Lecture 4 Techniques III
advertisement
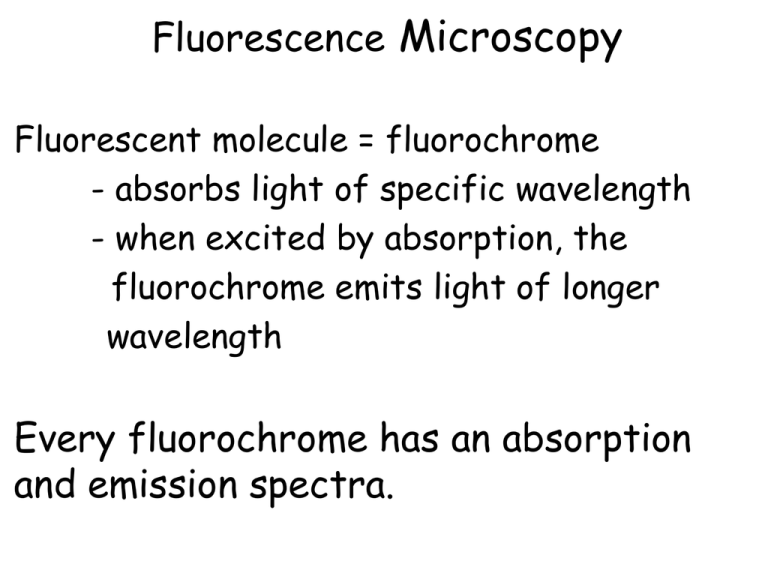
Fluorescence Microscopy Fluorescent molecule = fluorochrome - absorbs light of specific wavelength - when excited by absorption, the fluorochrome emits light of longer wavelength Every fluorochrome has an absorption and emission spectra. Fluorescence Microscopy Fluorochrome Structurally unstable when excited Fluorescence Microscopy EXCITATION SPECTRA EMISSION SPECTRA WAVELENGTH Fluorochrome DAPI FITC Rhodamine Fluorescence Microscopy SPECIMEN Components: Light source Excitation filter Emission filter Dichroic mirror -reflects short -passes long EYE PIECE Frog Neuromuscular Junction Texas RedAcetylated TUBULIN FITC ACTIN By Stephanie Moeckel-Cole Flurochromes can be used in combination to mark different structures and/or molecules. “Multicolor "DiOlistic" labeling of the nervous system using lipophilic dye combinations.” Gan WB, Grutzendler J, Wong WT, Wong RO, Lichtman JW. Labeled neurons in brain with different combination of fluorochromes. Fluorchromes: DiO DiI DiD FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY PROBLEM: Photobleaching (fading) Photobeaching: Fluorochrome loses ability to fluoresce, absorb and emit light, due to damage or covalent modification. http://microscopyu.com/articles/fluorescence/fluorescenceintro.html Fluorochrome PHOTOBLEACHING (a-f) Images collected at 2 minute intervals. http://microscopyu.com/articles/fluorescence/fluorescenceintro.html Quantum Dots : semiconductor nanoparticles, such as cadmium selenide, that emitted light after light excitation. Advantages: brighter, no photobleaching, broad excitation Disadvantages: potential toxicity for in vivo imaging Alivisatos et al.; Quantum dots as cellular probes.; Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2005;7:55-76. FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY PROBLEM: Image degradation (blurring effect) due to light scattering http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/confocal/confocalintrobasics.html CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY Light source: laser illumination with coherent light http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/optmod/qualig.html#c4 CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY Collects light from one plane of the sample at a time Excludes out of focus light scatter REGULAR FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE CONFOCAL MICRSCOPE CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY Collect series of images from different focal planes Can assemble the image series to yield a 3-d image Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Very thin section Beam of electrons (=0.005 nm) Electromagnetic lenses Stain with metals Stain: electron dense: dark Unstained: light Nerve- osmium=myelin http://www.utsa.edu/tsi/assign/histo/Images/histst1.gif www.itg.uiuc.edu/ms/techniques/ Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Surface structure Sectioning not required Metal coating of specimen Electron scattering Primary electrons Secondary electrons Detector http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/pt/diamond/jamespthesis/chapter2_files/image002.gif Ant Head Pollen FREEZE FRACTURE Purpose: to analyze the distribution and density of integral membrane proteins in cell membranes Freeze a fragment of tissue Fracture using a sharp metal blade -fracture plane passes through lipid bilayers of a cell membrane Observe with SEM FREEZE FRACTURE Cell Membrane: Lipid Bilayer EXTRACELLULAR SPACE CYTOPLASM FRACTURE EXTRACELLULAR SPACE CYTOPLASM FREEZE FRACTURE EXTRACELLULAR SPACE Cell Membrane CYTOPLASM P face: inner face of inner membrane. EXTRACELLULAR SPACE CYTOPLASM E face: inner face of the outer membrane. Intestinal Epithelium Microvilli Zonula adherens Neuromuscular Junction Synaptic site: Active Zone: release site of synaptic vesicles Heuser and Reese STAINING Histochemistry or Cytochemistry: dyes bind to certain types of molecules Charged dyes bind to molecules of opposite charge Charged dyes bind to molecules of opposite charge Acidic Dye ---> dye Eosin Extracellular fibers, cytoplasmic filaments, and others Basic Dye ---> dye + Toluidine Blue Alcian Blue Cresyl Violet Hematoxylin Nuclei acids, glycosaminoglycans, ribosomes Hematoxylin and Eosin Intestine Staining Techniques There are many dyes. http://medinfo.ufl.edu/~dental/denhisto/stains.html Examples: Sudan black -Lipids Myelinated axons- blue ihcworld.com/imagegallery/displayimage.php?al... Weigert Stain -Reticular fibers Staining Techniques Histochemical Stains: involve chemical reactions Feulgen reaction -DNA http://bioquantcom.bioquantusers.org/products.php?page=ls&content=gall ery&sub=feulgen Periodic Acid Shiff (PAS) -neutral and acidic polysaccharides - glycogen, mucous, basal laminae Intestinal Villus Goblet cells PAS stain Carbohydrate-rich Basal Laminae stain with PAS stain Staining Techniques Localization (staining) of an enzyme AB + T ENZYME AT + B provide substrate generate visible product Staining Techniques AB + T ACETYL CHOLINESTERASE AT + B Acetylcholinesterase- neuromuscular junction Other stains for ATPases, alkaline phosphatases, and others IMMUNOCYTOCHEMISTRY A technique to localize specific molecules in an organ, tissue or cell. First, a bit of immunology………. An organism creates antibodies to foreign molecules, ANTIGENS. An antigen may have different regions, EPITOPES, that are recognized as foreign by an organism. Polyclonal antibodies -A collection of distinct types of antibody molecules that recognize the same antigen (antibodies A + B + C) but often several different epitopes Monoclonal antibodies -A single type of antibody molecule that recognizes only one epitope on an antigen (antibody A OR B OR C)