The Internet and Fiber Optics
advertisement
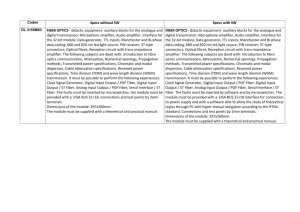
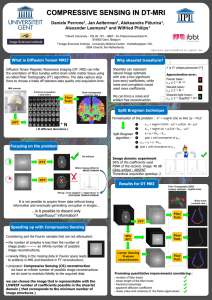
The Internet and Fiber Optics Key: AWL to Study, Low-frequency Vocabulary What is the connection between the Internet and fiber optics? The Internet • The Internet has been lauded as the greatest innovation of the 20th century. conceived by the US Federal Department of Defense grown into a global network revolutionized global communications, information access, and commercial transactions For what purposes do you use the Internet? A Complex System • Visual representation of the Internet resembles the human brain. • Allows for instantaneous communication • Provides instant information search engines and websites • Broadens social circles online forums and message boards How is the Internet like the human brain? Increasing Internet Speed • Fiber Optics is a data-delivery system. transmits light through glass fibers connects the developed world deployed in intercity and transoceanic communication delivers clear and secure signal delivers information 1000 times faster and 100 times farther than copper-wire technology Why do you think fiber optics is not used extensively within cities? How Fiber Optics Works • Light source adjacent to the fiber laser produces and digitally encodes signal light travels through core of glass mirrored layer reflects light off walls light moves through channel Using the diagram, explain how fiber optics works. Signal Loss • To make up for signal loss over distance laser amplifiers convert weakening signal into a stronger one. Upon reaching its destination, an optical receiver decodes the digital signal, so it can be read by a computer, TV, or telephone. Physical Constraints • Creating a fiber optic infrastructure in cities is difficult. need to distribute fibers to millions of users within one city • Fiber optics has been reserved until recently for long-distance applications. What is meant by the phrase “fiber optic infrastructure”? Telecommunications • Telecommunications companies solve “last-mile” connectivity problems by complementing fiber with existing copper-wire systems. To what does the phrase “‘last-mile’ connectivity problem” refer? Fiber-to-the-neighborhood • FTTN delivers fiber optic service to an area where cable or DSL copper-wire provides high-speed Internet. • Cable and DSL are intermediate measures. Bandwidth is inferior to fiber. They provide adequate service without huge undertaking of replacing and rerouting fiber to individual residences. Fiber Optics for the Future • Internet traffic is estimated to increase fifty-fold within next two years. • Light colors that can be routed through a fiber doubles every six to nine months. Bandwidth potential of fiber is limitless. 3-D virtual world applications will demand faster connection speeds. What kinds of 3-D computer applications do you know? Fiber-to-the-home • Asian countries have taken the lead with FTTH technology. • The not-so-distant future: FTTH will be the standard international medium of Internet connectivity. Why do you think Asian countries have taken the lead with FTTH?