1
Objectives
By the end of today’s lesson, you will be able to:
• Define mitosis and meiosis
• Distinguish the differences between the cell division processes
• Recognize the cellular activity that takes place in the various
phases of each
2
Cell Reproduction
3
Cell Cycle
4
Mitosis: Asexual Reproduction
5
Mitosis: Asexual Reproduction
6
Diploid Cells
Most plant cells are “diploid” – which
means their chromosomes are paired.
Diploid = two identical sets of
chromosomes
For example:
• A soybean plant has 40 chromosomes
(20 pairs)
• A corn plant has 20 chromosomes
(10 pairs)
Think of Mitosis as “Mi-two-sis”
Mitosis: Asexual Reproduction
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
4. Telophase
8
3. Anaphase
Purpose of Mitosis
Asexual cell reproduction in living organisms
Replicated chromosomes are
divided into two identical cells
Three Minute Checkup
Label the flowchart using the terms below.
(1)
(2)
(6)
(3)
(4)
(5)
10
parental cell
daughter cells
Metaphase
Prophase
Telophase
Anaphase
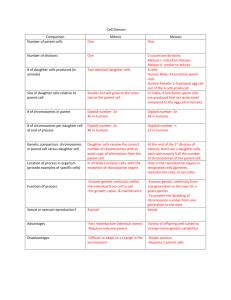
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Mitosis:
Meiosis:
• Involves the division of one
• Involves the division of two
parental cell
parental cells
• Produces two identical cells
• Produces gametes (sex cells)
• Involves diploid cells (2N) with • Involves haploid cells (N)
two sets of chromosomes
with one set of chromosomes
11
Meiosis Cellular Division
During meiosis, the parental cell
(or nucleus) will divide twice.
As a result, each of these cells,
will have only half the number of
chromosomes, but each
chromosome will contain genetic
information from both parents.
Meiosis – A Two Phase Process
Meiosis is a two phase process:
Meiosis I – Involves the phases of Prophase I, Metaphase I,
Anaphase I, and Telophase I. It is a reduction division,
in which each progeny cell has two chromosomes and
two sister chromatids.
Meiosis II – Involves Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and
Telophase II. It is a normal mitotic division, in which
the sister chromatids are separated and the number
of chromosomes remain constant.
13
Meiosis I
Prophase I
14
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Meiosis II
Prophase II
15
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Purpose of Meiosis
Sexual cell reproduction in multi-cell organisms
Three Minute Checkup
Mitosis
Meiosis
1.
Produces cells for growth and repair
2.
One nuclear division
3.
Four daughter cells produced
4.
Produces cells for growth & repair
5.
Daughter cells haploid
6.
Two nuclear divisions
7.
Two daughter cells produced
8.
Produces sex cells
9. Daughter cells are genetically identical to
the parental cell
10. Daughter cells diploid
11. Daughter cells have only half the genes
from the parental cell
17
Summary
Mitosis
18
Meiosis
Produces cells for growth and
repair
“Gametes” or sex cells produced
for sexual reproduction
One nuclear division
Two nuclear divisions
Two daughter cells produced
Four daughter cells produced
Daughter cells diploid (2N)
Daughter cells haploid (N)
Daughter cells have two sets
(pairs) of chromosomes
Daughter cells have one member
of each pair of chromosomes
Daughter cells are genetically
identical to the parent
Daughter cells are genetically
diverse
Occurs in all organisms
Occurs in humans, animals, plants,
and fungi
Questions
19