Tobacco and Alcohol tobacco_and_alcohol
advertisement

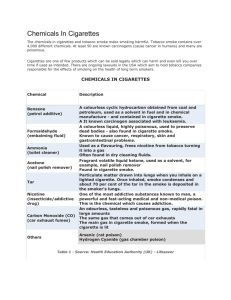
Smoking is the leading preventable cause of death in the USA Smoking causes more ill health than any other single behavior or combination of behaviors Teens Look mature Be like their friends Experiment Adults Stress & pressure Control their weight (7 pounds less then non- smokers) Made from dried tobacco leaves, as well as ingredients added for flavor and other reasons Chemicals, chemicals chemicals 60 chemicals known to cause cancer (carcinogens). Nicotine The predominant psychoactive drug present The addictive agent in tobacco • Tobacco use is psychological and physical dependence on nicotine Must keep a continuous amount in the blood and going to the brain If that amount falls below a certain level, they experience withdrawal symptoms Made up of several hundred different chemicals Just some chemicals in tobacco smoke: Benzene (found in gasoline) Butane( used in lighter fluid) Ammonia (used in household cleaners) Toluene (found in paint thinners) Cadmium (used in making batteries) Hydrogen cyanide (used in making chemical weapons) Tar Carbon monoxide Heart disease and stroke Coronary heart disease (2-4 x’s more likely) Doubles risk of stroke Reduces circulation by narrowing the blood vessels Increase risk of cancer 23 times more likely to develop lung cancer then a person who doesn’t smoke Cancer of the lip, oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, pancreas, larynx (voice box), uterine cervix, urinary bladder, and kidney Affects skin smokers have paler skin and more wrinkles. This is because smoking reduces the blood supply • Stains teeth and gums Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease conditions that block airflow and make breathing more difficult Examples: emphysema, chronic bronchitis • Breathing in smoke that comes from burning tobacco Two different types of secondhand smoke Sidestream smoke – the smoke that comes from the end of a lighted cigarette, pipe, or cigar Mainstream smoke- the smoke that is exhaled by a smoker Exposure to second hand smoke increase their heart disease risk by 25-30% Lung cancer risk by 20-30% Increase chances of heart attacks Tobacco that isn’t smoked Two types of smokeless tobacco chewing tobacco snuff Cancer Cancer of the oral cavity Oral health Leukoplakia- precancerous lesion of the soft tissue in the mouth that consists of a white patch or plaque that cannot be scraped Recession of gums, gum disease, and tooth decay • Reproductive Reduce sperm count and abnormal sperm cells Causes health problems for both mothers and babies, such as: Pregnancy complications Premature birth Low-birth-weight infants Stillbirth Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) Curiosity To feel good, reduce stress, and relax To fit in To feel older Yes, it is a drug. It’s a depressant central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) Ethyl alcohol is the psychoactive ingredient present in alcoholic drinks Grains, fruits, or vegetables Beer Wine Liquor Absorbed by the stomach, enters the bloodstream and goes to all the tissues Blood alcohol content (BAC) Percentage of alcohol in the blood For instance, a BAC of 0.10 means that 0.10% (one tenth of one percent) of a person's blood, by volume, is alcohol. Binge drinking For women, 4 or more drinks during a single occasion. For men, 5 or more drinks during a single occasion. Heavy drinking For women, more than 1 drink per day on average. For men, more than 2 drinks per day on average Person's size Weight Age Sex Amount of food consumed Depressant Slows function of central nervous system • Alters a persons perceptions, emotions, movement, vision, and hearing • Feel more relaxed or less anxious • Low doses of alcohol Impairs judgment Impairs coordination High doses of alcohol Dizziness Talkativeness Slurred speech Disturbed sleep Nausea Vomiting Hangovers Headache, nausea, thirst, dizziness, fatigue High Doses of alcohol Decreased heart rate Slower respiration Loss of taste and smell Inability to feel pain Short-attention span Memory problems Sexual dysfunction (loss of sensation, temporary impotence) Vision problems (light sensitivity, color impairment, blurred vision) Unintentional injuries, including traffic injuries, falls, drownings, burns, and unintentional firearm injuries. Risky sexual behaviors, including unprotected sex, sex with multiple partners, and increased risk of sexual assault. These behaviors can result in unintended pregnancy or sexually transmitted diseases. Alcohol poisoning The body has become poisoned by large amounts of alcohol Symptoms of alcohol poisoning: Violent vomiting Extreme sleepiness Unconsciousness Difficulty breathing Seizures • May lead to death, call for help Liver disease Cirrhosis- slowly deteriorates; scar tissue replaces regular tissue blocking partially blocking the blood through the liver Alcoholic hepatitis- inflammation of the liver Heart disease Cancer Mouth, throat, esophagus, liver, colon, and breast Pancreatitis Neurological problems Dementia Stroke Alcoholism- physical addiction to alcohol and continues to drink, despite problems with physical health, mental health, and social, family, or job responsibilities. Alcohol may control your life and relationships Alcohol abuse- drinking leads to problems, but not physical addiction Mild to moderate symptoms swift changes in emotions from high to low nausea difficulty sleeping including insomnia rapid or increased heart rate cold or clammy skin change in eyes or pupils (enlarged or dilated) excitability irritability vomiting movements out of the ordinary nervousness depression hand tremors pulsating headaches lack of focus and the inability to think straight fatigue anxiety pale skin twitchy eyes nightmares. excessive irritability blackouts extreme anxiety convulsions increased depression muscle tremors visual hallucinations more extreme changes in fever emotions and mood swings seizures difficulty in thinking clearly is increased severe autonomic nervous system overactivity Almost 80% of high school students have tried alcohol 79,000 deaths attributable to excessive alcohol use each year in the United States In the single year 2005, there were more than 1.6 million hospitalizations3 and more than 4 million emergency room visits4 for alcohol-related conditions. In 2009, 10,839 people were killed in alcohol-impaired driving crashes, accounting for nearly one-third (32%) of all traffic-related deaths in the United States Of the 181 child passengers ages 14 and younger who died in alcohol-impaired driving crashes in 2009, about half (92) were riding in the vehicle with the with the alcoholimpaired driver Prior to any drinking, designate a non-drinking driver when with a group. Don’t let your friends drive impaired. Take their keys away. If you have been drinking, get a ride home or call a taxi. If you’re hosting a party where alcohol will be served, remind your guests to plan ahead and designate their sober driver; offer alcohol-free beverages; and make sure all guests leave with a sober driver.