Why do Covalent Compounds have Low Conductivity?
advertisement

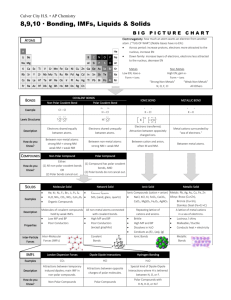
Why do Covalent Compounds have Low Conductivity? • Have a wider variety of properties than ionic compounds • Atoms are held together with strong covalent bonds (<0.5) • Bonds do NOT break • Covalent compounds are also called molecular compounds Evidence for Intermolecular Forces • The forces that bond the atoms to each other within a molecule are called intramolecular forces. • Covalent bonds are intramolecular forces • The forces that bond molecules together are called intermolecular forces. Look at the difference between these two types of forces. Pure covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points, you know that the intermolecular forces must be very weak in comparison to the intramolecular forces or covalent bonds. It does not take very much energy to break the bonds that hold the molecules to each other. Polar Bonds and Molecular Shape Other examples of polar molecules (asymmetrical) Non- Polar Molecules Carbon Dioxide Bonds: DEN = 1 = so Polar Covalent BOND BUT, is the whole molecule polar?? No!, The molecule is straight and symmetrical meaning that the effects of polar bonds cancel each other out So, although the BONDS are POLAR, the molecule is NON-POLAR Other examples of Non-Polar molecules • CF4 • CH4 • Remember inter-intra molecular forces? • Non-polars have relatively weak intermolecular forces, so their melting points are lower than polar molecules. • Eg. CO2 is a gas at room temp, Melting point is 57 degrees. Other Properties • Polar: +/- ends means that the molecule will easily “stick” to itself = High melting point and boiling point • Non-Polar: do not attract each other as much due to not having +/- poles = low melting and boiling points. • Non-polar compounds are often gases at room temperature. Concept Organizer pp.93 • Make sure to do your homework questions • Let’s investigate further in respect to molecular shape • Lesson #4 in the green book.