothal, is 7.4. If a patient is given sodium pentothal orally instead of iv, will it put the patient to sleep? What information is needed to answer this fundamental anesthesiology (“gas passer”) question? A drug has a pKa of 7.8 and is a known teratogen. If given iv to a pregnant woman whose blood pH is within normal levels, will this drug cross the placenta and affect the baby? What information is needed to answer this anesthesiology (“gas passer”) question? Lewis Acids and Bases • Lewis Acid: electron pair acceptor • Lewis Base: electron pair donor • Example: Al3+ + 6 O H H Al H 3+ O H 6 Question: 11 Select the chemical equation that depicts the correct movement of electrons in the reactionof ammonia with hydrogen chloride. A) B) C) D) Acid-Base Reactions Showing a reaction with arrows CH3 SCH3 + BF3 CH3 + H2O CH3 O + CH3 SH (CH3)2 S–BF3 CH3 OH2 CH3 OH + CH3S O OH CH3 CCH3 + H3O H2O + CH3CCH3 HCC HCC–CH2–O + H2C=O CH2 =CH2 + HCl I + CH3Br CH2 –CH3 + Cl ICH3 + Br Worksheet 5: Acids & Bases http://chemconnections.org/organic/chem226/226assign-09.html#Worksheets Acid-Base Reactions Predicting Products O + HCO3 CH 3C OH B(CH3 )3 + (CH3) 3N NH3 + OH H 3C + MgCl2 C O H 3C H2SO 4 + CH3OCH3 BF3 + O O + AlCl3 CH 3C OH Worksheet 5: Acids & Bases http://chemconnections.org/organic/chem226/226assign-09.html#Worksheets Predicting if reactions occur and the products if they do a. b. c, HO + Br–CH3 HO–Br + HO + Br–CH3 HO–CH3 + Br CH 3 H–CC + H2 C=O H–CC–CH 2-O H–CC + H2 C=O H–CC–O–CH2 NH2 + H–OCH3 H2N–OCH3 + NH2 + H–OCH3 H2N–H + H OCH 3 Worksheet 5: Acids & Bases http://chemconnections.org/organic/chem226/226assign-09.html#Worksheets