Chapter 7 Power Point
advertisement

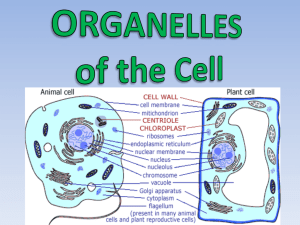
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7 Biology Miller • Levine The Scientists… ○ Robert Hooke (1665) ● ● ○ Viewed cork under a microscope Called the chambers he saw “cells” Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) ● First to see living organisms in a drop of water The Scientists… ○ Matthias Schleiden (1838) ● ○ Theodor Schwann (1839) ● ○ All plants are made of cells All animals are made of cells Rudolf Virchow (1855) ● All cells come from preexisting cells The Cell Theory ○ ○ ○ All living things are composed of cells Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things New cells are produced from existing cells Unicellular vs. Multicellular ○ ○ Unicellular – single-celled organism Multicellular – many-celled organism ● ● Cell specialization – cells are specialized to perform certain functions Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ systems → Organism Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes ○ Prokaryotes ● ● ○ Have a cell membrane & cytoplasm, but do not have a nucleus Ex. Bacteria such as E.coli Eukaryotes ● ● Have a nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm & organelles Ex. Plants, Animals, Fungi Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Basic Cell Structures ○ Cell membrane – thin, flexible barrier around the cell; protects the cell Present in all cells ● Selectively permeable ● Contains floating layers ● ○ SS The Fluid Mosaic Model Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic Hydro = water Phobic = fear/hate Philic = love Cytoplasm – ○ material inside the cell membrane (not including the nucleus) ● Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes Cell Wall ○ ○ ○ ○ Found in many organisms, including plants, algae, fungi and nearly all prokaryotes Not found in animal cells Lies outside the cell membrane but is porous Main function is to provide support & protection for the cell Nucleus ○ ○ ○ Almost all eukaryotic cells, including plants and animals have a nucleus Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus Controls most cell process and contains the DNA Nucleolus and Nuclear Envelope ○ Nucleolus: ● ● ○ Inside the nucleus Where ribosomes are made Nuclear Envelope: ● ● Double-membrane layer around the nucleus Allows material to move into and out of the nucleus Nucleus Cytoskeleton ○ ○ ○ ○ Found in all eukaryotic cells Not found in prokaryotes A network of protein filaments that helps the cell maintain its shape It also is involved in cell movement Microfilaments and Microtubules made of actin, tough and flexible, functions for cell movement, assemble and disassemble the microtubules for cell movement made of tubulis, maintain cell shape, used in cell division with centrioles and build the projections of cilia and flagella Ribosomes ○ ○ ○ Found in all cells Main function is to make proteins Can be found floating in the cytosol or attached to endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) ○ ○ ○ Found only in eukaryotic cells Where components of the cell membrane are assembled Two kinds: Smooth ER & Rough ER ● ● Smooth ER: no ribosomes; makes lipids Rough ER: has ribosomes; involved in making proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus ○ ○ ○ Found only in eukaryotic cells Enzymes attach carbohydrates & lipids to proteins Send proteins to their final destination Lysosomes ○ ○ ○ ○ Found in animal cells only Break down lipids, carbohydrates & proteins from food into particles that can be used by the cell Also break down “dead” organelles Vacuoles ○ ○ ○ ○ Not found in prokaryotes Animal cells have small or no vacuoles Plant cells have a large central vacuole Store materials such as water, salts, proteins & carbohydrates How endocytosis and exocytosis works in animal cells: Note the food Vacuole and Lysosomes Chloroplasts ○ ○ ○ ○ They have their own DNA Found in all plant cells Some prokaryotes have them, but most do not Use the energy from sunlight to make energy-rich food molecules (carbohydrates) during photosynthesis Mitochondria ● converts stored energy to a usable form ● double membrane with folds to increase surface area ● it also has its own DNA Endosymbiotic Theory (CH 19) Diffusion ○ ○ ○ ○ Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Movement continues until equilibrium is reached Many substances move across the membrane by diffusion Does not require energy (passive transport) Diffusion concentration gradient Rate of Diffusion is affected by: 1. Temperature 1. Steepness of the gradient 1. Size of Molecules Facilitated Diffusion ○ ○ ○ ○ Some molecules cannot cross the membrane without help Some of the proteins in the membrane form protein channels Materials still move from higher to lower concentrations No energy is required Facilitated Diffusion htlfacilitated diffusion (fast and specific but energy free) Osmosis: A special name for a special Molecule! ○ The diffusion of water ● Isotonic – equal concentration ○ ● Hypertonic – higher concentration ○ ● osmosis Water moves out of the cell (shrivels) Hypotonic – lower concentration ○ ○ Nothing happens (normal) Water moves into the cell (pops at the extreme) No energy is required Effects of Osmosis on Cells Osmotic Pressure ○ ○ ○ In pure water, an animal cell would burst Plant cells are protected by their cell wall Some freshwater organism have special structures like contractile vacuoles to get rid of extra water Active Transport: Working to go Uphill---Up the gradient. ○ ○ ○ Materials move from lower concentration to higher concentration Requires an input of energy Works kind of like a pump Transport of Large Amounts Bulk Transport ○ Endocytosis – movement into the cell ● ● ○ Phagocytosis – “cell eating” – solid particles Pinocytosis – “cell drinking” – particles dissolved in water Exocytosis – movement out of the cell Phagocytosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pvOz4V699gk Pinocytosis animation Homeostasis and Cells (homeo = same Stasis = state SIngle and cells and Multicellular organisms - maintain a certain level of conditions in its environment Multicellular organisms divide and conquer tasks and jobs to maintain homeostasis. This takes communication! Cell to cell communication: ● cellular signals speed up or slow down cell activities ● receptors (1)in the cell membrane and (2) inside the cytoplasm carry electrical and chemical messages. ● review of phospholipid membrane and receptor visual