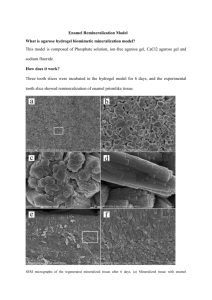
Powerpoint slides (Office document, 4601kB)
advertisement
From Blood to Tooth Fairies Dr Sue Ring ResearchFest 9th September 2012 Sue Ring Head of Laboratories From blood to tooth fairies • • • • • ALSPAC Samples The Laboratory Blood Processing Blood Related Research Findings Tooth Research ALSPAC Samples • Helen Pearson (2012), Nature 484, 155-158 ALSPAC Samples 6,000 milk teeth 16,000 saliva samples 100,000 Blood tubes 8,000 Placentas 6,000 slices umbilical cord 15,000 urine samples 25,000 hair samples 20,000 toe nails Background to Laboratory LAB TEAM 14 in total : Researchers, technicians, students, Bioinformatics and IT support Sample Processing DNA Cell lines Analysis Storage Facilities 1.2 Million individual tubes 30,000 DNA samples 20,000 cell lines Blood Processing Cell lines White cells DNA RNA Spin blood sample at 3500rpm to separate Cell line production Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes (white blood cells) isolated from blood Add Epstein Barr Virus and put in solution containing sugars, protein and growth factors. 37oC for 6 to 8 weeks “feed” every 3 to 4 days “Transformed” cell line which will grow indefinitely and provide infinite supply of cells and DNA PLASMA Cellular assays Cell lines Biomarkers White cells DNA RNA Spin blood sample at 3500rpm to separate A measurable substance in an organism whose presence is indicative of some phenomenon such as disease, infection, or environmental exposure. Blood Related Research Findings Coeliac Disease (Bingley et al (2004) BMJ 328;322-323) • • • < 1 in 2,500 children diagnosed Subclinical disease common in adults, is it in children? Measured antibody (IgA-EMA) in blood samples taken at 7yr clinic – 5470 children tested 1% had IgA-EMA – Shorter and weighed less (equivalent to 9 months growth) – Higher incidence of diarrhoea and overall intestinal symptoms but not vomiting, stomach pain or constipation • • • Ie – similar frequency of undetected in children and adults Consequences of undiagnosed condition not yet established but indicate that if screening is ever considered should start in childhood Long term follow up can be looked at in CO90’s in adulthood to see if long term effects Long-chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (LC-PUFA) Lattka et al (2012) british Journal of Nutrition -in press • Important in maintenance of metabolism and health • In pregnancy important for brain growth, visual and cognitive development • Obtain LC-PUFA from – Diet – fish, eggs – Synthesised by body from essential fatty acids from vegetable oils • Controlled by enzymes – desaturases • Fatty Acid desaturase (FADS) genes code for the enzymes – Minor variants in FADS genes alter efficiency of enzymes and decrease the amount of LC-PUFA people with the variants can make. What happens during pregnancy? • Looked at mother and child genes and at levels of LC-PUFA in cord blood at birth. • Does foetus obtain all LC-PUFA from mother or can it synthesis itself? – BOTH – Some types of LC-PUFA are present at levels predicted by Mum’s genotypes and others by child’s » Newborn metabolism greater capacity to synthesise more highly unsaturated omega-6 fatty acids and some evidence to show DHA but not all processes appear to be active – Also looked at blood taken at 7yrs of age when all influence of mother’s genotype had disappeared and levels of all LC-PUFA reflect child’s genotype – ie by 7yrs child’s metabolism fully functioning. (Steer et al 2012 Human Molecular Genetics 21;1504-1512 • Work to date has measured a small number of biomarkers in samples. • Samples from early time points are especially valuable. • High throughput methodology which uses very small volumes of sample to measure many different markers is now becoming affordable. Anticipate large increase in number of projects and publications utilising biological samples in next few years. Metabolomics – Professor Mika Ala-Korpela • "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind“ • 216 serum metabolic markers from each sample in one experiment Tooth Related Research Tooth Research Dr Louise Humphrey Professor Christopher Dean - Natural History Museum - University College London • Teeth represent an archive of infancy – still learning what it means • Project is exploring how structure and chemistry of deciduous teeth relates to health and diet in first year of life • Teeth form during pregnancy and in first year of life – growth process recorded in marks in enamel - The Straie of Retzius which occur every 8-10 days, similar to tree rings • Accentuated lines - Permanent record of growth disruptions experienced while the tooth is forming, eg caused by flu or chicken pox. We are hoping to find out more about the causes of these accentuated lines. • Laser ablation – chemical composition Enamel cusp Polished section Dentine Image courtesy of Christopher Dean ( Growth markers in enamel Striae of Retzius: regular growth lines Accentuated Line: growth disruption (image courtesy of Christopher Dean) Tooth Research Dr Louise Humphrey Professor Christopher Dean - Natural History Museum - University College London • Teeth represent an archive of infancy – still learning what it means • Project is exploring how structure and chemistry of deciduous teeth relates to health and diet in first year of life • Teeth form during pregnancy and in first year of life – growth process recorded in marks in enamel - The Straie of Retzius which occur every 8-10 days, similar to tree rings • Accentuated lines - Permanent record of growth disruptions experienced while the tooth is forming, eg caused by flu or chicken pox. We are hoping to find out more about the causes of these accentuated lines. • Laser ablation – chemical composition • Neonatal Line – Expression may relate to the type of birth and other factors such as birth weight or gestation length. Neonatal line in a deciduous tooth (image courtesy of Christopher Dean)