TOBACCO
advertisement

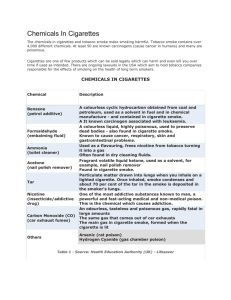
Six types of tobacco products Cigarettes Chew Snuff Pipe Cigars Clove/herbal Cigarettes Nicotine Addictive ingredient in tobacco Low doses-mild stimulant and muscle relaxant Higher doses-powerful nerve poison 60 mg of nicotine are enough to kill most people. 1 or 2 mg are inhaled when a cigarette is smoked. TAR Thick, black substance in tobacco smoke. Coats inside of airways Contains many carcinogens Chemicals 4000 chemicals in cigarette smoke 40 of the chemicals are carcinogens (chemical agents that cause cancer) Six of the dangerous chemicals found in tobacco smoke Cyanide-poisonous gas used to develop photographs Formaldehyde-substance used to preserve laboratory animals and as embalming fluid Lead-dangerous metal Continued: Vinyl chloride-flammable gas used to make plastic products Carbon monoxide-gas that blocks oxygen from getting into the bloodstream Ammonia-chemical found in bathroom cleaners Smokeless Tobacco Snuff Chewing tobacco They contain: nicotine, tar, arsenic, nickel, benzopyrene, polonium They lead to mouth sores, mouth cancer Leukoplakia Black Hairy Tongue Short term effects (1 second for inhaled nicotine to get into the bloodstream) Stimulates brain reward system Increases heart rate and blood pressure Increases breathing rate Increases blood sugar levels Stimulates the vomit reflex Long term effects 1. Addiction-changes the way the brain reward system functions 2. Bronchitis-paralyzes then kills cilia so mucus builds up in lungs 3. Emphysema-air cannot move in and out of the lungs because alveoli are damaged 4. Heart and Artery Disease Nicotine increases heart rate, narrows blood vessels and eventually causes arteries to become hardened and clogged Nearly 170,000 die yearly Healthy Unhealthy 5. Cancer Types that can be caused from tobacco: Lung, Pancreas, Bladder, Cervix, Kidney, Oral, and Throat Lung cancer often spreads to other parts of the body; leading cancer killer 6. Immune System Suppression Reduces the activity of immune system Leads to susceptibility to disease 7. Other Excess stomach acid build up Damage to stomach and small intestines Stains on fingers and teeth Mouth sores Odor and tar film on clothes Dulls senses of smell and taste Effects of Smoke on Nonsmokers Sidestream smoke - smoke that escapes from the tip of a cigarette, cigar, or pipe Mainstream smoke - smoke that is inhaled through a tobacco product and exhaled by a tobacco smoker Environmental tobacco smoke (second hand smoke) - both of the above Dangers of Second hand smoke Lung cancer-for every 8 smokers killed by their own smoking, 1 nonsmoker is killed by exposure Headaches, nausea, dizziness, reduced heart functions, asthma Smoking during Pregnancy Chemicals pass through placenta to fetus and affect fetus the same way they affect the mother Can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, low birth weight Baby at risk for SIDS Can affect fetus brain development May be addicted to nicotine at birth Tobacco and Family Over $1,500 per year for buying tobacco products Lost wages due to illness Medical bills Funeral costs (20% of premature deaths in the US are caused by tobacco use Tobacco and Society Estimated $138 billion per year (related to medical care that cannot be paid) Insurance costs go up Accidental fires Law Cannot sell to anyone under 18