Chapter 11-4: Meiosis
Production of Sex Cells
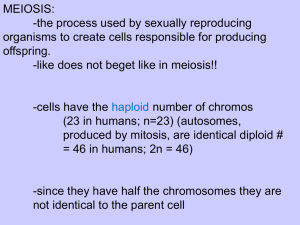
Introduction
• Mitosis and Meiosis are somewhat similar,
but have 2 completely different goals.
• Mitosis used in growth, healing, and
reproduction in unicellular organisms.
Whereas, Meiosis is SOLELY used for the
production of gametes (sex) cells in
multicellular organisms.
Mitosis
Process:
1 round of
division.
Start: 2n
End
Result:
2 identical
daughter
cells
Finish: 2n
VS.
M
Meiosis
Process:
2 rounds of
division
Start: 2n
End result:
4 genetically
different
daughter cells
Finish: n
•Humans have two full
sets of chromosomes
•(one set from our male
parent and one from our
female parent.)
•Each pair of chromosomes are known as
“homologous” because they share the same genes,
but likely very different alleles.
Ploidy: How many sets of chromosomes an
organism has.
•Because we
(humans) have two
complete sets of
chromosomes, we are
said to be diploid.
Homologous pair
Ploidy
The diploid number
is referred to as 2N.
For humans, 2N =
46.
Each human
somatic or body cell
contains 46
chromosomes.
Human Karyotype
Ploidy
Each human gamete
or sex cell only has
a single set of
chromosomes and
are referred to as
haploids.
Human Karyotype
For our sperm or eggs, the haploid number is 23.
n
23 (sperm and eggs)
________
= _______
2n = _______
46 (every other cell in our body)
________
Image by Riedell
Image by Riedell
n
n
EGG
haploid
+
http://www.angelbabygifts.com/
2n
SPERM
haploid
diploid
http://www.acmecompany.com/stock_thumbnails/13217.forty-six_chromosomes.jpg
The Process of Meiosis - click
How are haploid (N) gamete cells produced from diploid (2N)
cells?
Meiosis is a process of reduction and division in which
the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through
the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid
cell.
Watch
carefully!
Diploid
number?
4 chromosomes
Homologous
pairs?
2 pairs
http://www.tokyo-med.ac.jp/genet/anm/mimov.gi
By the end of G2,
meiosis is ready to
begin.
End of Meiosis I:
If female – the process pauses here until the menstrual cycle
begins during puberty. Once a month, one egg is released and may
entire Meiosis II if fertilized.
If male – the process does not pause, it goes right into Meiosis II.
No time wasted to make sperm!!
Notice how meiosis differs between males and
females.
Spermatogenesis: Creates 4
genetically different sperm
• Occurs in
testes
• Prompted
by
testostero
ne
• Creates 4
cells
Notice how meiosis differs between males and
females.
Oogenesis: Creates 1 viable
egg and 3 polar bodies that
are digested by lysosomes.
• Occurs in
ovaries
• Born with a
finite number
of primary
oocytes
• Creates 1 egg
and 3 polar
bodies
Mitosis resulted
in the
production of
two genetically
identical diploid
cells, whereas
meiosis
produces four
genetically
different haploid
cells.
Summary of MITOSIS: (Genetically Identical)
Mitosis allows an organism's body to grow and replace cells.
In asexual reproduction, a new organism is produced by
mitosis of the cell or cells of the parent organism.
Summary of MEIOSIS: (Genetically Different)
A diploid cell but produces four haploid (N) cells.
These cells are genetically different from the diploid
cell and from one another.
Meiosis is how sexually reproducing organisms
produce gametes.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=6z3tafuoN0k National
Geographic in the womb. Start
at 5:30
Image by Riedell
Image by Riedell
n
_
EGG
haploid
+
http://www.angelbabygifts.com/
__
SPERM
________
diploid