Water Frayer Packet
advertisement

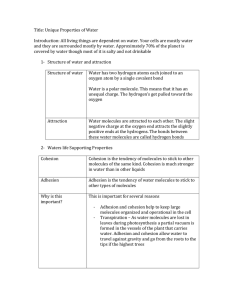
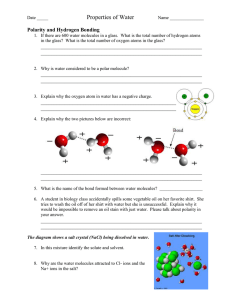
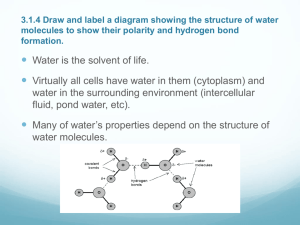
Water Frayer Packet Water • Structure – H2O – water has a bent “V” shape because oxygen pulls electrons more strongly than each hydrogen • Define Polar Molecule – Molecule with opposite charges at either end because of an unequal sharing of electrons • Type of Bond – Each water molecule is formed by covalent bonds – Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together • Why does oxygen pull electrons more strongly than hydrogen? – Oxygen has 8 protons and each hydrogen only has 1 – Remember that opposite charges attract, so protons like to be near electrons Bonds In and Between Water Molecules Covalent Bonds • Definition Density – The amount of matter in a given volume • Example – Ice floats because its molecules are less densely packed than those in liquid water. • Properties – Solid water is LESS dense than liquid water – Due to hydrogen bonding • Role in Living System – If ice sank, bodies of water (ponds, lakes etc.) would freeze from the bottom up and organisms would not have access to nutrients on the muddy bottom. Instead, ice floats and creates an insulated barrier for life below. Which is less densely packed? Cohesion • Definition – Molecules of the same kind sticking together • Example – Water sticking to other water molecules • Properties – Cohesion is stronger for water than most other liquids – Surface tension (caused by cohesion & hydrogen bonding) allows water striders to walk on water • Role in Living Systems – Needed to helps plants transport water from their roots to their leaves Adhesion • Definition – Attraction between unlike molecules (different kinds of molecules) • Example – Water sticking to a glass or leaf • Properties – Water can stick to other surfaces • Role in Living Systems – Needed to helps plants transport water from their roots to their leaves – In plants, adhesion between water molecules and the tiny “tubes” inside plants helps keep water from moving downward with the force of gravity Cohesion and Adhesion needed for Plants • Definition pH – Measure of how many hydrogen ions (H+) are in a solution • Example – Acids donate H+ to a solution (ex. Stomach acid) – Bases remove H+ from a solution (cleaners) • Properties – Each pH unit is a tenfold change in the concentration of H+ ions – pH of 7 has equal H+ and OH- concentrations • Role in Living Systems – pH of the solution in most living cells is close to 7 – Maintaining the correct pH inside cells is critical to life; buffers help to do this by removing and donating H+ to maintain homeostasis pH scale Solvent • Definition – Substance that dissolves other substances • Example – Sugar water : sugar is solute and water is the solvent • Properties – Water is the universal solvent • Role in Living Systems – Water is the main solvent inside all cells, blood, and in plant sap – Helps with chemical reactions in living organisms