Flip-Flops: Basic Concepts & Types - Digital Electronics
advertisement

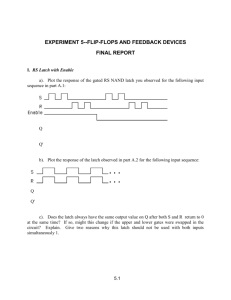
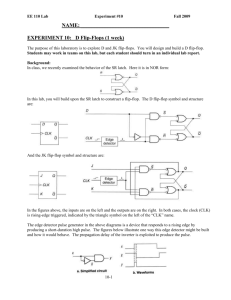
Flip-Flops Basic concepts Flip-Flops A flip-flop is a bi-stable device: a circuit having 2 stable conditions (0 or 1) 3 classes of flip-flops 1/50 latches: outputs respond immediately while enabled (no timing control) pulse-triggered flip-flops: outputs response to the triggering pulse edge-triggered flip-flops: outputs responses to the control input edge A. Yaicharoen 2 Conventions The circuit is set means output = 1 The circuit is reset means output = 0 Flip-flops have two output Q and Q’ or (Q and Q) Due to time related characteristic of the flipflop, Q and Q’ (or Q) are usually represented as followed: 1/50 Qt or Q: present state Qt+1 or Q+: next state A. Yaicharoen 3 4 Types of Flip-Flops SR flip-flop JK flip-flop S R Qt+1 Q’t+1 J K Qt+1 Q’t+1 0 0 Qt Q’t 0 0 Qt Q’t 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 Prohibited 1 1 Q’t Qt D flip-flop 1/50 T flip-flop D Qt+1 Q’t+1 T Qt+1 Q’t+1 0 0 1 0 Qt Q’t 1 1 0 1 Q’t Qt A. Yaicharoen 4 SR Latch An SR (or set-reset) latch consists of S (set) input: set the circuit R (reset) input: reset the circuit Q and Q’ output: output of the SR latch in normal and complement form S R Qt+1 Q’t+1 0 0 Qt Q’t 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 Prohibited Application example: a switch debouncer 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 5 SR latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 6 An application of the SR latch (a) Effects of contact bounce. (b) A switch debouncer. 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 7 S R latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 8 Gated SR latch (c) 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 9 Gated D latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 10 Timing Consideration When using a real flip-flop, the following information is needed to be considered: 1/50 propagation delay (tpLH, tpHL) - time needed for an input signal to produce an output signal minimum pulse width (tw(min)) - minimum amount of time a signal must be applied setup and hold time (tsu, th) - minimum time the input signal must be held fixed before and after the latching action A. Yaicharoen 11 Propagation delays in an SR latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 12 Timing diagram for an SR latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 13 Minimum pulse width constraint 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 14 Timing diagram for a gated D latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 15 Unpredictable response in a gated D latch 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 16 Master-slave SR flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 17 Timing diagram for a master-slave SR flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 18 Master-slave JK flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 19 Timing diagram for master-slave JK flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 20 Master-slave D flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 21 Master-slave T flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 22 Positive-edge-triggered D flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 23 Timing diagram for a positive-edge-triggered D flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 24 Negative-edge-triggered D flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 25 Asynchronous Inputs do not require the presence of a control signal 1/50 preset (PR) - set the flip-flop clear (CLR) - reset the flip-flop useful to bring a flip-flop to a desired initial state A. Yaicharoen 26 Positive-edge-triggered D flip-flop with asynchronous inputs 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 27 Positive-edge-triggered JK flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 28 Positive-edge-triggered T flip-flop 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 29 Master-slave JK flip-flop with data lockout 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 30 Characteristic Equations 1/50 algebraic descriptions of the next-state table of a flip-flop constructing from the Karnaugh map for Qt+1 in terms of the present state and input A. Yaicharoen 31 Characteristic equations 1/50 A. Yaicharoen 32