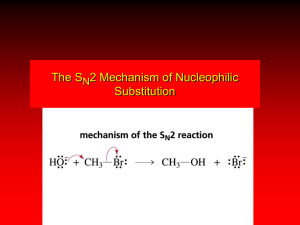
OCR organic mechanisms VERSION 2
advertisement

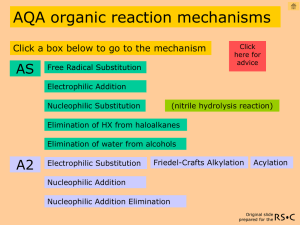
OCR organic reaction mechanisms Click a box below to go to the mechanism AS Click here for advice Free Radical Substitution Electrophilic Addition Nucleophilic Substitution A2 Electrophilic Substitution Nucleophilic Addition Original slide prepared for the Free radical substitution chlorination of methane i.e. homolytic breaking of covalent bonds Overall reaction equation CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl Conditions ultra violet light excess methane to reduce further substitution Original slide prepared for the Free radical substitution mechanism ultra-violet Cl2 Cl + Cl initiation step two propagation steps CH4 + Cl CH3 + HCl CH3 + Cl2 CH3Cl + Cl CH3 + Cl CH3Cl termination step CH3 + CH3CH3 minor termination step CH3 Original slide prepared for the Further free radical substitutions Overall reaction equations CH3Cl + Cl2 CH2Cl2 + HCl CH2Cl2 + Cl2 CHCl3 + HCl CHCl3 + Cl2 CCl4 + HCl Conditions ultra-violet light excess chlorine Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic addition bromine with ethene Overall reaction equation CH2=CH2 + Br2 CH2BrCH2Br 1,2-dibromoethane mechanism Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic addition mechanism bromine with ethene H H C H C H H + Br Br - H H carbocation C + C H Br- Br H H Br H C C Br 1,2-dibromoethane Br Br reaction equation H Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution mechanism water with bromoethane CH3CH2Br + H2O CH3CH2OH + HBr ethanol hydroxide ion with bromoethane CH3CH2Br + OH- (aqueous) mechanism CH3CH2OH + Brethanol Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution mechanism water with bromoethane H + CH3 C H Br CH3 C + O H H H O H H - Br H H ethanol CH3 C H reaction equation OH H Br Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution mechanism hydroxide ion with bromoethane H + CH3 C H OH- Br H CH3 C OH H Br ethanol reaction equation Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic Substitution Nitration of benzene C6H6 + HNO3 C6H5NO2 + H2O Conditions / Reagents concentrated HNO3 and concentrated H2SO4 50oC mechanism Original slide prepared for the electrophilic substitution mechanism (nitration) + 1. Formation of NO2 the nitronium ion + HNO3 + 2H2SO4 NO2 + 2HSO4- + H3O+ 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene + NO2 + NO2 H - O SO3H 3. Forming the product and re-forming the catalyst reaction equation NO2 H O SO3H Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition addition of hydrogen cyanide to carbonyls to form hydroxynitriles RCOR + HCN RCHO + HCN RC(OH)(CN)R RCH(OH)CN Conditions / Reagents HCN (aq) and NaOH(aq) to form the CN- nucleophile HCN + OHCN- + H2O Room temperature and pressure Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Mechanism hydrogen cyanide with propanone CH3COCH3 + HCN CH3C(OH)(CN)CH3 HCN / NaOH (aq) is a source of cyanide ions C N CN + CH3 C O CH3 CN H O CH3 C CH3 CN CN O CH3 C H CN CH3 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile Original slide prepared for the Advice To get back to the mechanism links page from anywhere in the presentation, click the button at the top right corner of the screen. This version provides the organic mechanisms specified (2002/3) by the OCR exam board. Each stage of a reaction equation, its conditions and mechanism are revealed in turn on a mouse click or keyboard stroke. Note that there is another version available where each reaction and mechanism play automatically after an initiating click or key stroke. The number of ways of navigating through this presentation may depend on the version of PowerPoint being used and how it is configured. Some possible ways of advancing: left mouse click or return key or right arrow key or up arrow key. Some possible ways of reversing: backspace key or left arrow key or down arrow key. Original slide prepared for the References Steve Lewis for the Royal Society of Chemistry Original slide prepared for the