Intro to Bonding
advertisement

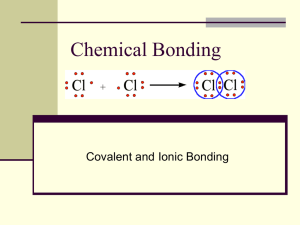
Chemical Bonding How compounds are held together Review Questions When representing a water molecule as H-O-H, what do the lines represent? Write e- configs for argon, chlorine, neon, and sodium Ar = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 Cl = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 Ne = 1s2 2s2 2p6 Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Why is the phrase “sodium chloride molecule” incorrect? Objectives Learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed Learn about polar covalent bonds Understand nature of bonds and their relationships to electronegativity Understand bond polarity and how it is related to molecular polarity What is a BOND??? Force holding two or more atoms together Makes atoms function as a unit Strength of the force = energy required to break bond = bond energy Types of bonding Focus on two types of chemical bonds: IONIC BONDING COVALENT BONDING Ionic Bonding Oppositely charged ions - strong bonding force Electron is transferred to another atom Metal + NonMetal e- from Na transferred to Cl. Na atom stable (“looks” like Ne) Cl is stable (“looks” like Ar) QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. Covalent Bonds Atoms share e2 Cl atoms share eBoth Cl stable (both “look” like Ar) Occurs between nonmetallic atoms QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. Polar Covalent Bond • Sometimes, there is an unequal sharing of the electrons • Known as Polar Covalent bond. • Partial charge on atoms shown using lower case greek letter delta ∂ Questions What is meant by the term chemical bond? What subatomic particles are most important in bonds? How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? How is a polar covalent bond different from a covalent bond? Objectives Learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed Learn about polar covalent bonds Understand nature of bonds and their relationships to electronegativity Understand bond polarity and how it is related to molecular polarity Nature of bonds Type of Bond What happens to Element Types e- Transferred to other atom Na + Cl NonMetal + Pure Covalent NonMetal Equally Shared Bond (Same Element) Cl + Cl NonMetal + Polar Covalent NonMetal Bond (Diff. Elements) H + Cl Ionic Bond Metal + NonMetal Example Unequally Shared Electronegativity Ability of atom in molecule to attract shared e- to itself Increases going left to right across periodic table Decreases going down a group Electronegativity Range: Fluorine 4.0...Francium & Cesium 0.7 Effect: Higher electronegativity of an atom, the closer shared e- will be to that atom when it forms a bond Electronegativity Bond Polarity Bond Polarity depends on difference in electronegativity values of atoms forming bond Atoms with very different electronegativities form very polar bonds Ionic bonds are extreme case of bond polarity Electronegativity difference greater than 2.0 considered ionic bond Bond Polarity Continuum Thinking question... How do electronegativity trends compare to trends of atomic size? Problem Arrange the following bonds in order of increasing polarity: H-H, O-H, Cl-H, SH, F-H Selected Electronegativity Values Silicon 1.8 Hydrogen 2.1 Phosphorous 2.1 1. H-H (2.1 - 2.1 = 0.0) Sulfur 2.5 2. S-H (2.5 - 2.1 = 0.4) Carbon 2.5 3. Cl-H (3.0 - 2.1 = 0.9) Nitrogen 3.0 Chlorine 3.0 Oxygen 3.5 Fluorine 4.0 4. O-H (3.5 - 2.1 = 1.4) 5. F-H (4.0 - 2.1 = 1.9) Problems For each of the following bond pairs, choose the one that is most polar H-P & H-C (2.1 - 2.1) < (2.5 - 2.1) H-C O-F & O-Cl (4.0 - 3.5) = (3.5 - 3.0) same N-O & S-O (3.5 - 3.0) < (3.5 - 2.5) S-O N-H & Si-H (3.0 - 2.1) > (2.1 - 1.8) N-H Selected Electronegativity Values Silicon 1.8 Hydrogen 2.1 Phosphorous 2.1 Sulfur 2.5 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 3.0 Chlorine 3.0 Oxygen 3.5 Fluorine 4.0 Match the compounds HF, NaCl, and O2 with the figures above How do electronegativity values help in determining the polarity of a bond? Objectives Learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed Learn about polar covalent bonds Understand nature of bonds and their relationships to electronegativity Understand bond polarity and how it is related to molecular polarity Bond Polarity & Molecular Polarity Molecule such as H-F that has a center of positive charge (∂+) and a center of negative charge (∂-) is said to have a dipole moment Dipole moment represents molecular polarity Any diatomic molecule with a polar bond has a dipole moment Some Polyatomic Molecules have dipole moments Water is a polar molecule (it has a dipole moment) Properties of H2O surrounds and attracts both + and - ions dissolves ionic substances attract one another strongly (hbonds) high boiling temperature Questions For each binary molecule given, indicate direction of its dipole moment. Some may have no dipole moment. H-Cl H-H H-I Br-Br C-O Summary Chemical bond = force holding 2 or more atoms together Types of Bonds = Ionic and Covalent Ionic = transfer of eCovalent = sharing of ePolar Covalent = unequal sharing of eElectronegativity = how much an atom “pulls” on ePolar bonds -> polar molecules