Biochemistry LTF
advertisement

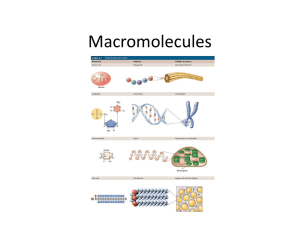
Biochemistry Exploring Macromolecules Organic Chemistry - study of chemistry of carbon - molecules of life made of elements carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen - functional groups – determines the characteristics of that compound Hydroxyl goup: -OH (see fig. 2) Carboxylic acid group: -COOH (see fig. 3) Amine group: -NH2 (see fig. 4) Large carbon molecules = macromolecules - large polymers – composed of repeating units called monomers - monomers are joined in condensation or dehydration synthesis reactions to form polymers (fig. 5) - breaking polymers down into monomers occurs by hydrolysis reactions - four main classes of macromolecules: *Proteins * Carbohydrates * Lipids * Nucleic Acids Proteins - composed of amino acids = monomers - all amino acids have a: a. carboxyl group –COOH b. amine group –NH2 - 20 common amino acids in living organisms - joined by peptide bonds = polypeptide - sequence of amino acids determines protein’s structure and function - [examples] - primary structure = sequence of amino acids - R groups often form attractions that cause the protein to fold (add the following to handout) - secondary structure = regular folding - tertiary structure = irregular folding - quaternary structure = more than one polypeptide joined to make a functional protein - Denaturing a protein changes its shape - change in temperature or pH Primary structure Hemoglobin Secondary (fig. 6 and 7) Tertiary Quaternary Carbohydrate - general formula Cn(H2O) - provide energy - exist as monosaccharides, disaccharide, polysaccharides - monomers = monosaccharides (glucose/fructose) - monosaccharides are linked by condensation reactions - sucrose is a disaccharide (fig. 8) - three important polysaccharides a. glycogen – animal energy storage b. starch – plant storage c. cellulose – in plant cell walls Lipids - large nonpolar molecules that are not very soluble in water - very efficient energy storage molecules – store twice as much energy as carbohydrates - simplest are fatty acids with long, straight carbon chain with a –COOH, carboxyl group, at one end - carbon chain is hydrophobic (water fearing) - carboxyl group end is hydrophilic (water loving) - form membranes of cells (phospholipids) (fig. 10) - saturated fats have all single bonds - unsaturated fats have some multiple bonds - Four basic categories: a. Triglycerides b. Phospholipids c. Waxes d. Steroids – ex. Cholesterol and hormones Nucleic Acids - transmit genetic information - DNA and RNA - DNA carries genetic information from between generations - monomers are nucleotides - each monomer has a sugar, phosphate group, and a base (fig. 13) - four bases in DNA in different orders code for all characteristics of life! - adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine (fig. 15) - DNA is double helix - hydrogen bonds hold it together - DNA is found in nucleus (fig. 14) - RNA is single stranded - DNA codes for RNA - RNA carries genetic code to cytoplasm where it codes for protein synthesis