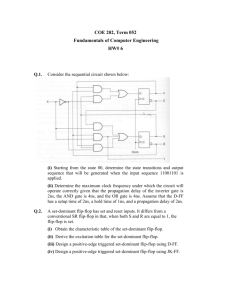
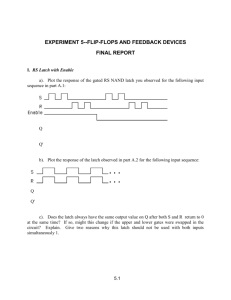
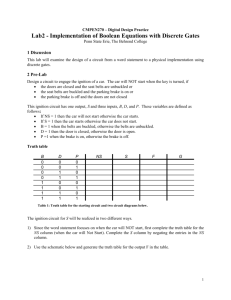
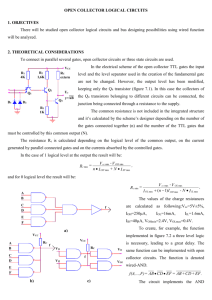
on Logic Design (from your textbook)
advertisement
Appendix A Logic Circuits Logic circuits • Operate on binary variables that assume one of two distinct values, usually called 0 and 1 • Implement functions of logic variables • Circuits have inputs and outputs • Circuits are implemented using electronic logic gates Standard logic gate symbols Implementation of the XOR function using AND, OR, and NOT gates Synthesis of logic functions Synthesis is the process of designing and implementing a logic circuit defined by its functional specification. The expression for f in the previous circuit is said to be in a sum-of-products form, because the OR and AND operations are sometimes called the sum and product functions. Implementation of a logic function Proving equivalence of expressions Rules of binary logic Minimization of logic expressions As illustrated in the previous example, a logic function can be implemented with circuits of different complexities. It is useful to minimize a logic expression to reduce the cost of the synthesized circuit. Three-variable Karnaugh maps Four-variable Karnaugh maps Using don’t cares NAND and NOR gates Equivalence of NAND-NAND and AND-OR networks Cascading of gates Representation of logic values by voltage levels Tri-state buffer A basic latch implemented with NOR gates Gated SR latch Gated SR latch implemented with NAND gates Gated D latch Master-slave D flip-flop A negative-edge-triggered D flip-flop T flip-flop JK flip-flop Master-slave D flip-flop with Preset and Clear Shift register Parallel-access shift register A 3-bit up-counter A two-input to four-output decoder A BCD-to-7-segment display decoder A four-input multiplexer Multiplexer implementation of a logic function A block diagram for a PLD Functional structure of a PLA A simplified sketch of the previous PLA An example of a PAL Inclusion of a flip-flop in a PAL element Organization of a CPLD A conceptual block diagram of an FPGA Sequential circuits A logic circuit whose output is determined entirely by its present inputs is called a combinational circuit (e.g. decoders and multiplexers). A logic circuit whose output depends on both the present inputs and the state of the circuit is called a sequential circuit (e.g. counters). State diagram of a mod-4 up/down counter that detects the count of 2 State table State assignment table The next-state expressions are: The output expression is Implementation of the up/down counter Timing diagram for the designed counter A formal model of a finite state machine