Punnett Square Examples (Notebook)

Monohybrid Cross (Dominant and Recessive Inheritance)
Involves chromosomes 1-22
Involves only one gene
Can have two alleles (upper case/lower case)
Can have two phenotypes (ex. Blonde hair or brown hair)
AA (homozygous dominant), Aa (heterozygous), aa (homozygous recessive)
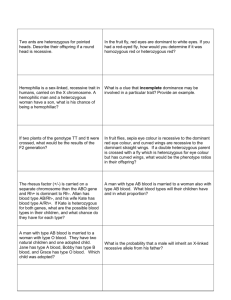
Example: In humans brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. What type of offspring would you expect if you crossed a heterozygous brown eyed person to a heterozygous brown eyed person?
Sex-Linked Inheritance
Sex chromosomes (XX-female, XY-male)
Alleles in superscript
Carrier means heterozygous
Males only have one allele
Example: Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disorder. A woman who is heterozygous for hemophilia marries a normal male. What are the possible phenotypes of their children? What is the probability that they will have an offspring with the disorder?
Dihybrid Cross (Dominant and Recessive Inheritance)
Involves chromosomes 1-22
Involves two genes
Can have up to four different phenotype combinations
Sides of Punnett square are gamete allele combinations
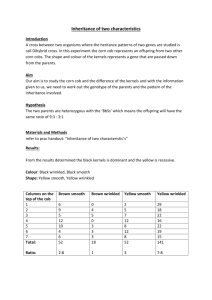
Example: Suppose that black hair (B) is dominant over blonde hair (b) and brown eyes (E) are dominant over blue eyes (e). The father has black hair (heterozygous) and brown eyes
(heterozygous) and the mother has blonde hair and blue eyes. What percent of offspring will have blonde hair, blue eyes?
Cross: X
Gamete Combinations ____ _____ _____ _____X ____ _____ _____ _____
Codominance Inheritance
No dominant and recessive
Heterozygous is a blend of colors (ex: Red, pink, White)
Example: blood type
Example: A roan bull (red and white both expressed) is mated with a white cow (recessive).
What are the possible offspring?
Incomplete Dominance Inheritance
No dominant and recessive
In heterozygous, both colors are expressed (ex: Red, Red&White, White)
Example: blood type
Example: A red carnation is crossed with a white carnation and the resulting offspring are all pink (indicating incomplete dominance). What would be the result of a cross between a pink and a white carnation?