Meiosis
Vocabulary
1. Parent cell: original cell before division
2. Daughter cell: cells after division
3. Gamete/sex cell: eggs and sperm
4. Somatic cell: all other body cells besides eggs and sperm
5. Haploid (n): one set of unique
chromosomes
6. Diploid (2n): two sets of unique
chromosomes
Vocabulary
7. Alleles: different forms of a gene. For
example, there are at least two different alleles
for eye color. Different combinations of alleles
give organisms different variations of the same
trait, such as brown eyes or blue eyes.
8. Homologous chromosomes: chromosomes
that are similar, but not identical. For example,
the larger chromosomes to the left are
homologous to each other, and the smaller
chromosomes are homologous to each other.
They may not have the exact same alleles, but
they have the same genes in the same places
(and the same chromosome number).
9. Non-homologous chromosomes:
chromosomes that are not similar at all. In the
picture on the left, the large and small
chromosomes are non-homologous because
they carry different genes.
Vocabulary
10. Sister chromatids:
identical halves of a
chromosome that has
replicated
11. Tetrad: a complex of 4
homologous chromatids
Vocabulary
12. Chromosome: a molecule of DNA
13. Fertilization: when an egg cell and a
sperm cell join to form a
zygote
14. Zygote: a fertilized egg that has not yet
started to divide
15. Mitosis: the process of cell division that
results in two identical daughter cells
(2n 2n)
16. Meiosis: the process of cell division that
results in four haploid sex cells (2n n)
Vocabulary
17. Karyotype: the number and visual appearance
of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an
organism
or species.
(This is a picture of a
normal karyotype. Is
this individual male or
female?)
Key Point #1: Mitosis and Meiosis are
two different types of cell division
Mitosis
vs.
-Mitosis creates two identical
daughter cells from one parent
cell
-ALL of your somatic cells do
mitosis
-after mitosis, the daughter cells
have the same number of
chromosomes as the parent cell
(2n 2n)
Meiosis
-Meiosis creates four unique
daughter cells from one parent
cell
-Meiosis is ONLY used to make
sex cells
-each daughter cell has HALF
the number of chromosomes
as the parent cell (2nn)
Key Point #2: Mitosis is cell division
that results in two diploid cells
identical to the original cell
1. The diploid (2n) parent cell replicates its DNA to go
from I-shaped to X-shaped double chromosomes
2. The parent cell divides (splitting the X shaped double
chromosomes into I-shaped single chromosomes) to
create two identical cells that are both 2n.
Do you want all of your skin cells to be different, or the
same?
Check for Understanding
1. If a skin cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes
mitosis, how many chromosomes will each
daughter cell have?
2. If two daughter cells in a cabbage leaf have
18 chromosomes each, how many
chromosomes did the parent cell have?
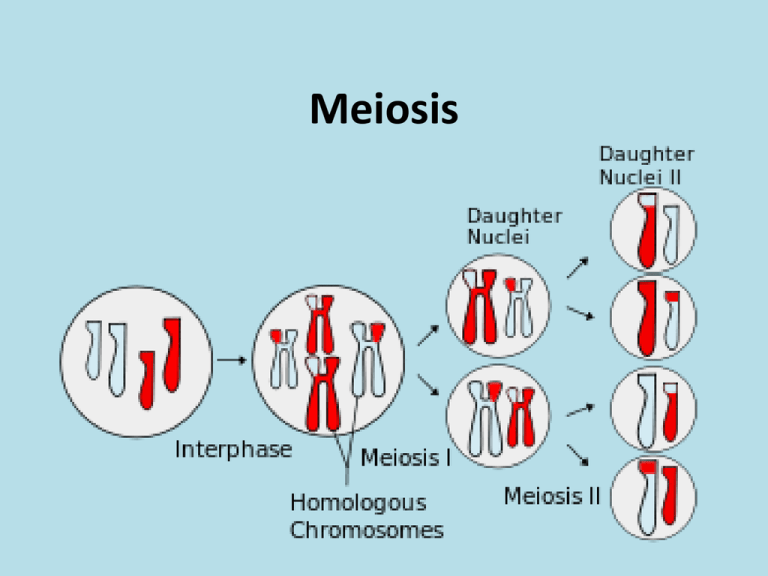
Key Point #3: Meiosis is two cell divisions that results in
four haploid, nonin non- identical daughter cells
• Step 1: The parent cell
duplicates (copies) its DNA.
The chromosomes have gone
from I shaped to X shaped.
This cell is still considered
diploid (Why?).
• Step 2: The parent cell divides
to make two haploid daughter
cells (the X shaped
chromosomes split up)
• Step 3: Each daughter cell
divides. The X shaped
chromosomes split into I
shaped chromosomes to make
a total of 4 haploid daughter
cells
Key Point #4: Meiosis only happens in
reproductive organs to create sex cells
In females, meiosis happens in
the ovaries to create egg cells.
In males, meiosis happens in
the testes to make sperm cells.
Egg and sperm cells are called
gametes.
Meiosis Diagram
-The parent cell is diploid (2n) and has 2
of each chromosome.
-After the DNA duplicates and the
chromosomes are X shaped, the cell is
still considered diploid.
-The parent cell divides and one
chromosome from each pair goes to
each cell. The daughter cells are now
haploid, but the chromosomes are still in
duplicate form, so they are still Xshaped.
-Each haploid (n) cell divides into 2
daughter cells that are also haploid (the
duplicated X shaped chromosomes
separate into I shaped chromosomes)
Filling in the Diagram
(write this in your notes)
In humans, this is the number
of chromosomes in each cell
during meiosis.
So what about frogs? Frogs are
diploid and have 26
chromosomes in their somatic
cells.
Copy this meiosis diagram for
Sparky.
Check for Understanding
Copy this meiosis
diagram for coyotes.
Coyotes are diploid
and have 76
chromosomes in their
somatic cells.
Check for Understanding
If a human somatic cell has 46 chromosomes,
how many chromosomes would there be in a
human cell after meiosis?
If a goat gamete produced during meiosis has
30 chromosomes, how many chromosomes
would a goat skin cell have? Assume goats are
diploid.