Radiation Interaction Q&A
advertisement

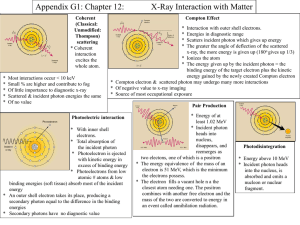
Radiation Interaction Q&A Robert Metzger, Ph.D. RAPHEX General Question 2001 G56: The fractional number of photons removed from a beam per cm of absorber is called the _______. A. Linear attenuation coefficient B. Mass absorption coefficient C. Scatter coefficient D. Mean attenuation length RAPHEX Answer for 2001 Question G56 A. Linear attenuation coefficient. The mass energy absorption coefficient is the linear attenuation coefficient divided by the density (i.e., attenuation per unit mass rather than per cm.) The mean attenuation length is the linear attenuation coefficient X 1.44. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G50: The mass attenuation coefficients for most materials (except hydrogen) are similar when________ interactions predominate. A. Photoelectric B. Compton C. Pair Production D. Photonuclear disintegration RAPHEX Answer for 2003 Question G50 B. Compton The mass attenuation coefficient is similar for most materials in the Compton region, except those containing hydrogen. This is because most materials have approximately one electron per two nucleons (one proton and one neutron), while hydrogen has one electron per nucleon, or twice the number of electrons per unit mass as most other elements. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G52: The process whereby energy is transferred from a photon beam to electrons in the medium is called ______. A. Electron capture B. Absorption C. Bremsstrahlung D. Scatter RAPHEX Answer for 2003 Question G52 B. Absorption. In the interaction of radiation with matter, energy is generally transferred to electrons and photons. The energy reemitted as photons is called “scatter”. The energy transferred to electrons is called “absorbed dose” and is dissipated locally in collisions with atoms. RAPHEX General Question 2001 G60: A photoelectric interaction occurs between an 8 keV photon and a K shell electron. A 3.6 keV photoelectron is emitted. The binding energy of the K shell is ________ keV. A. 3.6 B. 4.0 C. 4.4 D. 8.0 E. 11.6 RAPHEX Answer for 2001 General Question G60 C. 4.4 The energy of the photon is totally absorbed by the electron, which uses 4.4 keV to overcome its binding energy, leaving 3.6 keV as the energy of the emitted photoelectron. RAPHEX General Question 2002 G57: At x-ray energies between 40 and 100 keV, ________ absorbs more energy than ________ per gram. A. fat, muscle B. muscle, bone C. iodine, bone D. fat, air E. air, muscle RAPHEX Answer for 2002 General Question G57 C. Iodine, bone. The absorbed dose per unit exposure is called the f-factor, and depends on both Z and the photon energy. f factors listed from lowers to highest are: fat, air, muscle, bone, and iodine. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G63: In diagnostic x-ray systems, filters are used to “harden” the beam. This process is mainly due to: A. Coherent scattering. B. Photoelectric effect. C. Compton effect. D. Pair production. E. A, B, and C only. RAPHEX Answer for 2003 General Question G63 B. Photoelectric Effect With the exception of the K edges, photoelectric interaction are more likely at low energy than at high energy. After passing through a filter, the total beam intensity is reduced, but the beam contains a relatively greater number of high-energy photons than before filtration. RAPHEX General Question 2002 G59: The ratio of the number of Compton interactions in one gram of calcium to one gram of carbon is about ________ . A. 2:1 B. 1:1 C. 1:2 D. It depends on the photon energy E. In the ratio of their densities RAPHEX Answer for 2002 General Question G59 B. 1:1 The number of Compton interactions depends on the number of electrons. Most materials have about the same number of electrons per gram. (An exception to this is hydrogen, which has twice as many electrons as it has no neutrons in the nucleus.) RAPHEX General Question 2003 G56: if a technologist were to stand 2 m away from a patient during fluoroscopy (outside the primary beam) the dose received by the technologist would be mainly due to: A. Compton electrons. B. Photoelectrons. C. Compton scattered photons. D. Characteristic x-rays generated in the patient. E. Coherent scatter. RAPHEX Answer for 2003 General Question G56 C. Compton scattered photons Even at low KV, coherent scatter contributes only a small part of the total scatter. The characteristic x-rays created by photoelectric interactions within the patient are of very low energy (because of the low Z of tissue) and have extremely small range. Compton and photoelectrons also have a short range and are unlikely to leave the patient’s body. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G58: The probability, per gram, of a Compton interaction: A. Increases as energy increases. B. Is independent of energy. C. Is proportional to E2Z2 D. Is proportional to Z3E-3 E. None of the above. RAPHEX Answer for 2003 General Question G58 E. None of the above. Compton interactions, per unit mass, are approximately independent of Z, and decrease with increasing energy. RAPHEX General Question 2001 G63: Concerning pair production, which of the following is true? A. Photons can be backscattered. B. The electron acquires most energy when it is scattered forward. C. Compton electrons can be backscattered. D. Any dose measured at a diagnostic x-ray operator’s console would be due to Compton scattered photons. RAPHEX Answer for 2001 General Question G63 B. The electron acquires most energy when it is scattered. The threshold energy for pair production is 2 mec2 = 1.02 MeV. The electron and the positron share the photon energy less 1.02 MeV. When the positron loses its kinetic energy and annihilates with an electron, two 0.51 MeV photons are emitted in opposite directions. RAPHEX General Question 2002 G63: In pair production, which of the following is true? A. The incident photon is scattered with reduced energy B. Annihilation photons always have an energy of 0.51 MeV each C. A pair of orbital electrons are ejected from the atom D. Two positrons are emitted at 180 degrees E. It cannot occur if the photon energy is above 1.02 MeV RAPHEX Answer for 2002 Question G63 B. Annihilation photons always have an energy of 0.51 each. Annihilation photons have an energy equal to the rest energy of the positron and electron. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G61: After a 1.5 MeV photon undergoes pair production, production of ____ will always occur. A. A pair of 0.51 MeV photons B. A pair of 0.51 MeV positrons C. A pair of 0.51 MeV electrons D. A single 0.51 MeV photon E. An electrons a positron, each with kinetic energy 0.51 MeV RAPHEX Answer for 2003 Question G61 A. A pair of 0.51 MeV photons It takes 2 X 0.51 MeV to create the electronpositron pair. The remaining 1.28 MeV is divided between the two particles as kinetic energy. This kinetic energy is deposited locally and when the positron and an electron combine and annihilate, two 0.51 MeV phtons are emitted. RAPHEX General Question 2002 A. B. C. D. E. G67-G68: Match the type of interaction mainly responsible for the effect: Compton scattered photons Compton electrons Pair production Photoelectric interaction Photo-nuclear disintegration G67: Differential absorption in diagnostic radiographs G68: Loss of contrast in a lateral pelvic radiograph of a large patient. RAPHEX Answer for 2002 General Questions G67-G68 G67: D. Photoelectric interaction. This is due to the Z3 dependence of the photoelectric interaction G68: A. Compton scattered photons. The use of high ratio grids and limiting the field size will help to reduce the unwanted Comptonscattered photons, which degrade contrast in the image RAPHEX General Question 2002 G69: PET scan images are created by detecting: A. Positrons emitted from the region of uptake B. Annihilation photons C. Protons emitted from the region of uptake D. The paths of the positrons traveling through tissue RAPHEX Answer for 2002 Question G69 B. Annihilation photons PET (Positron Emission Tomography) relies on coincidence counting of the annihilation photons that are emitted at 180 degrees from the point where a positron and electron annihilate. The positron emitter is labeled to a substance which is taken up by, or metabolized by, the tissue to be imaged. RAPHEX General Question 2001 G64-G69: Match the most appropriate interaction to the description (answers may be used more than once) A. B. C. D. Coherent scatter Photoelectric Compton Pair production G64: Chiefly responsible for loss of contrast in diagnostic radiograph G65: Most probably at photon energies between 100 keV and 2MeV G66: No energy is transferred or locally absorbed G67: Probability of interaction, per unit mass, does not dpend on Z G68: Involves “bound” electrons G69: Increases with increasing photon energy RAPHEX Answer for 2001 Questions G64-G69 G64: C. Compton scattered photons decrease the contrast by increasing the level of background fog G65: D. Compton is actually most probably for monoenergetic photon energies between 25 kV and 25MV G66: A. Coherent scatter (also known as Raleigh or unmodified scatter) occurs only at very low photon energy, and is of little concern in radiology G67: C. The probability of a Compton interaction depends on the number of electrons per gram, which is roughly the same for all elements except hydrogen G68: B. G69: D. RAPHEX General Question 2001 G70: Which type of nuclear radiation has the shortest range in tissue? (assume equal energy) A. Gamma rays B. Betas C. Neutrinos D. Alphas E. Neutrons RAPHEX Answer for 2001 Question G70 D. Alphas Alphas have the highest linear energy transfer (LET) because of the their larger mass and charge. RAPHEX General Question 2002 G11: Directly ionizing radiation includes all of the following EXCEPT: A. Electrons B. Positrons C. Alpha particles D. Neutrons E. Betas RAPHEX Answer to 2002 Question G11 D. Neutrons Neutrons are not charged particles and, therefore, cannot ionize atoms directly. However, they transfer some of their energy to protons or light nuclei, which then cause ionization. Thus they are indirectly ionizing. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G67: An electron, proton, and an alpha particle each have 20 MeV kinetic energy. Which of the following statements is true? A. The alpha particle travels at almost the speed of light B. The alpha particle has the least total energy C. The proton has the highest total energy D. The electron travels almost the speed of light E. None of the above RAPHEX Answer to 2003 Question G67 D. The proton has the highest total energy The electron’s rest mass is low compared to its kinetic energy so it must be traveling at nearly the speed of light. The alpha particle has the greatest total energy. RAPHEX General Question 2003 G68: When protons interact with soft tissue, all of the following are true EXCEPT: A. Linear energy transfer (LET) increases towards the end of the proton track B. Protons have a finite range C. Protons undergo exponential attenuation D. The proton track ends in a “Bragg Peak”. RAPHEX Answer to 2003 Question G68 C. Protons undergo exponential attenuation Protons, like all charged particles, have a finite range; photons are attenuated exponentially RAPHEX General Question 2001 G71: Concerning neutron interactions with matter, which of the following is FALSE? The neutron: A. May remain in the target nucleus B. Interacts primarily with the oxygen in H20 C. May cause the ejection of an alpha particle D. May induce radioactivity in the target nucleus E. May transfer a large traction of its energy in the process of elastic scattering RAPHEX General Question 2002 G72: Neutrons have a higher Quality Factor than electrons because: A. They transfer energy to protons which have a high LET B. They slow down in tissue, and deposit a lot of energy at the ends of their tracks C. They have a large mass and charge D. They are directly ionizing RAPHEX Answer for 2002 Question G72 A. They transfer energy to protons which have a high LET. Neutrons are indirectly ionizing. They transfer energy to protons, which have a large mass, and are densely ionizing, especially at the end of their track (the “Bragg Peak”) RAPHEX Diagnostic Question 2002 D2-D5: Select the interaction that predominates in the following situations: A. Compton Scattering B. Photoelectric interaction C. Pair production D. None of the above D2: 30 kVp, adipose tissue D3: 90 kVp, muscle D4: 90 kVp, iodine contrast D5: 90 kVp, LaOBr Intensifying screen RAPHEX Answer to 2002 Question D2-D5 D2: B. Photoelectric interaction. Photoelectric interaction predominate in tissue below 30 keV, which is equivalent to a kVp of about 60-90 kVp. D3: A. Compton Scattering. Compton scatter predominates above about 90 kVp (30 keV) in muscle. D4: B. Photoelectric interaction. The probability of of photoelectric inteardtion is proportional to Z-3. Therefore photoelectric interactions predominate at all diagnostic energies for iodine. D5: B. Photoelectric interaction. The K-edge is the reason rare earth screen have a high absorption efficiency. RAPHEX Diagnostic Question 2001 D3: Carbon dioxide can be used as an angiographic contrast medium because: A. The K absorption edges of CO2 are significantly higher than tissue B. The K absorption edges of CO2 are significantly lower than tissue C. The linear attenuation coefficient of CO2 is significantly higher than tissue D. The linear attenuation coefficient of CO2 is significantly lower than tissue E. Of differences between the mass attenuation coefficients RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D3 D. The linear attenuation coefficient of CO2 is significantly lower than tissue. This is because the physical density is much less. The mass absorption coefficients (attenuation per gram) and K edges are very similar.