(HFMD). - Megamas
advertisement

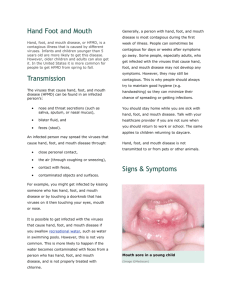
Stay safe from Hand, Mouth & Foot Disease What is HFMD? Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a mild, contagious viral infection common in young children less than 10 years of age, with occasional cases infecting adults as well. Characterized by sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet, hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most commonly caused by a coxsackie virus. HMFD is an infection. It cause by germs called viruses. Can HMFD make you sick? Yes, it can. You may develop o Small blister filled with fluid on hands, feet and sometimes on the buttock, arms & legs. o Mouth ulcers. Is HFMD Contagious? Yes, HFMD is moderately contagious. Infection is spread from person to person by direct contact with infectious virus. Infectious virus is found in the nose and throat secretions, saliva, blister fluid, and stool of infected persons. The virus is most often spread by persons with unwashed, viruscontaminated hands and by contact with virus-contaminated surfaces. Both adults and children can be affected, but young children below five years are particularly susceptible. Signs and symptoms of Hand Foot Mouth Diseases Parents are advised to seek medical attention if you experience the following symptoms. The following signs and symptoms of Hand Foot Mouth Diseases may occur: o One or two days of fever o Painful red sores may develop in the throat, on the gums, on the inside of the cheeks and on the tongue. o Rashes may appear with small blisters on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and may spread to the buttocks. o May have headache and irritability (in young children). o While the diseases is mild and self-limiting but complications affecting the heart and brain could occur that lead to death. o Loss of appetite o Vomiting and/or diarrhoea How to prevent from HFMD? The likelihood to reduce infected with Hand Foot Mouth Diseases is by practicing good hygiene. Only maintaining high standards of personal and environmental hygiene can really minimize getting any infectious diseases. Washing hands is necessary to reduce the potential of spreading any infectious diseases, especially after using the toilet or changing diapers, as well as before eating or preparing foods. Disinfecting common areas and object that is close encounter with children like kitchen, utensils, toys, baby pacifiers. This is necessary since the virus can live on objects or surfaces for several days. Look out for signs and symptoms in other family members, both children and the adults. Cover nose and mouth while sneezing and coughing; and dispose off mouth and nasal discharge properly. Children who are ill should be kept out of school until their fever and rash have subsided and all the vesicles have dried and crusted. Avoid going to crowded places. Parents should teach your children and ensure your child practice good hygiene. • Wash their hand frequently • Covering your month and nose when coughing or sneezing following washing of hands after that. • Take a bath at least twice everyday. • Not to put their fingers, hands or any other objects into their mouths. • Not to share utensils. • Not to share foods • Avoiding contact with infected individuals. How it is spread HFMD is spread from person to person by direct contact with the nasal discharge, saliva, faeces and fluid from the rash of an infected person. Both adults and children can be affected, but young children below five years of age are particularly susceptible. Complications Severe ulcers in the mouth can be very painful and this may interfere with intake of food and drink resulting in dehydration. Dehydration may also be caused by persistent vomiting/diarrhoea coupled with a reduced fluid intake. Complications such as brain, lung or heart infections may occur occasionally, usually due to the EV 71 virus and can be serious. Some signs and symptoms of complications include: o severe headache, giddiness and neck stiffness o disorientation, drowsiness and/or irritability o fits o breathlessness or turning blue Treatment There is no specific treatment for the infection other than symptomatic relief of symptoms. Treatment with antibiotics is not effective and is not indicated. If you suspect your child has HFMD, please bring him/her to see the family doctor. Ease your child’s discomfort and help your child recover : o Encourage your child to drink plenty of fluids o Change to a soft diet (e.g. porridge, pureed fruit) if the mouth ulcers are a problem o Give medications as prescribed by the doctor, e.g. paracetamol syrup to relieve fever and pain o Ensure your child gets plenty of rest by keeping him/her at home More checks to stem HFMD at School HYGIENE checks should be carried out at all schools & childcare centre's to stem cases of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD). The viral infection is now on the rise because of a seasonal peak. REMINDER Place consult a doctor immediately if your child has the following symptoms and signs of complications: § § § § § § § § § § § Prolonged fever Drowsiness and malaise Irritability Repeated vomiting and loss of appetite Shortness of breath Increased heart rate Abdominal distension Not passing urine Weakness of lower legs Muscle jerks Abnormal eye movements HAND WASHING PREVENT INFECTION PERSONAL HYGIENE IS IMPORTANT OF HAND FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE USEFUL LINK http://www.moh.gov.bn/highlights/hfmd200 6.htm