Different Patterns of Inheritance
Blood Types, Sex-Linked and
Polygenic
Traits
Blood Typing!
Phenotype
Genotype
A
AA or AO
B
BB or BO
AB
AB
O
OO
Blood Types
A person who
has:
A-, O- blood
A+ blood
A-, A+, O-, O+ blood
B- blood
B-, O- blood
B+ blood
B-, B+, O-, O+ blood
AB- blood
AB-, O- blood
AB+ blood
Can receive:
A- blood
AB-, AB+, A-, A+, B-, B+, O-, O+
blood
O- blood
O- blood
O+ blood
O-, O+ blood
Type O-negative blood does
not have any antigens.
It is called the "universal
donor" type because it is
compatible with any blood
type.
Type AB-positive blood is
called the "universal
recipient" type because a
person who has it can
receive blood of any type.
+ = have Rh protein
- = no Rh protein
Blood Type Crosses!
Samara is type AB
Naveen is type A
his mother was A, Father O
What are their genotypes?
S= AB
Phenotyp
e
Genotype
A
AA or AO
B
BB or BO
AB
AB
O
OO
N = AO
What are their possible offspring’s
blood types?
50% A
25% AB
25% B
Blood Typing!
Kristina is type B
Kyle is type A
Is is possible for their
child to be type O?
Phenotyp
e
Genotype
A
AA or AO
B
BB or BO
AB
AB
O
OO
Polygenics
Multiple
Skin
GENES affect the traits being expressed
color
Hair color
Eye color
How it works…
Eye
Eye Color
Color == Brown
Hazel
Skin
SkinColor
Color==Light
Tan
Eye Color
Sex Linked Traits
Sex Chromosomes (X, Y)
In humans male determined sex of offspring
• Give X = female
• Give y= male
Genes can be located on sex chromosomes
= Sex Linked Traits
Mostly on X for humans
Fly Experiment
Eye color carried on X
R = red r = white
More males are white than female because..
SEX LINKED TRAIT!!
(only on X Chromosome)
XY Female XX
100%
50%
0%
50%
Male
Sex Linked Disease
Females can be carriers, males will show it
Red- green color blindness
Night Blindness
Fragile X syndrome
Sickle Cell Anemia
Huntington's disease
Cystic Fibrosis
Hemophilia
Sex-Linked Genetic Cross
Reinforcement
Pg 175- 176 ( 3 P.R.)
Pg 180-182 (3 P.R.)
PEDIGREE
CHARTS
A family history of
a genetic condition
What is a pedigree chart?
Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an
individual
They can be used to study the transmission of a
hereditary condition
They are particularly useful when there are large
families and a good family record over several
generations.
Studying Human
Genetics
Pedigree charts offer an ethical way of studying human
genetics
Today genetic engineering has new tools to offer
doctors studying genetic diseases
A genetic counsellor will still use pedigree charts to
help determine the distribution of a disease in an
affected family
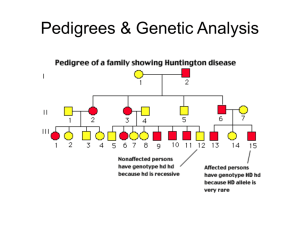
Symbols used in pedigree charts
Normal male
Affected male
Normal female
Affected female
Marriage
A marriage with five children, two
daughters and three sons. The second
born son is affected by the condition.
Eldest child Youngest child
Organising the pedigree
chart
A pedigree chart of a family showing 20
individuals
Organising the pedigree
chart
Generations are identified by Roman
numerals
I
II
III
IV
Organising the pedigree chart
Individuals in each generation are identified by Roman
numerals numbered from the left
Therefore the affected individuals are II3, IV2 and IV3
I
II
III
IV
Different Patterns of Inheritance
Sex-Linked
Passed
Recessive
on the X or Y chromosome
• Usually X
What
this means…
• Girls can be carriers (XX)
• Males either have it or are normal (XY)
• Examples:
• Hemophilia, color-blindness, muscular dystrophy
Sex-Linked Recessive
males get their X from their mother
fathers pass their X to daughters only
females express it only if they get a
copy from both parents.
expressed in males if present
Possible Carriers in females
Shown by half filled circles
Usually more males show this!!
Cannot have sick male, normal
mother
Autosomal Dominant
All unaffected
individuals are
homozygous for the
normal recessive
allele.
Autosomal Recessive
All affected are homozygous.
Incest matings are often (but
not always) involved.
Heterozygous are “normal”
Dominant vs. Recessive Autosomal
Is it a dominant pedigree or a recessive pedigree?
1. If two affected people have an unaffected child, it must be a dominant
pedigree
2. If two unaffected people have an affected child, it is a
recessive pedigree:
D is the dominant mutant allele and d is the recessive wild type allele. Both
parents are Dd and the normal child is dd.
R is the dominant wild type allele and r is the recessive mutant
allele. Both parents are Rr and the affected child is rr.
3. If every affected person has an affected parent it is a
dominant pedigree.
Dominant Autosomal Pedigree
1. If two affected people have
an unaffected child, it must be
a dominant pedigree
I
2
1
II
1
2
3
4
5
6
III
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Recessive Autosomal Pedigree
If two unaffected
people have an
affected child, it
is a recessive
pedigree
Recessive Sex Linked Pedigree
If I don’t tell you.. Look for
shading
If I tell you, shade it