yes - Learnblock
advertisement

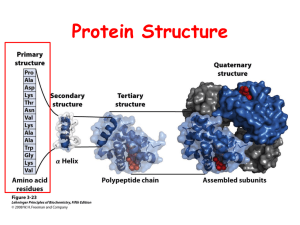
MBLG1001 Past Paper Questions 1-19 Proteins and Enzymes 1. Carbon based life • Life evolved to be carbon based rather than silicon based because: A. Silicon only allows 2 options for coding (1/0), whereas carbon allows 4 (A/T/G/C) silly! But nice to start with some humour! B. Silicon has a smaller atomic radius No, carbon is above silicon on the periodic table. C. Silicon reactions, unlike carbon, are controlled kinetically rather than thermodynamically ummm.., see D. Si-O bonds are stronger than Si-Si bonds E. Carbon is more abundant than silicon notes below yes. example sand & glass Opposite, there is heaps more silicon than carbon 2. Alpha helicies • Which of the following statements about the alpha helix is FALSE? A. The alpha helix is found in zinc finger motifs and leucine zippers yes B. The twist in the alpha helix is the result of repulsive forces acting on the phosphates no. hydrogen bonding… um, phosphates?? C. An alpha helix from any source has approximately the same phi angle yes, that’s what makes it a helix D. Proline is rarely found as an internal residue in alpha helices E. Alpha helices interact with the DNA bases through the major groove. indeed, they do yes, it’s a weird, inflexible shape peptide bond-wise 3. Anfinsen’s Experiment • Which of the following statements concerning Anfinsen’s experiment is FALSE? A. The aim of the experiment was to show that hydrophobic interactions drive water soluble proteins to fold Intuitively the statement is correct but didn’t they think that before got results? B. The 6 M guanidine HCl was added to reversibly disrupt the hydrophobic interactions yes C. Measuring the enzyme activity of RNase can be used to monitor the extent of folding extent of re-folding D. The fully denatured protein was inactive E. Dialysis was used to slowly remove the denaturant yes yes 4. More Anfinsen! • Caution must be applied when extrapolating Anfinsen’s conclusions to the folding of ALL proteins in vivo. Which of the following is NOT a valid reason for this caution? A. The cytoplasm contains many proteins ([protein] ~300 mg/mL) which may interfere with folding intuitively not. Confused by concn B. Some large proteins need chaperones to fold sounds right C. Some proteins fold in the membrane D. Ribonuclease is a small, unusually stable protein they don’t ‘become’ membranes very stable! a bit erudite, any enzyme that can be boiled and it survives is stable!! E. The experiment was never done with proteins that need to form disulphide bonds sounds reasonable and important 5. Glycine Titration Curve D amino group protonated carboxylic acid group 50:50 C pH E [H+] low but not swamping B A H+ added OH- added In which region of the titration curve (A – E) would you have Equal amounts of H3N+ -CH2-COOH and H3N+-CH2-COO-. 6. Glycine Titration Curve D amino group protonated carboxylic acid group not C pH E B A H+ added OH- added In which region of the titration curve (A – E) would you have Predominantly H3N+-CH2-COO-. 7. Glycine Titration Curve • Which region would make a good buffer? A. Any region could be used as the solution can be made to any pH no. Some very reactive B. No region would be suitable as the pH changes with the addition of H+ counter intuitive! C. Region C, as it is in the middle of the pH range a disaster D D. Only regions B or D yes E. Only regions A or E a disaster looking for a small change in pH after adding acid or base C p H B A H+ added OHadded E 8. Peptide Linking C O H3N+ CH CH2 C O HN CH C O HN CH CH3 CH2 B C NH2 C O HN CH C O- CH2 O SH E D OH A Peptide K is found as a covalent dimer under some conditions. Which of the circled features (A – E) would enable it to form covalent dimers? disuphide bonds - E 9. Absorbing Stuff C O H3N+ CH CH2 C O HN CH C O HN CH CH3 CH2 B C NH2 C O HN CH C O- CH2 O SH E D OH A Which of the circled features (A – E) would enable its detection at 280 nm? ring - A 10. Hydrogen Bonds C O H3N+ CH CH2 C O HN CH C O HN CH CH3 CH2 B C C O HN CH C O- CH2 O NH2 SH E D OH A Peptide K is often found associated with other neuropeptides by hydrogen bonding. Which of the circled features (A – E) could NOT participate in this hydrogen bonding? hydrophobic methyl - B 11. Phosphorylation C O H3N+ CH CH2 C O HN CH C O HN CH CH3 CH2 B C NH2 C O HN CH C O- CH2 O SH E D OH A As part of its neurotransmission regulatory role Peptide K is sometimes phosphorylated. Which of the circled features (A – E) would be most likely to be phosphorylated? looking for serine.. but tyrosine OK - A O A H2N O B CH C OH H2N CH C CH2 CH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 OH Your team has isolated a second neuropeptide, Peptide J, which is slightly longer. Peptide J was found to be composed of equal amounts of the following amino acids CH2 NH2 O C H2N CH C O D OH H2N CH CH2 CH2 CH2 C C O NH2 OH O E HN C OH C 12. Charges OH What is the overall charge of Peptide J at pH 13? O ends will have a single negative – amine unprotonated and neutral, carboxylic acid unprotonated and negative A unprotonated and neutral, B not affected, C unprotonated and negative, D not affected, E not affected minus 2 O A H2N O B CH C OH H2N CH C CH2 CH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 OH Your team has isolated a second neuropeptide, Peptide J, which is slightly longer. Peptide J was found to be composed of equal amounts of the following amino acids CH2 NH2 O C H2N CH C O D OH H2N CH CH2 CH2 CH2 C C O NH2 OH O E HN C OH C O 13. Charges OH How many charged groups will Peptide J have at pH 7? four ends will both be charged – amine protonated and positive, carboxylic acid unprotonated and negative A protonated and positive, B not affected, C unprotonated and negative, D not affected, E not affected O A H2N O B CH C OH H2N CH C CH2 CH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 OH Your team has isolated a second neuropeptide, Peptide J, which is slightly longer. Peptide J was found to be composed of equal amounts of the following amino acids CH2 NH2 O C H2N CH C O D OH H2N CH CH2 CH2 CH2 C C O NH2 OH O E HN C OH C O 14. Turns OH Peptide J was found to have a sharp bend in its backbone conformation, unlike peptide K. Which amino acid (A – E) would be responsible for this unusual backbone conformation Proline - E 15. Equilibria • One of the enzymes of glycolysis, Fructose Bisphosphate aldolase, is found in all cells. The reaction it catalyses has a Keq ([product]/[substrate] at equilibrium) of 6 X 10-5 at 25oC. What can NOT be concluded from this information? A. The ΔGof of the product is greater than the ΔGof of the substrate not sure how we infer this from the Keq B. The reaction is endergonic linked to E. delta G is positive C. The reverse reaction (formation of substrate) will be favoured at equlib [product] <<< [substrate] – so reaction wants to give substrate! D. The small Keq means the reaction rate will be slow can’t deduce speed from delta G E. The ΔGo for this reaction will be positive it will. Keq < 1 16. Equilibria • Which of the following statements concerning equilibrium is CORRECT? A. For a cellular reaction to reach equilibrium the product must be continually used by the cell elsewhere opposite. if used then equilibrium never attained B. At equilibrium the [products] always equals the [substrate] i.e. Keq = 0 no. Keq is 1 when P=S C. Reactions with large negative ΔGo reach equilibrium quicker no relationship between delta G and speed D. At equilibrium the entropy of the system is zero i.e. ΔS = 0 depends on the enthalpy E. The reaction will probably reach equilibrium quicker in the presence of an enzyme yes Enzymes don’t change the equlibrium position, just the rate it gets there!! 17. Weak Forces • Which of the following statements is CORRECT concerning weak forces? A. Hydrogen bonding is only significant in macromolecules such as proteins and DNA. what about water? B. Hydrophobic interactions result from hydrogen bonding between hydrophobic molecules. not H-bonding C. Hydrogen bonding results from minimizing the loss of entropy rather than forming bonds. No, this is hydrophobic interactions D. The strength of ionic interactions decreases in an environment with higher [salt]. It does as the ions shield the charges of interest E. Unlike the other weak forces (hydrogen bonding, ionic and hydrophobic interactions) van der Waal’s forces cannot be induced. they are induced and temporary 18. Protein Structure • Which of the following statements best describes the primary structure of a protein? A. The number of amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain. not bad.. but need identity B. The percent amino acid composition of the polypeptide chain. it’s 100! C. The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. that’s it! D. The regular folding of a single polypeptide chain in repeated patterns - the local conformation of the polypeptide backbone. conformation not described. Secondary. E. The unique three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide chain Tertiary. 19. Km • Which of the following is INCORRECT concerning Km? Km is: A. Used to predict the maximum attainable rate of the reaction. possibly. If know the rate at Km but by itself you can’t. B. The [substrate] that gives half the maximum attainable rate of reaction yes C. The [substrate] where half the enzyme present in the reaction is bound to substrate i.e. ES = Efree Yes, at the Km 50% of the enzyme exists as ES at any time. D. Used to determine the [substrate] when measuring the activity of an enzyme yes, want [S] >> Km E. A measure of the affinity the enzyme has for the substrate yes, low Km is high affinity