Six Kingdom Notes
advertisement

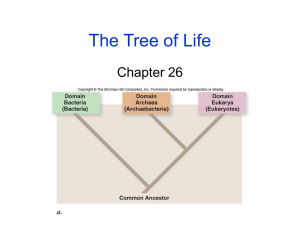
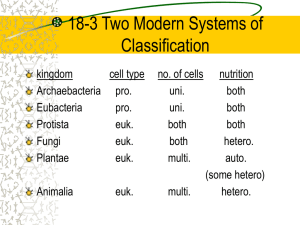
Warm up 2/2/2015 Monday Use the chart above to answer the following questions: 1. Which taxonomic groups do these organisms share? 2. At which taxonomic groups do Dog and Human diverge? 3. According to the chart which taxonomic group is the most general? 4. Which two organisms are the most closely related? Quiz tomorrow! OVER THE 6 KINGDOMS Record these vocabulary words in your notebook. Multicellular Unicellular Prokaryote Eukaryote Heterotroph Autotroph Overview of the Six Kingdoms Vocabulary Which term means one-celled? Many-celled? multicellular unicellular Which term means that the organism produces its own food? Consumes food? autotroph heterotroph Number of cells Multicellular- organisms made of two or more cells. Example: animal, plants, fungi Unicellular- organism made of single cell Example: bacteria, protist Vocabulary Prokaryotic – describes an organism with cells that have a cell membrane but do NOT have a nucleus Eukaryotic – describes an organism with cells that have a membrane bound organelles and a nucleus (nuclear membrane) Vocabulary Autotrophic – makes its own food Examples: photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs Heterotrophic – gets nutrients from the food it consumes List of the Three Domains and the Six Kingdoms 1. Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Domain Archaea Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Animalia Environment per kingdom (niche) Archaebacteria- extreme environment Eubacteria- everywhere in daily life (humans large intestine) Protista- Pond water, land, air Fungi-trees, ground Plantae-everywhere (land and water) Animalia – everywhere (land, air, water) Kingdom and Domain Characteristics Domain Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Characteristics Cell type Cell Structure Prokaryotic Cell Wall, Peptidoglycan Prokaryotic Body Type Nutrition Example Unicellular Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Enterobacteria Spirochetes Cell Wall, No Peptidoglycan Unicellular Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Methanogens Eukaryotic Mixed Unicellular and Multicellular Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Amoebas Euglenas Kelps Unicellular and Multicellular Heterotrophic Yeasts Mushrooms Eukarya Fungi Eukaryotic Cell Wall, Chitin Eukarya Plantae Eukaryotic Cell Wall, Cellulose Multicellular Autotrophic Ferns Pine trees Eukarya Animalia Eukaryotic No Cell Wall Multicellular Heterotrophic Birds Earthworms Kingdom Eubacteria Bacteria can live in many places on earth, inhabiting a wide variety of habitats, including other organisms Unicellular Prokaryotic Autotrophic or heterotrophic Thick cells walls with peptidoglycan Kingdom Eubacteria Bacteria come in different shapes, such as round, spiral and rod-shaped. Kingdom Eubacteria Bacteria can cause a wide variety of diseases, such as strep throat, food poisoning and the Black Death (bubonic plague of the Middle Ages) Kingdom Eubacteria Bacteria also play an important role in decomposition, nitrogen fixation and human digestion (E. coli) Soybean root containing billions of bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Procholorococcus – an autotrophic bacterium – What does that mean about how it gets its nutrients? Kingdom Eubacteria Bacteria from an Nitrifying Trickle Filter (NTF) stained with acridene orange. The stain makes DNA appear yellow and RNA appear orange. Kingdom Archaebacteria Bacteria that live in extreme habitats, such as hot springs, geysers, volcanic hot pools, brine pools, black smokers Unicellular Prokaryotic Autotrophic or heterotrophic Cell walls without peptidoglycan Kingdom Archaebacteria Morning Glory Pool in Yellowstone National Park – note the bright colors from the archaebacteria growing in the extremely hot water. Kingdom Archaebacteria Some like it hot! Bacillus infernus Kingdom Archaebacteria Archaebacteria can live deep in the ocean near geothermal vents called black smokers There is no light, so they carry out chemosynthesis instead of photosynthesis Kingdom Protista Extremely diverse group Eukaryotic Most unicellular, some colonial, some multicellular Autotrophic and heterotrophic Some with cell walls containing cellulose; some carry out photosynthesis with chloroplasts Kingdom Protista Euglena - autotrophic Volvox – a colonial protist A slime mold Amoeba - heterotrophic Kingdom Fungi Eukaryotic Most are multicellular Heterotrophic (decomposers) Cell walls made of chitin Kingdom Fungi Stilton cheese Bread mold Kingdom Plantae Eukaryotic Multicellular Autotrophic Cell wall of cellulose; chloroplasts present Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic No cell walls, no chloroplasts Kingdom Animalia Flatworm Sponge Jellyfish Octopus Coral snake Bear