Chapter 3: Water and the Fitness of the Environment
advertisement

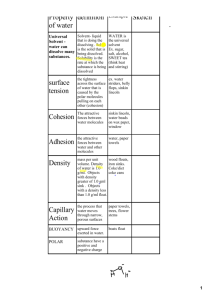
Chapter 3: Water and the Fitness of the Environment • • • • • • • • Makes life on Earth possible ¾ of Earth’s surface 60- 90 % of cells mass Cytoplasm and blood are mostly water Small, simple molecule Very common (occurrence) Very uncommon (chemistry) Several unique properties *** know these *** Polar covalent molecule • 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen • Mass of 18 • Strong zones of partial positive and partial • • negative – “poles” Cooperates in MANY hydrogen bonds Results in emergent properties – Conditions or traits that appear (emerge) because of the structure or relationships between components. – Ex: molecules have different properties than elements and a forest has different properties than a tree. Cohesion and Adhesion • Surface tension • Cohesion means water “sticks” to other water molecules….. “beads” – This helps keep water liquid, the form we need most as living organisms (cytoplasm to oceans) • Adhesion means that water “sticks” to other substances – Meniscus in graduated cylinder – Xylem and phloem in plant stems – Necessary for PHOTOSYNTHESIS Moderates temperature • Heat => measure of total kinetic energy • Temperature=> intensity of heat due to average • • • • kinetic energy Kilocalorie =>food cal., 1000 calories Calorie => amt of heat required to raise one gram of water by one degree Celsius Specific heat => amt of heat that must be gained or lost in order to heat or cool one gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius Water has relatively high specific heat Specific Heat • Because water has a high specific heat compared to other molecules its size – It take a long time to change temp. – Lake stays warm in fall – Ocean temperatures don’t vary much – Body temp stays steady Evaporative Cooling • Heat of vaporization => quantity of heat required to convert 1 gram of substance from liquid to gas • Evaporation of sweat (water) takes out a lot of body heat – Hottest molecules closest to phase change, lowers overall kinetic energy…. – Sweat, drool, pant, large ears, capillaries, etc Ice Floats • Liquid water has H bonds that hold water in a • • very density collection Solid water (ice) actually has longer bonds, liquid water’s bonds are further apart, less dense Floating ice – – – – – Doesn’t overflow Acts as insulation Allows for bottom to stay liquid Lake can “melt” completely in the summer Weather because of cold polar water and warm equatorial waters … flow and currents Solvent of Life • Solution =>homogenous liquid mixture of two or • • • • more substances Solute=> what is dissolved, solid, smaller amt. Solvent=> what did the dissolving, liquid, larger amt. Aqueous solution => solution where solvent is water Very common in nature Solutions • Blood is a solution that carries dissolved nutrients, oxygen and waste to and from cells • Cytoplasm ( cytosol ) is a solution that is mostly water and is the site of all chemical reactions in cells • Most biochemistry is carried out in aqueous solutions Solutions cont. • Hydrophilic =>water loving • Hydrophobic => water fearing • Molarity => number of moles per liter of solution (mole is atomic mass in grams) – ** Be able to calculate molar solutions ** • Dissociation=> degree to which a substance • • • separates when in solution. Water separates into H+ and OH Acid => has more H+ than OH- available Base => has more OH- than H+ available pH • pH is the negative log of the H+ concentration • • • • and is a measure of how much the water has dissociated and how much H+ is available Organisms are very sensitive to pH ranges. Some acids include gastic acid, lemon juice, soda, coffee, rain(6) and urine (6) Pure water should be neutral (7) Some bases would include sea water (8), blood (7.4), Tums, ammonia/bleach and many cleaners Acid Precipitation • Can be in any format (rain or snow) • Also exists as exhaust and run off • S and N in atmosphere bond to water creating • • • acids Changing pH of lakes or oceans is harmful to plant and animal life there Changing pH of soil changes the charge and availability of ions and nutrients that are used by plants Both can have impacts on food webs and our food/water/oxygen supply