Lecture - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

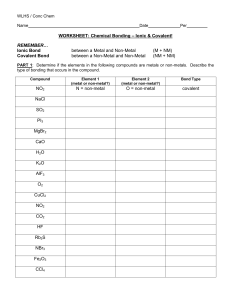
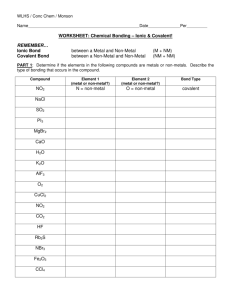
Covalent Bonding - Ionic bonding is the transfer of electrons between a metal that wants to give up an electron(s) and a non-metal that wants to gain an electron(s) - Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons. - This usually occurs between non-metal elements. - Like Ionic bonding, the octet rule can be used to explain covalent bonding because the elements are still trying to achieve 8 valence electrons - One of the best ways to model covalent bonding is by using lewis structures. - To draw the lewis structure for a colvalent compound. Start by writing the symbol of the element and then surround the “four” sides of the symbol with 1 dot for each valence electron. - Examples of the Halogens: - The single dot’s can form bonds by “sharing” the electrons between two elements. - Examples of the Halogens fulfilling the octet rule through covalent bonding: - The covalent compounds the result from the sharing of electrons have very different physical properties than ionic compounds - Covalent compounds… o Have very LOW melting points. Often times they are gases and liquids at room temperature o Vary greatly in the solubility o Only rarely form a crystal lattice