Culver City H.S. • AP Chemistry 8,9,10 · Bonding, IMFs, Liquids
advertisement

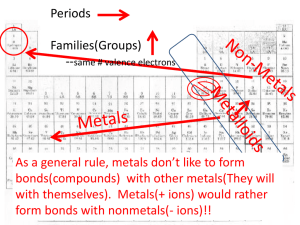
Culver City H.S. • AP Chemistry 8,9,10 · Bonding, IMFs, Liquids & Solids BIG PICTURE CHART ATOMS H He Li Be B C N O F Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Rb Sr Y Ti V Ne Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir I Xe Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Electronegativity: how much an atom wants an electron from another atom. (“TUG OF WAR”) [Noble Gases have no EN.) Across period: increase protons, electrons more attracted to the nucleus, increase EN Down family: increase layers of electrons, electrons less attracted to the nucleus, decrease EN Metals Low EN; lose eForm + ions Non-Metals High EN; gain eForm – ions “Strong Non-Metals” “Weak Non-Metals” N, O, F, Cl All Others Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn COVALENT BONDS BONDS Non-Polar Covalent Bond IONIC BOND Polar Covalent Bond δ+ δ– + METALLIC BOND – + + Example Cl – Cl Lewis Structures Cl Cl H Cl Description Electrons shared equally between atoms. Electrons shared unequally between atoms. Electrons transferred; Attraction between oppositely charged ions. Metal cations surrounded by “sea of electrons.” How do you Know? Between non-metal atoms: strong NM + strong NM weak NM + weak NM Between non-metal atoms: strong NM + weak NM Between cation and anion, often M and NM. Between metal atoms. COMPOUNDS Non-Polar Compound Polar Compound Ionic Solid Metallic Solid SOLIDS Description Properties Inter-Particle Forces K – Cl K + K–K Cl - Either: (1) Compound has polar covalent (1) All non-polar covalent bonds bonds, AND OR (2) Polar bonds do not cancel out. (2) Polar bonds cancel out. How do you Know? Examples H – Cl Molecular Solid Network Solid He, Kr, N2, F2, Br2, I2, P4, S8 H2O, NH3, CO2, NO2, C6H12O6 Organic Compounds Molecules of covalent compounds held by weak IMFs. Low MP and BP Poor Conductors Inter-Molecular Forces (IMFs) Ionic Compounds (cation + anion) Metals: Pb, Ag, Au, Cu, Fe, Zn NaCl, KCl, KI, FeCl3, CaCO3, Alloys: Brass (Cu+Zn), Bronze (Cu+Sn), CaCl2, MgSO4, Fe2O3, AgNO3 Stainless Steel (Fe+Cr+C) All non-metal atoms connected Repeating lattice of A lattice of metal cations with covalent bonds. cations and anions. in a sea of electrons. Cdiamond, Cgraphite SiO2 (sand, glass, quartz) High MP and BP Poor Conductors (except graphite) Covalent Bonds Brittle High MP and BP Dissolves in H2O Conducts as (ℓ) , (aq), (g) Ionic Bonds IMFS London Dispersion Forces Dipole-Dipole Interactions Hydrogen Bonding Examples CO2 HCl H2O Description Attractions between temporary induced dipoles; main IMF in non-polar compounds. Attractions between opposite charges of polar molecules. Special kind of Dipole-Dipole Interactions where H is tethered between N, O, or F. How do you Know? Non-Polar Compounds Polar Compounds Polar Compounds with H-N, H-O, or N-F Lustrous / shiny Malleable / Ductile Conducts heat + electricity Metallic Bonds