LabVIEW in 3 Hours: Introduction to Virtual Instrumentation
advertisement

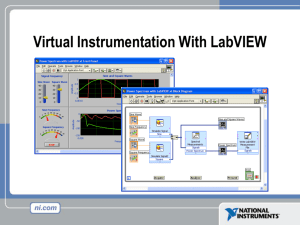
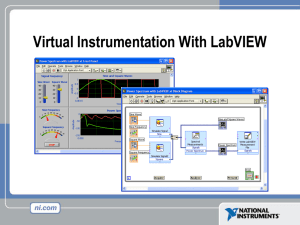
LabVIEW in 3 Hours What is Test & Measurement? Acoustic Quality Keypad Functionality Sound Quality RF Signal Analysis LCD Testing Battery Test EngineeringTelecom – Industries Manufacturing Electronics Automotive Test Industries Semiconductor Chemical Processing Aerospace Transportation Military Biomedical Instrumentation Instrumentation Data Acquisition Virtual Instrumentation Hardware and Driver Software Application Software Virtual Instrumentation Architecture LabVIEW Instrument / Data Acquisition Drivers GPIB/Serial and VXI Data Acquisition and Signal Conditioning Modular Instrumentation PXI/CompactPCI Vision Distributed I/O PLCs Section I – The LabVIEW Environment • LabVIEW terms • Components of a LabVIEW application • LabVIEW programming tools • Creating an application in LabVIEW LabVIEW Programs Are Called Virtual Instruments (VIs) LabVIEW Programs Are Called Virtual Instruments (VIs) 2 Work areas: 1. Front Panel Controls = Inputs to the computer LabVIEW Programs Are Called Virtual Instruments (VIs) 2 Work areas: 1. Front Panel Controls = Inputs to the computer Indicators = Outputs from the computer LabVIEW Programs Are Called Virtual Instruments (VIs) 2 Work areas: 1. Front Panel Controls = Inputs to the computer Indicators = Outputs from the computer 2. Block Diagram Instruction set for controls, indicators “Source Code” VI Front Panel Panel Toolbar Pull-down menu Boolean Control Double Indicator Waveform Graph VI Block Diagram Pull-down menu Thermometer Terminal Data Acquisition Function Temperature Indicator Delay While Loop Stop Loop Terminal Stop Button Terminal Controls and Functions Palettes Controls Palette Functions Palette (Front Panel Window) (Block Diagram Window) Graphical, floating palettes Used to place controls & indicators on the front panel, or to build the block diagram Tools Palette (Front Panel) Operating Tool Positioning/Resizing Tool Labeling Tool Coloring Tool Tools Palette (Block Diagram) Automatic Selection Operating Tool Wiring Tool Positioning/Resizing Tool Breakpoint Tool Labeling Tool Probe Tool Coloring Tool Status Toolbar Run Button Continuous Run Button Additional Buttons on the Diagram Toolbar Abort Execution Pause/Continue Button Text Settings Align Objects Distribute Objects Reorder Execution Highlighting Button Step Into Button Step Over Button Step Out Button Status Toolbar Run Button Continuous Run Button Additional Buttons on the Diagram Toolbar Abort Execution Pause/Continue Button Text Settings Align Objects Distribute Objects Reorder Execution Highlighting Button Step Into Button Step Over Button Step Out Button Open a Virtual Instrument Basic Spectral Measurement.vi Template Browser Create a New VI Creating a VI – Front Panel Front Panel Window Creating a VI – Front Panel Front Panel Window Creating a VI – Block Diagram Front Panel Window Block Diagram LabVIEW’s Context Help Creating a VI – Adding Functions Creating a VI – Adding Functions Creating a VI – Wiring Wire attachment points (nodes) flash when the wiring tool is passed over Right Click wiring tool Node Terminals (communication ports) Creating a VI – Adding Functions Creating a VI – Adding Functions Express Functions Same overall functionality Section II • What is a subVI? • Creating a subVI • Using a VI as a subVI SubVIs LabVIEW is modular • Any VI can be used as a subroutine (or subVI) to other programs • Advantages – Modular – Easier to debug – Don’t have to recreate code Creating a SubVI 1. 2. 3. Create code Select code for use in subVI Click Edit-Create subVI Editing a SubVI Insert the SubVI into a Top Level VI Accessing user-made subVIs Functions >> Select a VI Or Drag icon onto target diagram Create SubVI from your code View your subVI Section III – Data Acquisition • Data acquisition (DAQ) basics • Connecting Signals • Simple DAQ application DAQ – Data Acquisition • Plug-in board for a computer with: – Analog input channels – Analog output channels – Counters – Digital I/O • Controlled by a suite of LabVIEW VIs Functions>>Data Acquisition DAQ – Data Acquisition Hardware Connections BNC-2120 SC-2075 SCB-68 Channel Connections Motor Signal Single-Ended Ground Battery Measurement + Signal 1 Differential - Signal 2 Measurement Analog Signals Data Acquisition System 1.659487387 volts ADC 1010100111110 Digital Signals Measurement & Automation Explorer Channel Connections • Single-Ended Mode: ACHx and AIGND used to connect signal to channel x • Differential Mode: ACHx, ACHx+8 used to connect signal to channel x Section IV – Loops and Charts • For Loop • While Loop • Charts • Graphs Loops • While Loops – Terminated by condition – Always Runs Once – Delay between iterations may be added • For Loops – Terminate after N iterations – N specified on block diagram Loops (cont.) 1. Select the loop 2. Enclose Code to Repeat While Loop Charts and Graphs •Waveform Charts display a history of values over time - Strip Chart (continuous scrolling) - Scope Chart (repeatedly redraws over the same region) - Sweep Chart (redraws curve to the right of the old curve) •Waveform Graphs and X-Y Graphs - Wavefrom Graphs plot Y for regular increments of X - X-Y Graphs plot Y vs. X for any X-Y sets (non-regular) Charts Waveform chart – special numeric indicator that can display a history of values Controls >> Graphs >> Waveform Chart Wiring Data into Charts Single Plot Charts Multiplot Charts Combining data onto one graph File I/O Using The LVM Express Function File I/O Using Traditional Functions Easy File I/O VIs •Read/write to spreadsheet file •Read/write characters to file (ASCII) •Read lines from file •Read/write binary file Conclusion • See www.ni.com for more help, examples