Blood Typing: ABO, Rh Factors & Genetics Guided Notes
advertisement
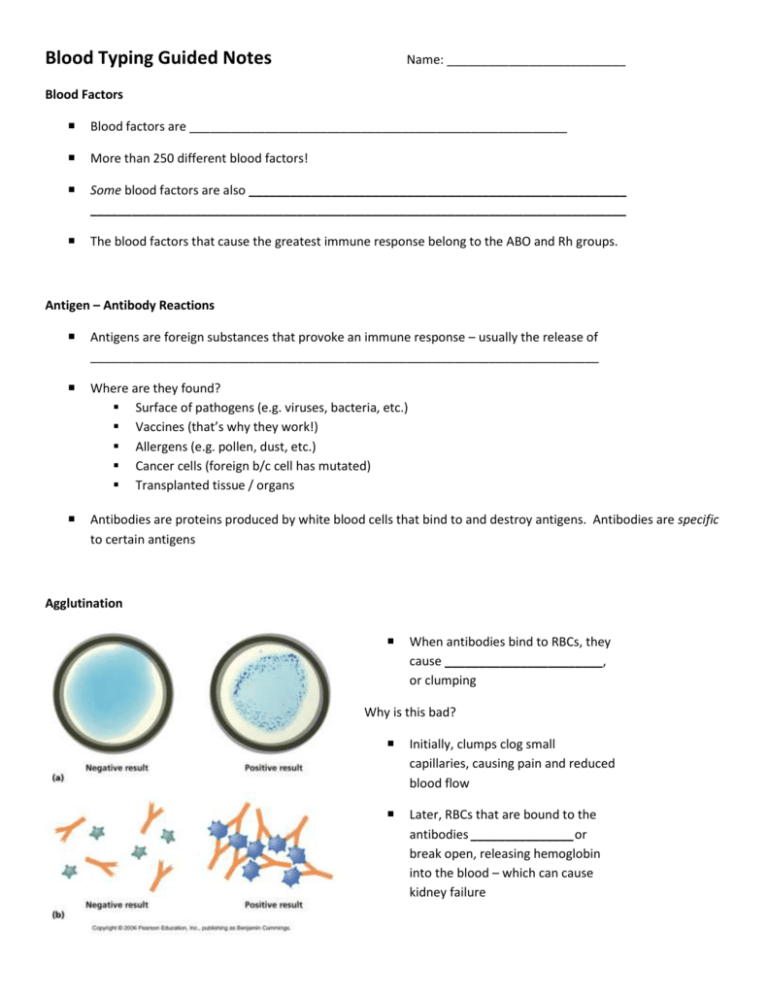
Blood Typing Guided Notes Name: __________________________ Blood Factors Blood factors are _______________________________________________________ More than 250 different blood factors! Some blood factors are also _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ The blood factors that cause the greatest immune response belong to the ABO and Rh groups. Antigen – Antibody Reactions Antigens are foreign substances that provoke an immune response – usually the release of __________________________________________________________________________ Where are they found? Surface of pathogens (e.g. viruses, bacteria, etc.) Vaccines (that’s why they work!) Allergens (e.g. pollen, dust, etc.) Cancer cells (foreign b/c cell has mutated) Transplanted tissue / organs Antibodies are proteins produced by white blood cells that bind to and destroy antigens. Antibodies are specific to certain antigens Agglutination When antibodies bind to RBCs, they cause _______________________, or clumping Why is this bad? Initially, clumps clog small capillaries, causing pain and reduced blood flow Later, RBCs that are bound to the antibodies _______________or break open, releasing hemoglobin into the blood – which can cause kidney failure ABO blood group In the ABO blood group, there are two antigens, “A” and “B”, found on the surface of RBCs You can have one type of antigen, both types, or neither You develop antibodies to the type of antigens you don’t have during infancy The key to transfusions: ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Blood Type Can donate to Can receive from A B AB O Which type is the universal donor? Which type is the universal recipient? Rh Blood Group The Rh blood group describes ~45 different (but similar) antigens on RBCs. These antigens are called antigen “D” People are Rh + if they have any of the various D antigens. They are Rh – if the do not have any D antigens. Unlike the ABO system, Rh- people must be ______________________to the D antigen before developing antibodies. That means Rh- people will NOT have an agglutination reaction the first time they encounter Rh+ blood … but they will if they have it a second time. Blood Type Can donate to Can receive from Rh+ Rh+ Rh-, Rh+ Rh- Rh-, Rh+ Rh- With this added group in mind, what is the true universal donor? … and the true universal recipient? Rh group and pregnancy Rh- moms can carry a Rh+ baby if the dad is Rh+ The first baby is usually born without any problems, but, during delivery, some of the baby’s D antigens will contact the mom’s blood, causing her to be sensitized to D antigens. If the mom becomes pregnant with a second Rh+ baby, her immune system will attack the baby’s blood, causing brain damage or death to the fetus. This can be prevented by giving the mother medicine that prevents her from developing antibodies against D antigens. Blood Typing __________________________ is a solution that contains antibodies against a specific antigen (i.e. antiserum A contains type A antibodies). Blood type is determined by adding antiserum A, B, and D to blood and observing whether or not agglutination occurs How is blood typing used in forensics? To identify people or link suspects to crime scenes To identify paternity Genetics Refresher We have two versions – or ______________________ – of every gene. One inherited from our mom, one from our dad. The two alleles (_______________________) interact to determine our trait (____________________) in predictable ways. Some alleles are _________________, some are ________________. Dominant genes show their trait and ‘cover up’ recessive genes. ▪ IA (A) and IB (B) are dominant to i (O). ▪ D (+) is dominant to d (–) Some alleles are ___________________. This means both alleles fully express their trait. ▪ IA and IB are codominant with each other. What blood type will result from each genotype? 1. IAiDD 2. iidd 3. IB IB Dd 4. IA IB dd 5. IB iDd What are the possible genotypes for each blood type? 1. A+ 2. AB3. O4. B+ Punnett Squares Punnett Squares are a tool for predicting the traits that will result from crossing certain genotypes.